|
Card: 1 / 40 |
India is referred to as a 'Union of States' rather than a 'Federation of States' because ___ and ___. |
|
Card: 2 / 40 |
It highlights the indestructible nature of the union and the lack of a state agreement forming the federation. |
|
Card: 5 / 40 |
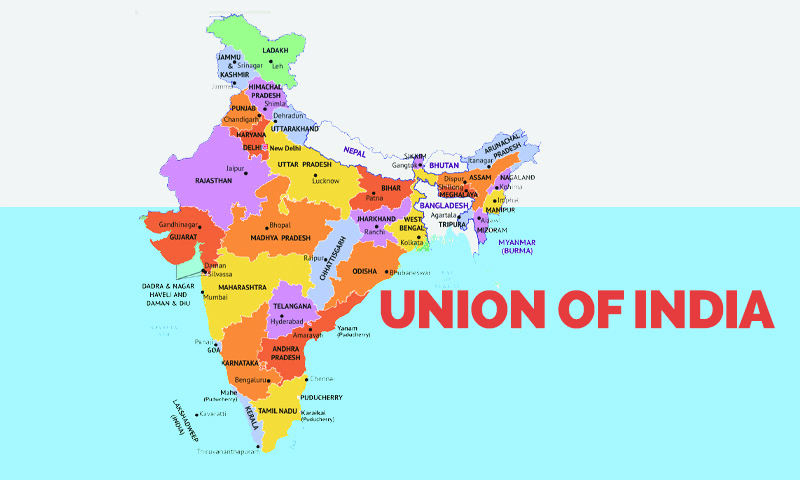
Fill in the blank: The Constitution's first schedule lists the names and territorial extents of ___ states and ___ union territories. |
|
Card: 8 / 40 |
Article 2 focuses on adding new states to India and forming new states, while Article 3 deals with changing existing states within India. |
|
Card: 9 / 40 |
True or False: The territory of India includes only the states and union territories currently recognized. |
|
Card: 10 / 40 |
False. The territory of India encompasses states, union territories, and potential future acquisitions. |
|
Card: 12 / 40 |
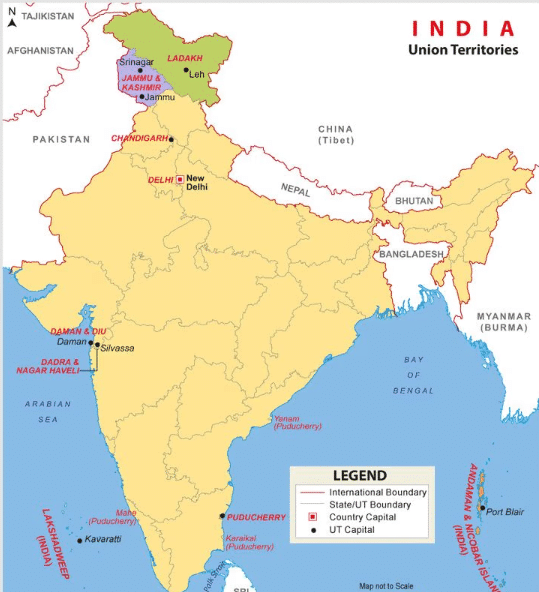
Union territories are directly governed by the Central government, unlike states which share powers with the Center. |
|
Card: 13 / 40 |
Parliament's power to reorganise states includes the ability to ___ the area of any state. |
|
Card: 15 / 40 |
True or False: The Indian Constitution guarantees the territorial integrity of states, similar to the United States. |
|
Card: 16 / 40 |
False. In India, the Union government can dissolve states, while states cannot dissolve the Union. |
|
Card: 17 / 40 |
What is the significance of Article 4 in the context of forming new states in India? |
|
Card: 18 / 40 |
Laws related to forming new states or altering existing ones are not considered constitutional amendments and can be passed with a simple majority. |
|
Card: 19 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: The Supreme Court ruled that transferring Indian territory to a foreign nation requires a ___ under Article 368. |
|
Card: 21 / 40 |
What distinguishes India's approach to state boundaries from that of the United States? |
|
Card: 22 / 40 |
In India, the Parliament can alter state boundaries without state approval, while in the US, states have guaranteed territorial integrity and require state approval for changes.  |
|
Card: 23 / 40 |
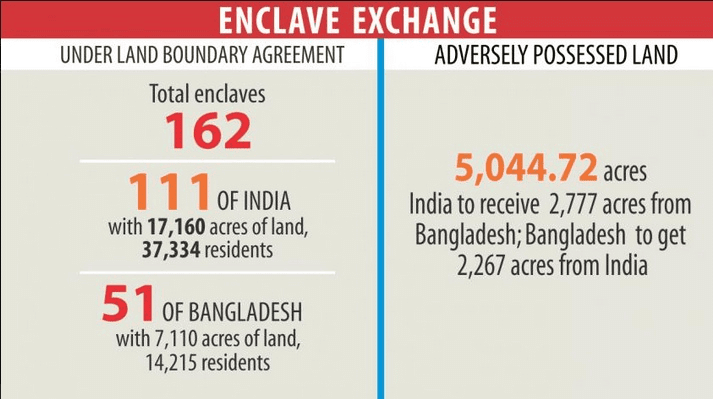
The 100th Constitutional Amendment Act of 2015 facilitated the exchange of territories between India and ___ . |
|
Card: 25 / 40 |
The transfer of 111 enclaves to Bangladesh was part of the agreement signed on ___ . |
|
Card: 27 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: The 100th Constitutional Amendment Act modified the provisions related to the territories of four states: Assam, West Bengal, ___, and ___ . |
|
Card: 29 / 40 |
True or False: The Constitution (9th Amendment) Act was implemented for territories in Bangladesh. |
|
Card: 30 / 40 |
False. The 1960 Amendment was not implemented due to ongoing legal battles and political changes. |
|
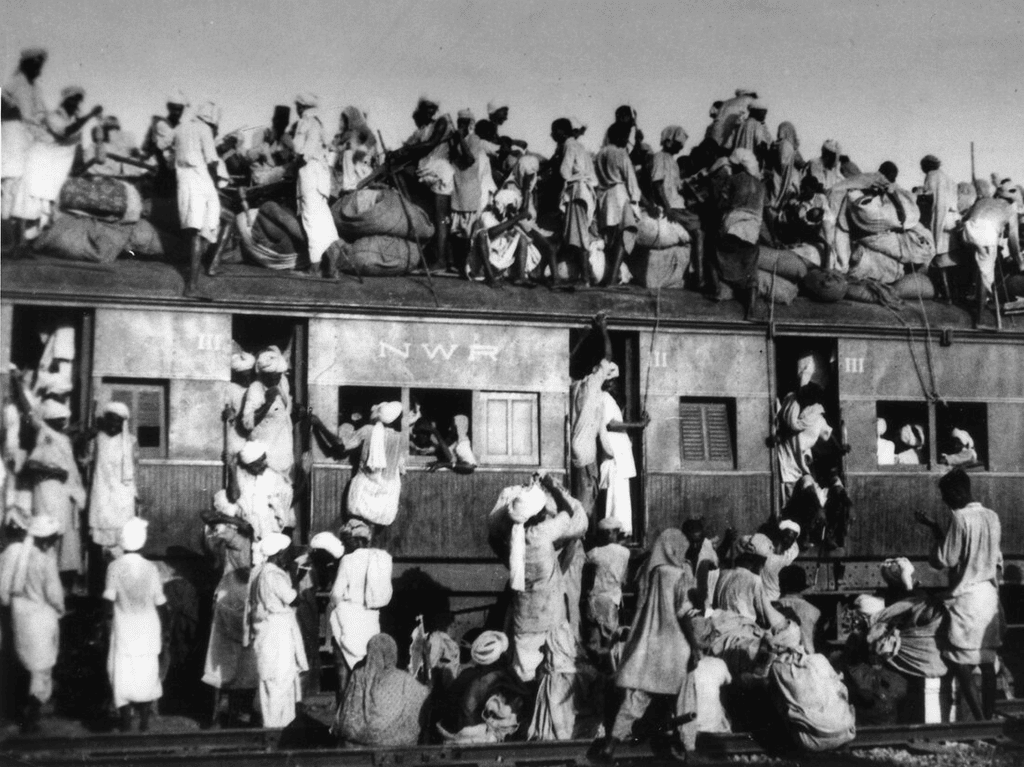
Card: 31 / 40 |
At the time of India's independence, princely states could choose to join which two dominions? |
|
Card: 33 / 40 |
True or False: Out of the 552 princely states in India, only 3 states chose to join India. |
|
Card: 39 / 40 |
What was the total number of states and territories classified by the Indian Constitution in 1950? |