Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Economics for GCSE/IGCSE > Free Trade
Free Trade | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Introduction
- International trade encompasses the exchange of goods and services between countries.
- It involves the movement of goods and services through both exports and imports.
- Trade is considered "free" when there is minimal government intervention, such as quotas or taxes, aimed at restricting or influencing trade flows.
The benefits of free trade
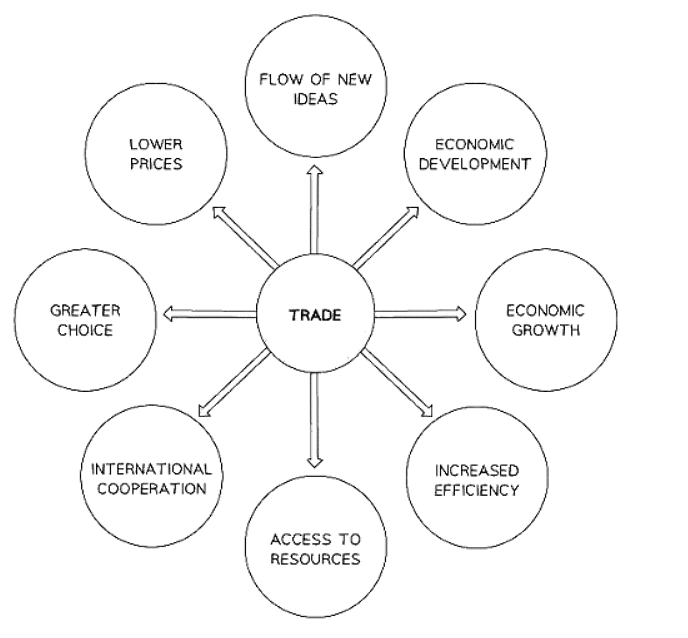
- Greater variety: Access to a broader range of goods and services enhances living standards.
- Lower costs: International competition drives prices down, enabling households to afford more.
- Global collaboration: Trade fosters better international relations, reducing hostilities.
- Knowledge exchange: Trade facilitates the sharing of innovative ideas and technology across borders.
- Resource accessibility: Increased access to raw materials boosts production output and reduces production costs.
- Enhanced efficiency: International competition promotes the emergence of the most efficient firms, optimizing global resource utilization.
- Economic expansion: Exports play a crucial role in many countries' GDP, driving economic growth.
- Socioeconomic progress: Increased output lowers unemployment rates, leading to higher incomes and an improved standard of living.
Question for Free TradeTry yourself: What is one of the benefits of free trade?View Solution
The document Free Trade | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Economics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
56 videos|97 docs|38 tests
|
FAQs on Free Trade - Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the main benefits of free trade? |  |
Ans. Free trade allows for increased competition, lower prices for consumers, improved efficiency, increased exports, and access to a wider variety of goods and services.
| 2. How does free trade benefit smaller economies? |  |
Ans. Smaller economies can benefit from free trade by gaining access to larger markets, attracting foreign investment, and increasing their competitiveness on a global scale.
| 3. Does free trade lead to job losses? |  |
Ans. While free trade can result in job losses in certain industries, it also creates new job opportunities in other sectors due to increased competition and efficiency.
| 4. How does free trade promote economic growth? |  |
Ans. Free trade promotes economic growth by increasing productivity, fostering innovation, promoting specialization, and allowing for the efficient allocation of resources.
| 5. What are the potential drawbacks of free trade? |  |
Ans. Some potential drawbacks of free trade include job displacement in certain industries, income inequality, environmental concerns, and the risk of overreliance on imports.
Related Searches




















