|
What key discovery in the 1930s laid the foundation for modern solid-state semiconductor electronics? |
Card: 1 / 42 |
|
The discovery that certain semiconductors and their junctions can control the flow and direction of charge carriers.
|
Card: 2 / 42 |
|
True or False: Semiconductor devices are known for their large size and high power consumption. |
Card: 3 / 42 |
|
False; they are compact in size and energy-efficient with low power consumption.
|
Card: 4 / 42 |
|
Fill in the blank: Semiconductor devices are characterized by their ___ operation and ___ reliability. |
Card: 5 / 42 |
|
Multiple Choice: Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of modern semiconductor devices? A) Low-voltage operation B) Requires external heating C) High reliability D) Energy-efficient |
Card: 7 / 42 |
|
Short answer: Describe the importance of charge carriers in semiconductor devices. |
Card: 9 / 42 |
|
Charge carriers are crucial as they facilitate the flow of electrical current within the semiconductor material, enabling the device to function effectively. 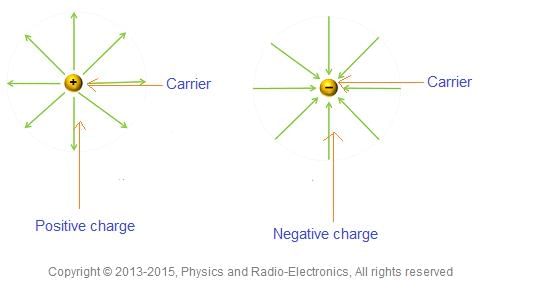 |
Card: 10 / 42 |
|
What is the relationship between electrical conductivity (σ) and resistivity (ρ)? |
Card: 11 / 42 |
|
The relationship is given by the formula ρ = 1/σ, where resistivity is the reciprocal of conductivity. 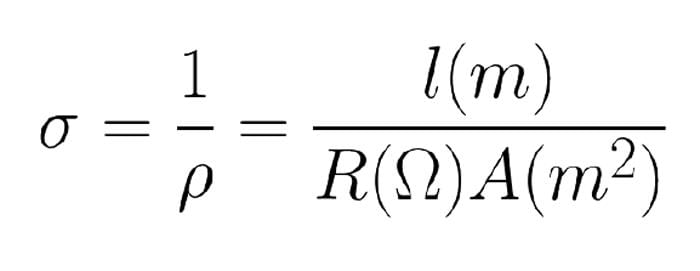 |
Card: 12 / 42 |
|
The resistivity of semiconductors is typically in the range of 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ Ω m. 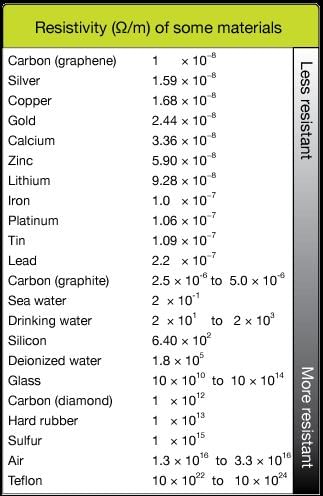 |
Card: 16 / 42 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
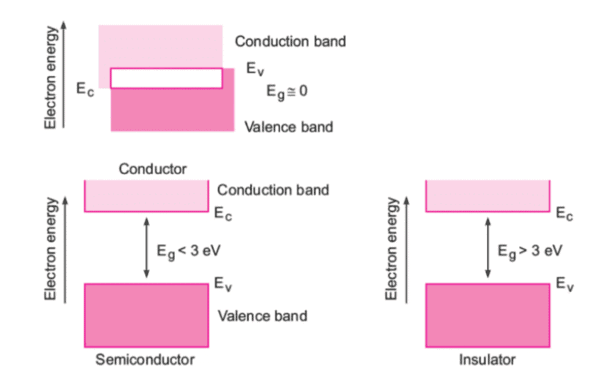
What does the band theory of solids explain regarding the movement of electrons? |
Card: 25 / 42 |
|
The band theory of solids explains that as atoms are close together in a substance, their energy levels form continuous bands, allowing electrons to move between these bands, specifically the valence band and conduction band. |
Card: 26 / 42 |
|
Fill in the blanks: The three types of energy bands in a solid are the ___ band, ___ band, and the ___ energy gap. |
Card: 27 / 42 |
|
True or False: The conduction band is filled with the maximum possible number of electrons. |
Card: 29 / 42 |
|
False. The conduction band is either empty or partially filled, allowing for electrical conduction. 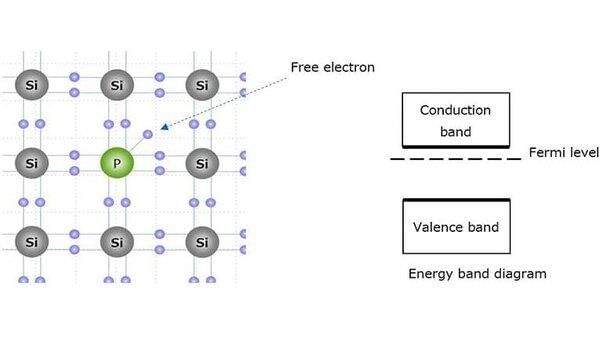 |
Card: 30 / 42 |
|
What is the significance of the forbidden energy gap in the context of electrical conduction? |
Card: 31 / 42 |
|
The forbidden energy gap, or band gap (Eg), is the minimum energy required for electrons to transition from the valence band to the conduction band. A smaller band gap facilitates easier conduction. |
Card: 32 / 42 |
|
A completely filled energy band is an energy band that contains the maximum possible number of electrons according to its capacity. |
Card: 34 / 42 |
|
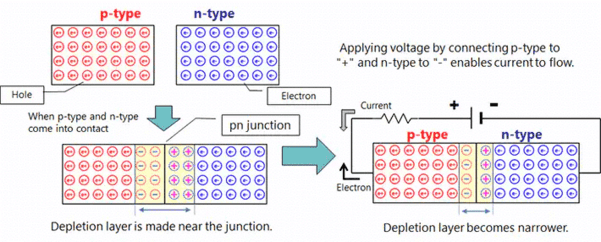
Explain how the arrangement of atoms in a crystal affects the flow of electrons. |
Card: 35 / 42 |
|
In a crystal, the close arrangement of atoms allows for the flow of electrons from one atom to another in the conduction band, facilitating electrical conductivity. |
Card: 36 / 42 |
|
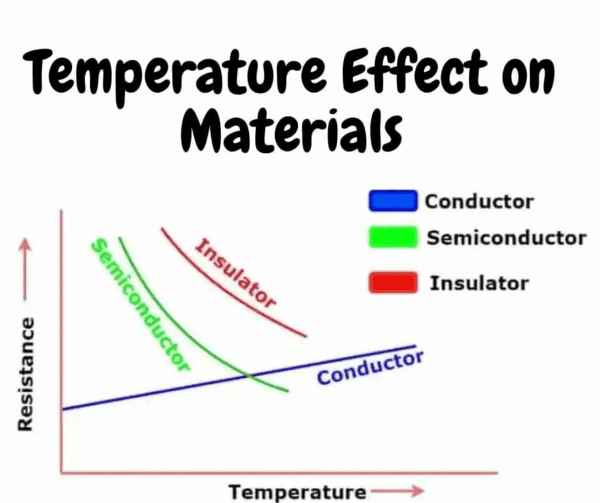
Fill in the blank: The resistance of conductors is ___ and their conductivity is ___. |
Card: 39 / 42 |
|
At high temperatures, some electrons in semiconductors gain enough energy to move from the valence band to the conduction band, increasing conductivity. 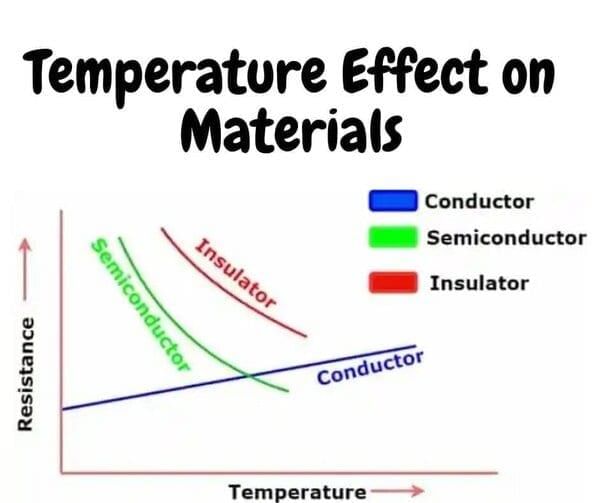 |
Card: 42 / 42 |