|
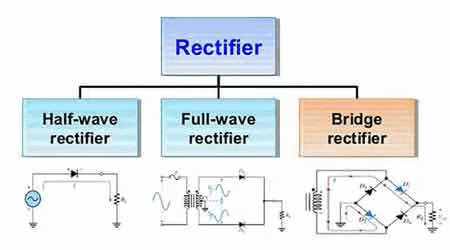
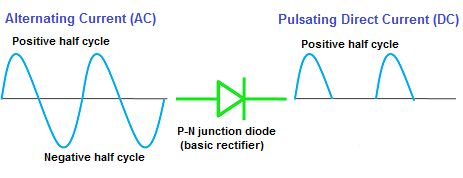
A rectifier is a device used for converting alternating current (AC) or voltage into direct current (DC) or voltage.
|
Card: 2 / 46 |
|
In a half-wave rectifier, what happens to the p-n junction diode during the negative half cycle of the input AC voltage? |
Card: 3 / 46 |
|
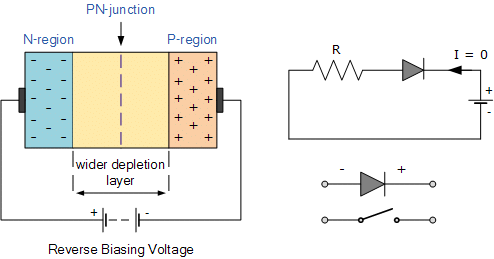
During the negative half cycle, the p-n junction becomes reverse biased, resulting in high resistance and no current flow through the circuit.
|
Card: 4 / 46 |
|
Fill in the blank: The resistance of a p-n junction diode becomes ___ when forward biased and ___ when reverse biased. |
Card: 5 / 46 |
|
True or False: In a half-wave rectifier, current flows continuously throughout both halves of the AC cycle. |
Card: 7 / 46 |
|
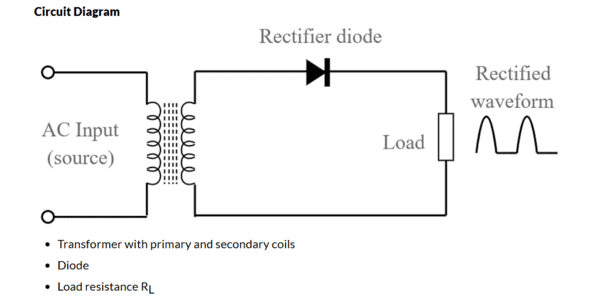
A half-wave rectifier circuit typically includes a transformer with primary and secondary coils, a diode, and a load resistance (RL).
|
Card: 10 / 46 |
|
How does inductance affect the behavior of the diode during the positive half cycle in a half-wave rectifier? |
Card: 11 / 46 |
|
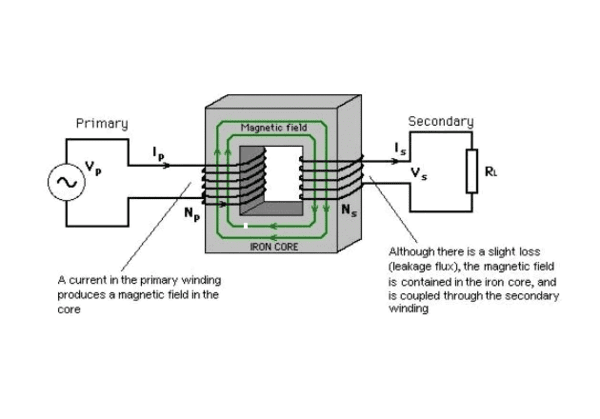
Inductance causes the secondary winding of the transformer to output a positive voltage, forward biasing the p-n junction and allowing current to flow.
|
Card: 12 / 46 |
|
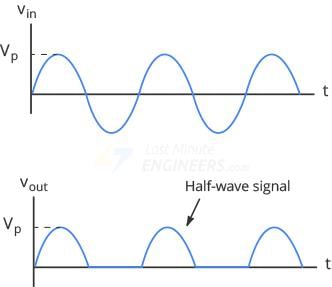
Fill in the blank: The output signal of a half-wave rectifier is available as ___ and is not continuous. |
Card: 13 / 46 |
|
What is the key principle behind the operation of a rectifier using a p-n junction diode? |
Card: 15 / 46 |
|
The key principle is that the diode allows current to flow when forward biased (low resistance) and blocks current when reverse biased (high resistance). 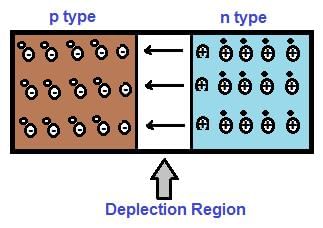 |
Card: 16 / 46 |
|
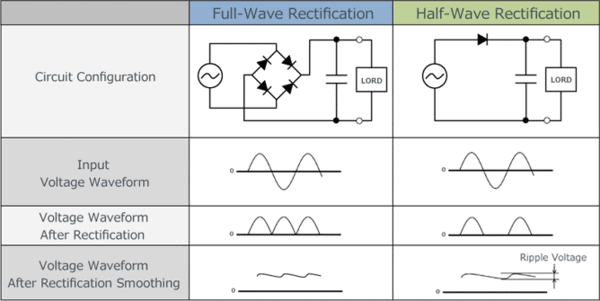
The main difference is that a full wave rectifier uses two diodes, allowing it to conduct current during both halves of the AC input cycle, while a half wave rectifier uses only one diode, conducting current during only one half of the cycle.
|
Card: 18 / 46 |
|
True or False: A full wave rectifier produces a purely direct current output without any ripple. |
Card: 19 / 46 |
|
False. A full wave rectifier produces a unidirectional output that contains ripple components, indicating both AC and DC components. 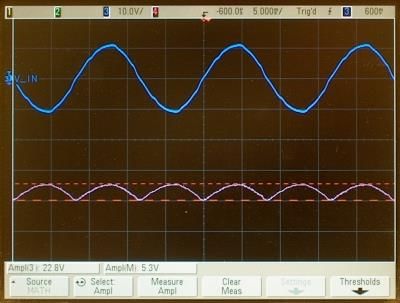 |
Card: 20 / 46 |
|
The filter circuit, which consists of resistance and capacitance, is used to eliminate the AC ripple from the output, allowing only the DC component to pass through. 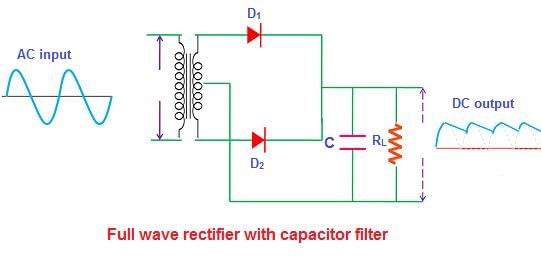 |
Card: 22 / 46 |
|
Fill in the blank: The capacitor in the filter circuit of a full wave rectifier is designed to have a ___ capacitance value. |
Card: 23 / 46 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
True or False: A normal p-n junction diode allows electric current in both forward and reverse bias conditions. |
Card: 25 / 46 |
|
False. A normal p-n junction diode allows electric current only in forward bias condition. |
Card: 26 / 46 |
|
In reverse bias, a p-n junction diode offers ___ resistance to electric current. |
Card: 27 / 46 |
|
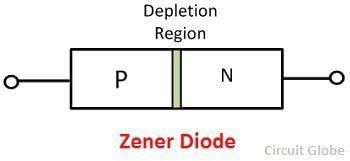
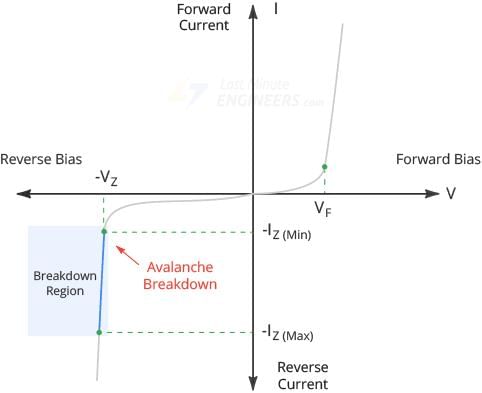
Zener voltage is the voltage at which zener breakdown occurs in a reverse biased p-n junction diode. 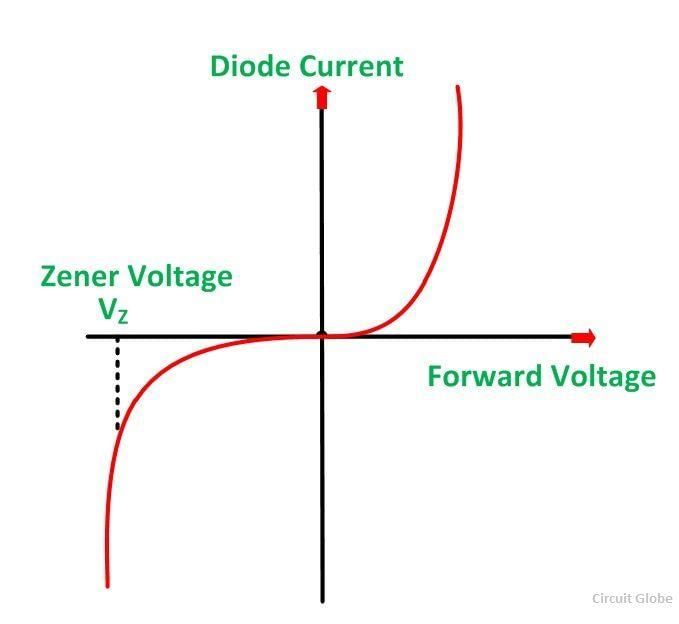 |
Card: 30 / 46 |
|
A sudden increase in current occurs, leading to a rapid increase in electric current with a small increase in voltage. |
Card: 32 / 46 |
|
Fill in the blank: The capacitance offers low impedance to AC components and ___ impedance to DC components. |
Card: 33 / 46 |
|
What is the primary difference between a normal p-n junction diode and a zener diode in terms of operation in the breakdown region? |
Card: 35 / 46 |
|
A normal p-n junction diode does not operate in the breakdown region to avoid permanent damage, while a zener diode is specifically designed to operate in the zener breakdown region. 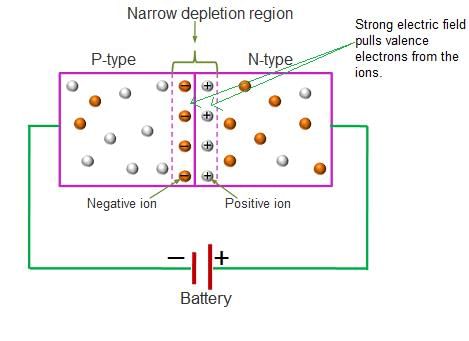 |
Card: 36 / 46 |
|
Zener diodes are heavily doped compared to normal p-n junction diodes, which results in a ___ depletion region. |
Card: 37 / 46 |
|
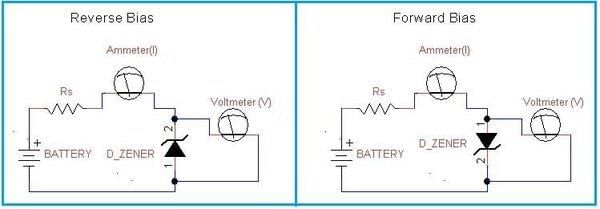
True or False: A zener diode allows current to flow in the reverse direction when the applied reverse voltage is less than the zener voltage. |
Card: 39 / 46 |
|
False; a zener diode only allows current to flow in the reverse direction when the applied reverse voltage is greater than the zener voltage. |
Card: 40 / 46 |
|
Fill in the blank: A zener diode behaves like a normal p-n junction diode when it is ___ biased. |
Card: 41 / 46 |