|
Card: 6 / 44 |
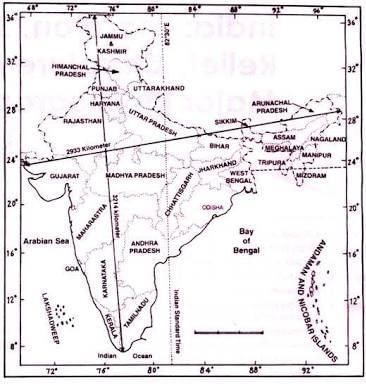
It is used to determine Indian Standard Time, which is ahead of Greenwich Mean Time by 5 hours and 30 minutes. 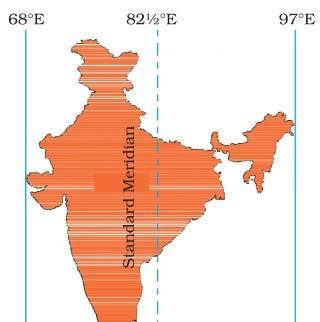 |
|
Card: 7 / 44 |
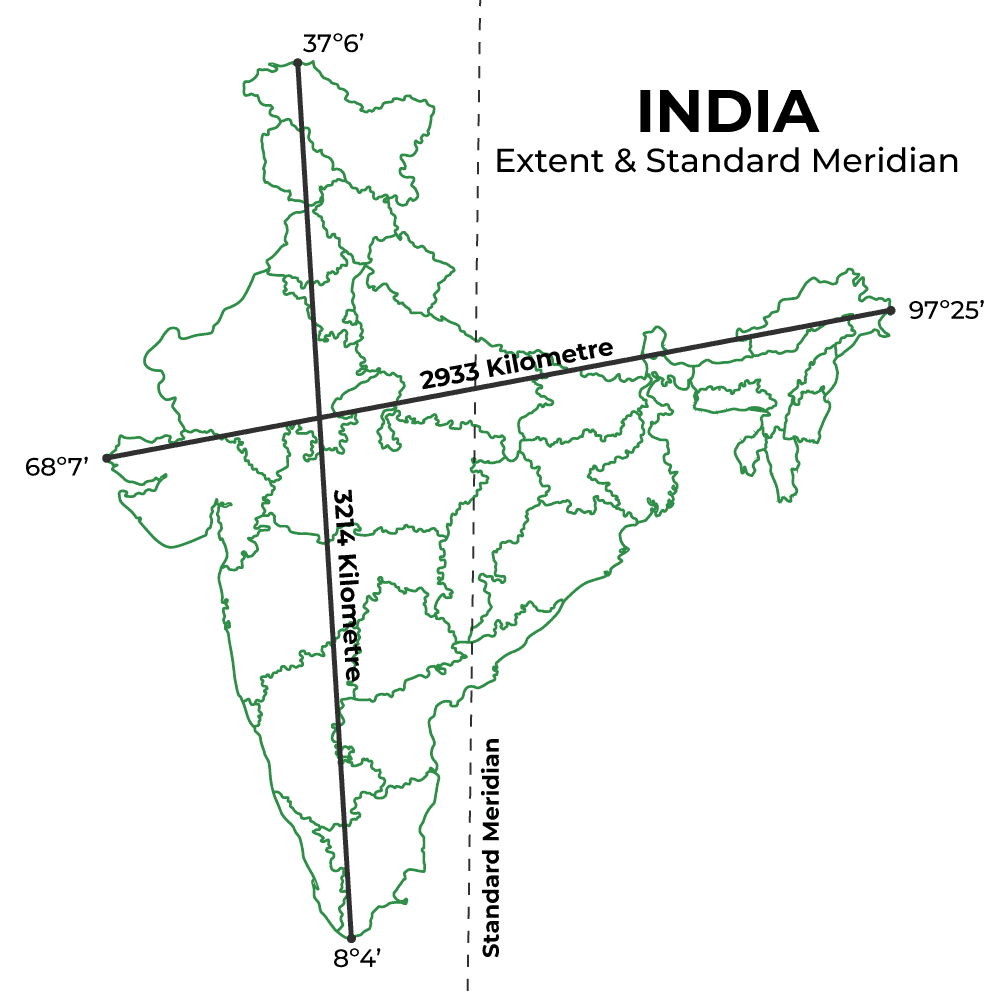
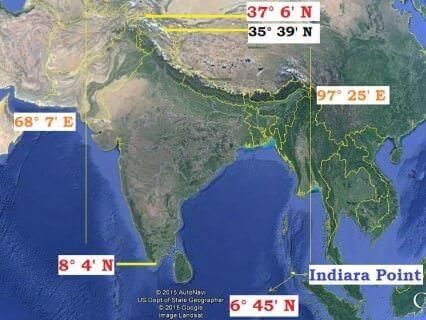
Fill in the blank: The actual distance measured from north to south extremity of India is ___ km. |
|
Card: 9 / 44 |
What variation in degrees is observed in the longitudinal extent of India, and what does this imply? |
|
Card: 10 / 44 |
The variation is nearly 30 degrees, which causes a time difference of nearly two hours between the easternmost and westernmost parts of the country.
|
|
Card: 12 / 44 |
False. The northern part lies in the sub-tropical zone or warm temperate zone. 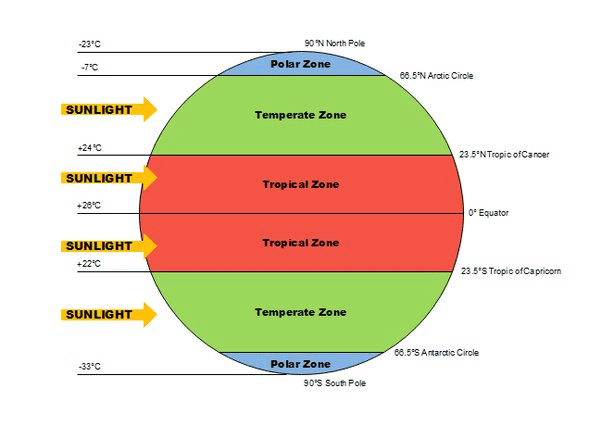 |
|
Card: 13 / 44 |
Fill in the blank: The southern boundary of India extends up to ___ N latitude in the Bay of Bengal. |
|
Card: 16 / 44 |
The Peninsular Block is primarily composed of very ancient gneisses and granites.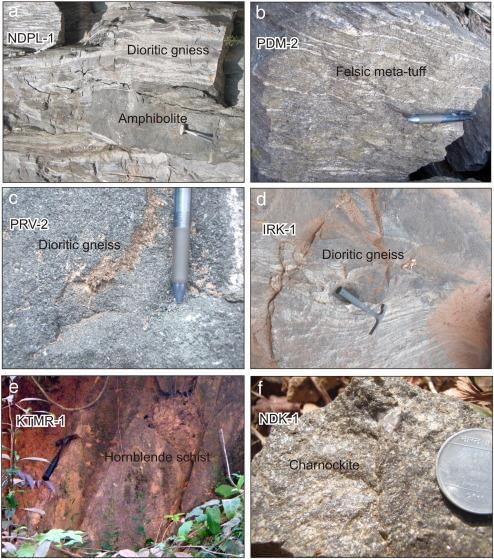  |
|
Card: 18 / 44 |
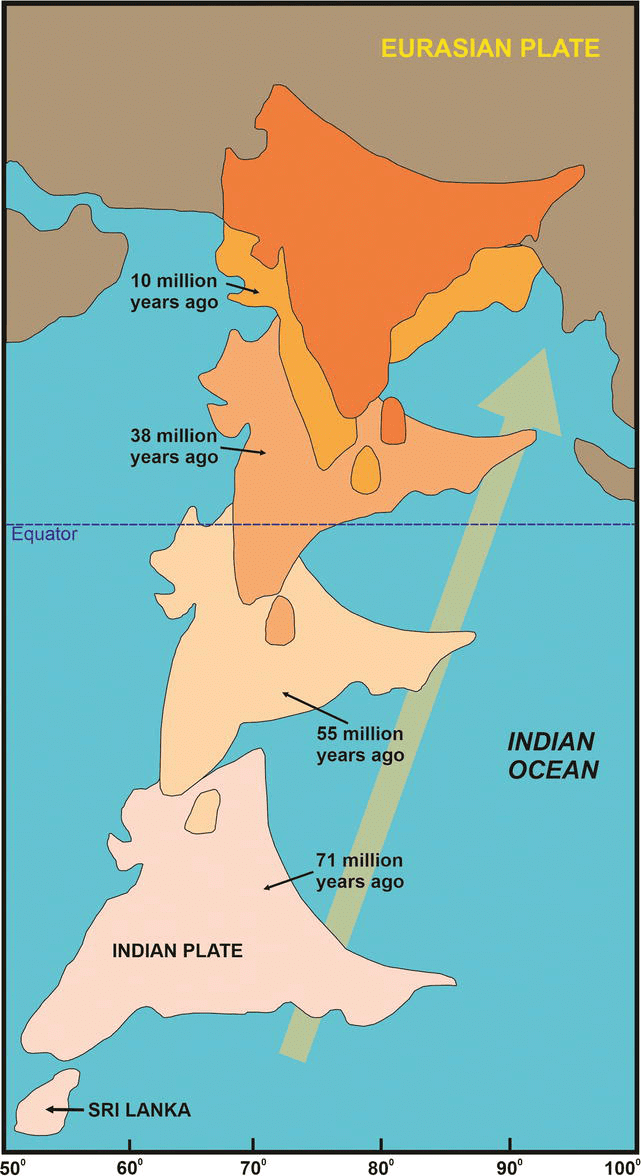
False. The Himalayas are not part of the Indo-Australian Plate; they are a result of the collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate. 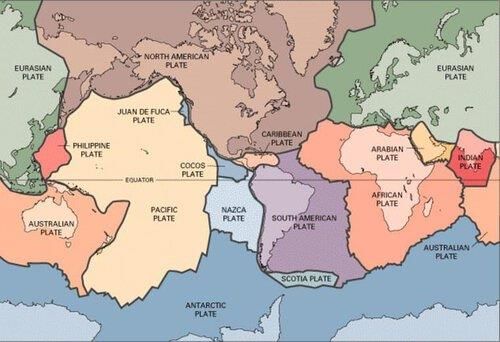 |
|
Card: 19 / 44 |
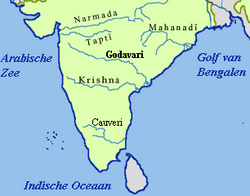
___ and ___ are examples of east-flowing rivers that form deltas before entering into the Bay of Bengal. |
|
Card: 21 / 44 |
What geological feature separates the northeastern parts of the Peninsular Block from the Chotanagpur plateau? |
|
Card: 22 / 44 |
The Media fault in West Bengal separates the northeastern parts of the Peninsular Block from the Chotanagpur plateau. |
|
Card: 23 / 44 |
Fill in the blank: India's area accounts for ___ percent of the world’s land surface area. |
|
Card: 25 / 44 |
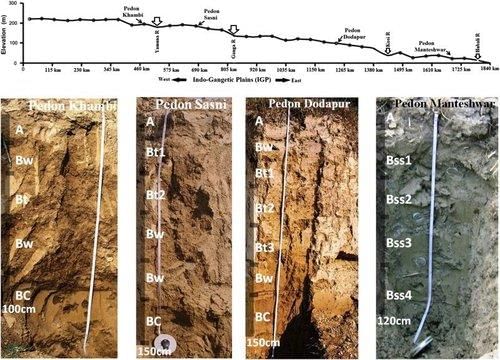
True or False: The Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain was originally a geo-synclinal depression. |
|
Card: 27 / 44 |
Fill in the blank: The average depth of alluvial deposits in the Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain ranges from ___ to ___ meters. |
|
Card: 31 / 44 |
True or False: The Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain was formed solely by the river Indus. |
|
Card: 33 / 44 |
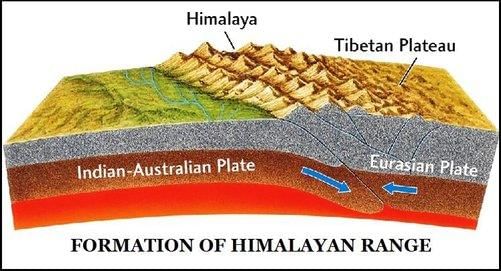
What is the primary cause of the development of faults, folds, and thrust plains in the Himalayas? |
|
Card: 35 / 44 |
The northern and northeastern Himalayas were formed as a result of the convergence of which two tectonic plates? |
|
Card: 39 / 44 |
True or False: The altitudinal variations in the western half of the Himalayas are greater than those in the eastern half. |
|
Card: 40 / 44 |
False. The altitudinal variations are greater in the eastern half than in the western half. |
|
Card: 41 / 44 |
Fill in the blank: The outermost range of the Himalayas, composed of unconsolidated sediment, is called the ___. |
|
Card: 43 / 44 |
True or False: The Great Himalayas consist of the lowest peaks in the Himalaya range. |
|
Card: 44 / 44 |
False. The Great Himalayas consist of the loftiest peaks in the Himalaya range. |