Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE > Fractions
Fractions | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Basic Fractions
What is a fraction?
- A fraction represents a part of a whole.
- It is written as a/b, where a and b are whole numbers (integers).
- The number on the top, a, is called the numerator.
- The number on the bottom, b, is called the denominator.
- For example, 1/2 means splitting something into 2 parts and taking 1 of these parts.
- Another example is 2/3, which signifies splitting something into 3 parts and taking 2 of these parts.
- Similarly, 4/5 indicates splitting something into 5 parts and taking 4 of these parts.
How do I find equivalent fractions?
- "Splitting something into 2 parts and taking 1 of these parts" is equivalent to "splitting something into 4 parts and taking 2 of these parts".
- This equivalence demonstrates that 1/2 is equal to 2/4.
- Extending this concept, 2/4 is equivalent to 4/8, 8/16, or 3/6, and so on.
- Equivalent fractions represent the same amount, just expressed differently.
- To create equivalent fractions, multiply both the numerator and denominator of a fraction by the same value.
- For example, 5/6 is equivalent to
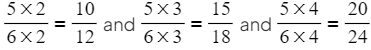 and so forth.
and so forth. - Every fraction has an infinite number of equivalent fractions.
- For example, 5/6 is equivalent to
- To simplify a fraction to its "simplest" form, divide both the numerator and denominator by the largest whole number that divides into both (the "common factor").
- For instance,
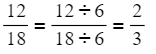
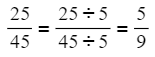
- For instance,
How do I find a fraction of an amount?
- When calculating a fraction of a quantity, there are several methods to consider:
Method 1: Division and Multiplication
- To find a fraction of an amount, divide the amount by the denominator and then multiply the result by the numerator.
- For example, to calculate 2/5 of 60, divide 60 by 5 to get 12, then multiply by 2 to get 24.
Method 2: Converting Fractions to Decimals
- If you can convert fractions to decimals, this method involves changing the fraction to a decimal and then multiplying it by the amount.
- For instance, to find 1/4 of an amount, you would multiply the amount by 0.25.
Method 3: Multiplying Fractions
- This method requires you to express both numbers as fractions and then multiply them together to find the desired fraction of a quantity.
- For example, To determine

- To determine

- To determine
Mixed Numbers & Top Heavy Fractions
What are mixed numbers & top heavy fractions?
- Mixed Numbers: A mixed number consists of a whole number part and a fraction part. For example,
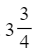 has the whole number 3 and the fraction 3/4, representing "three and three quarters".
has the whole number 3 and the fraction 3/4, representing "three and three quarters". - Top Heavy Fractions: Also known as improper fractions, top heavy fractions have a numerator larger than the denominator. For instance, 15/4 means "fifteen quarters".
Turning mixed numbers into top heavy fractions
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator (whole number × denominator).
- Add the result to the numerator.
- Express the new value as the numerator over the same denominator.
Turning top heavy fractions into mixed numbers
- Divide the numerator by the denominator to obtain the whole number part.
- Use the remainder as the new numerator.
- Keep the original denominator.
Question for FractionsTry yourself: What does the numerator represent in a fraction?View Solution
The document Fractions | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
38 videos|413 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Fractions - Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are equivalent fractions? |  |
Ans. Equivalent fractions are fractions that have the same value, even though they may look different. They represent the same part of a whole or a set, but are written in different forms.
| 2. How can I find fractions of amounts? |  |
Ans. To find a fraction of an amount, you can multiply the fraction by the total amount. For example, to find 1/4 of 20, you would multiply 1/4 by 20 to get the answer.
| 3. What are mixed numbers and top-heavy fractions? |  |
Ans. Mixed numbers are a combination of a whole number and a fraction, such as 3 1/2. Top-heavy fractions, also known as improper fractions, have a numerator that is greater than the denominator, such as 5/3.
| 4. How can I simplify fractions? |  |
Ans. To simplify a fraction, you need to find the greatest common factor (GCF) of the numerator and denominator, and then divide both numbers by the GCF. This will give you the simplest form of the fraction.
| 5. Can fractions be added or subtracted? |  |
Ans. Yes, fractions can be added or subtracted by having a common denominator. If the fractions do not have a common denominator, you can find a common denominator by multiplying the denominators together.
Related Searches





















