|
Card: 1 / 40 |
The Indian National Congress (INC) was founded in ___ at its first meeting attended by 72 delegates. |
|
Card: 3 / 40 |
True or False: A.O. Hume was a key figure in the formation of the Indian National Congress to represent the interests of only the elite class. |
|
Card: 4 / 40 |
False; A.O. Hume aimed to create a platform for all politically conscious Indians to express their demands.  |
|
Card: 5 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: The first woman graduate from Calcutta University who spoke at the INC meeting in 1890 was ___. |
|
Card: 9 / 40 |
True or False: The Moderates believed that British intentions were entirely unjust and harmful to India. |
|
Card: 10 / 40 |
False; the Moderates believed British intentions were just but lacked awareness of Indian conditions. |
|
Card: 13 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: The prominent leaders of the Moderate phase included Dadabhai Naoroji, Pherozshah Mehta, and ___. |
|
Card: 15 / 40 |
The drain theory was introduced to explain ___ and ___ in the context of British rule in India. |
|
Card: 16 / 40 |
British exploitation of India's resources and the economic backwardness of India.  |
|
Card: 17 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: Early nationalists aimed to establish a broad public opinion that British rule was a primary cause of India's ___. |
|
Card: 19 / 40 |
What were the specific demands of early nationalists regarding economic reforms? |
|
Card: 20 / 40 |
Reduction in land revenue, abolition of the salt tax, improvement in working conditions for plantation labor, decrease in military expenditure, and encouragement of modern industry through tariff protection and government aid. |
|
Card: 21 / 40 |
True or False: The Indian Councils Act of 1892 significantly widened the democratic base of Indian governance. |
|
Card: 22 / 40 |
False. It faced criticism and did not significantly widen the democratic base or include the masses. 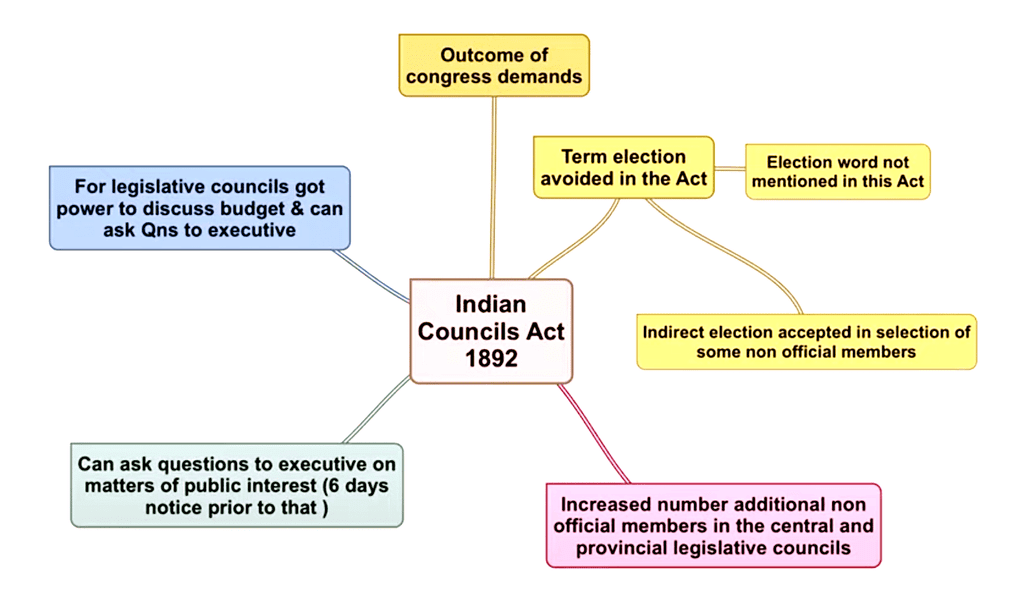 |
|
Card: 23 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: The early nationalists' campaign for self-government was inspired by models from countries like ___ and ___. |
|
Card: 25 / 40 |
The demand for an increase in expenditure on welfare during the Indian independence movement included improvements in ___ and ___. |
|
Card: 27 / 40 |
True or False: The criticism of the British foreign policy during the independence movement included the annexation of Burma and the attack on Afghanistan. |
|
Card: 29 / 40 |
The protection of civil rights during the freedom struggle included the rights to ___, ___, and a free press. |
|
Card: 31 / 40 |
What event in 1897 intensified public discontent regarding civil rights in India? |
|
Card: 33 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: Civil rights became an integral part of the freedom struggle, emphasizing ___ and the link between democratic ideals and nationalism. |
|
Card: 35 / 40 |
The early nationalists believed that India should be ruled in the interest of ___ instead of foreign powers. |
|
Card: 37 / 40 |
What was the British Indian Government's attitude towards the Congress during the early nationalist movement? |
|
Card: 38 / 40 |
The government showed hostility towards the Congress, despite its moderate methods and loyalty to the British Crown. |
|
Card: 39 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: The early nationalists created a wide national awakening among Indians having common interests and the need to rally against a common ___. |