|
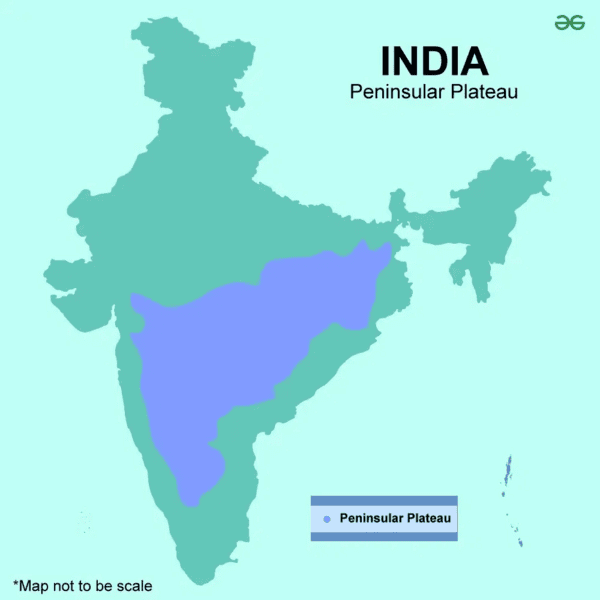
The Peninsular Plateau of India is characterized by a ___ shape, with a wide base in the south and narrowing towards Kanyakumari. |
Card: 1 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The average elevation of the Peninsular Plateau ranges between ___ and ___ meters above mean sea level. |
Card: 5 / 40 |
|
True or False: The Peninsular Plateau is surrounded by water bodies on all sides. |
Card: 7 / 40 |
|
False. The plateau is surrounded by mountain ranges on three sides, not water bodies.  |
Card: 8 / 40 |
|
The northern boundary of the Peninsular Plateau follows an irregular line from Kutch to regions near ___ and ___ rivers. |
Card: 9 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Peninsular Plateau covers an area of approximately ___ lakh sq. km. |
Card: 11 / 40 |
|
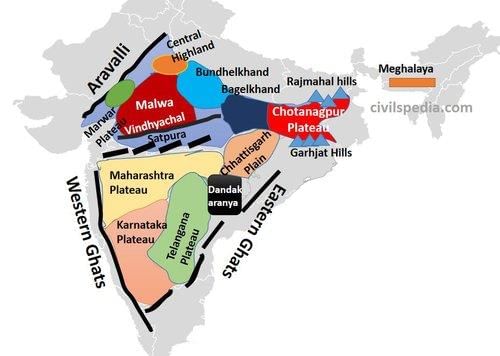
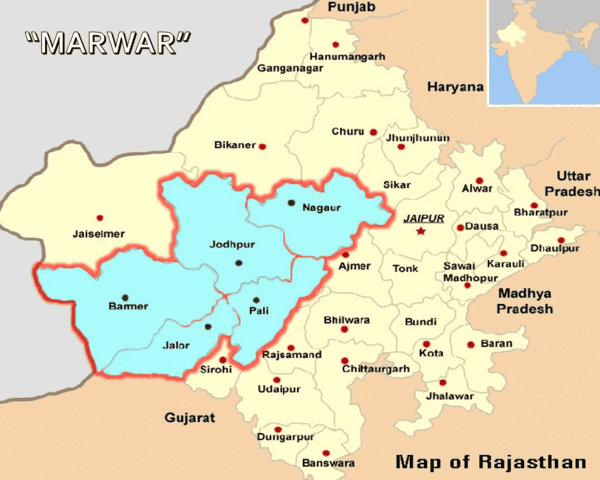
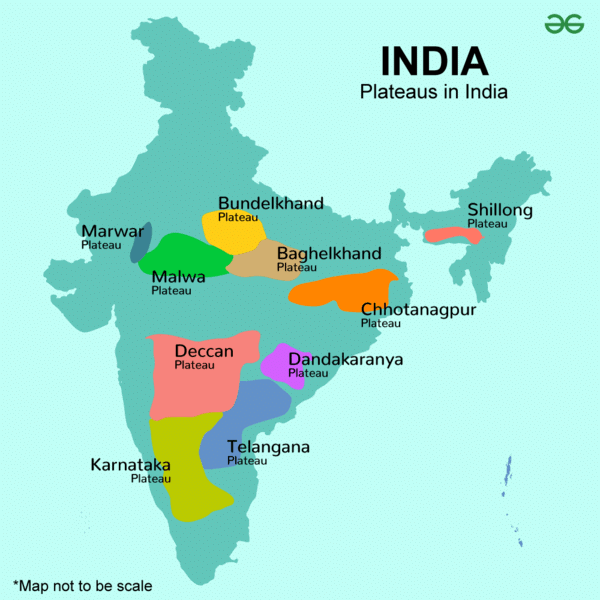
The Marwar Upland primarily serves as a watershed for several rivers, influencing the ___ of the region. |
Card: 13 / 40 |
|
True or False: The Bundelkhand Upland is characterized by a flat landscape suitable for extensive cultivation. |
Card: 15 / 40 |
|
False. The Bundelkhand Upland has an undulating landscape due to extensive erosion, making it unsuitable for cultivation. 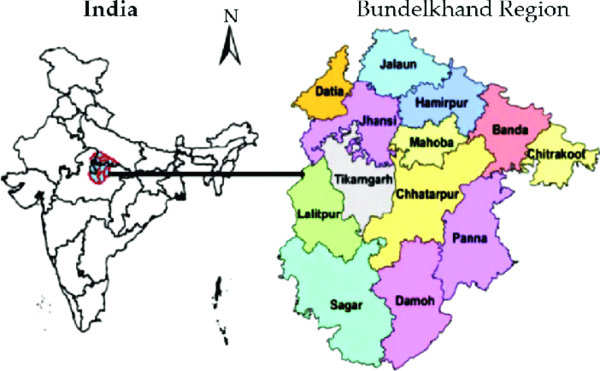 |
Card: 16 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Malwa Plateau is primarily formed by ___ lava flow and is covered with ___ soils. |
Card: 17 / 40 |
|
One flows towards the Arabian Sea (Narmada, Tapi, Mahi) and the other towards the Bay of Bengal (Chambal, Sindh, Betwa, Ken). |
Card: 20 / 40 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
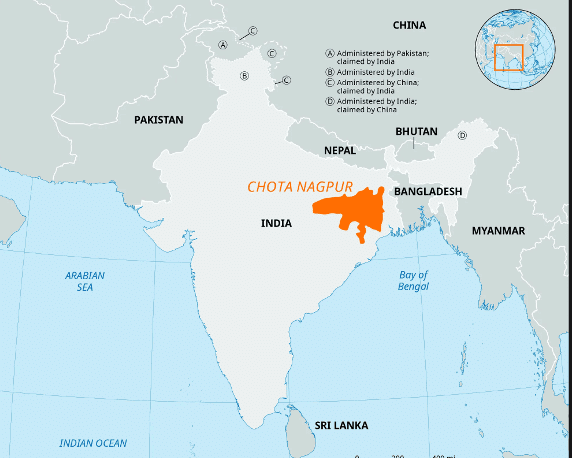
True or False: The Chotanagpur Plateau is known for its mineral-rich resources and plays a crucial role in India's industrial development. |
Card: 21 / 40 |
|
The Central Highlands are characterized by ancient rock formations interspersed with sandstone hills and are predominantly located in the Chambal River Basin. 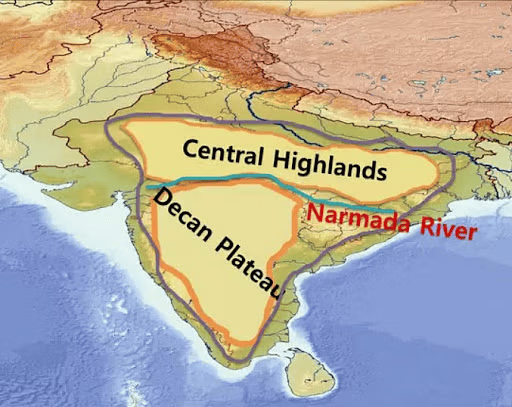 |
Card: 24 / 40 |
|
The Meghalaya Plateau is geographically located between the Brahmaputra Valley in the north and the ___ Valley in the south. |
Card: 25 / 40 |
|
What significant geological feature separates the Meghalaya Plateau from the Indian Peninsula? |
Card: 27 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Meghalaya Plateau predominantly consists of ___ or ___ quartzites, shales, and schists. |
Card: 29 / 40 |
|
The Deccan Plateau is bordered by the Satpura and Vindhya ranges in the northwest and the ___ and ___ ranges in the north. |
Card: 31 / 40 |
|
The Deccan Trap is characterized by horizontal lava sheets that create a unique topography in the Maharashtra Plateau.  |
Card: 36 / 40 |
|
The Karnataka Plateau is drained by key rivers including the Godavari, Krishna, and ___ river. |
Card: 37 / 40 |