Fundamentals of Operations Management | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
- Operations are a crucial component of any business entity. Operations management entails overseeing the resources directly involved in product manufacturing or service provision within an organization, all geared towards achieving the organization's strategic objectives. Resources typically include personnel, materials, technologies, and information.
- These resources are consolidated through various processes to facilitate their utilization in delivering the organization's primary service or product. Operations management can be conceptualized as a transformative process wherein inputs (resources) are converted into outputs (products or services) through these processes.
Historical Overview
- For centuries, operations management has been recognized as a pivotal factor in the economic development of nations. The traditional perspective on manufacturing management emerged in the eighteenth century when Adam Smith acknowledged the economic advantages of labor specialization. Smith advocated for breaking down jobs into subtasks and assigning workers to specialized tasks, leading to increased skillfulness and efficiency.
- In the early twentieth century, F.W. Taylor built upon Smith's theories and pioneered scientific management. From that point until the 1930s, numerous techniques were developed, building upon the existing traditional view.
Fundamental Concept of Operations Management
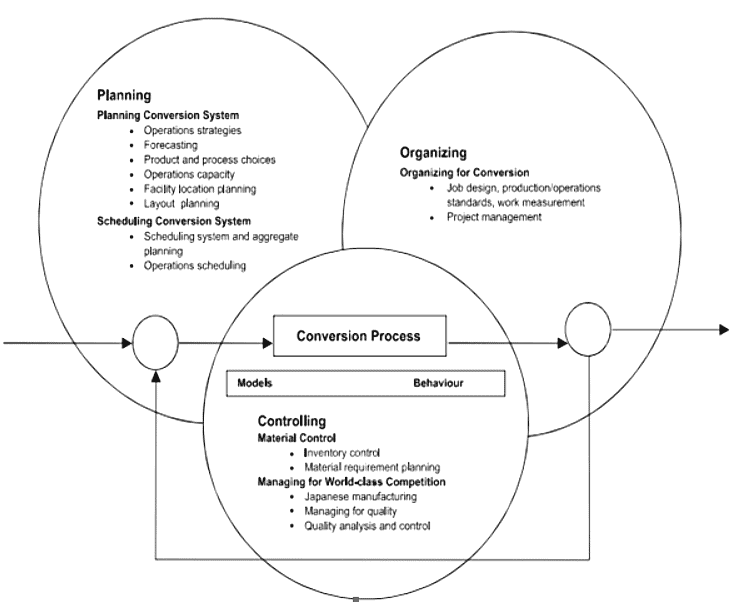
Operations management encompasses the activities, decisions, and responsibilities involved in overseeing the production and delivery of products and/or services (Slack et al., 2007:4). Other theorists define it as the management of the processes responsible for producing or delivering goods and/or services (Greasley, 2009:3). Operations managers engage in planning, organizing, and controlling activities that influence human behavior through various models. This concept can be further elaborated upon.
Planning
Planning involves establishing a course of action and guiding future decision-making. Operations managers set objectives for the operations subsystem of the organization and develop policies and procedures to achieve these objectives. This stage includes defining the role and focus of operations within the organization's overall strategy, as well as product planning, facility design, and the utilization of the conversion process.
Organizing
Organizing entails establishing a structure of tasks and authority within the operations subsystem. Operations managers define roles and information flow, determine the activities required to achieve goals, and assign authority and responsibility for carrying out these activities.
Controlling
Controlling ensures that actual performance aligns with planned performance. Operations managers exercise control by measuring actual outputs and comparing them to planned operations management. Key functions include controlling costs, quality, and schedules.
Behavior
Operations managers are concerned with how their planning, organizing, and controlling efforts influence human behavior. They also consider how subordinate behavior can impact management's actions. Decision-making behavior is of particular interest.
Models
As operations managers navigate the planning, organizing, and controlling of the conversion process, they encounter various problems and decisions. Models such as aggregate planning models, break-even analysis, linear programming, computer simulation, decision tree analysis, and simple median models help simplify these challenges and aid in decision-making processes.
The general model of operation management:
Responsibilities of Operations Managers
- Operations managers play a crucial role in making significant decisions concerning product development, process optimization, layout design, site selection, and capacity planning. At the tactical level, operations management involves addressing issues related to efficient scheduling of materials and labor while adhering to the firm's strategic constraints and making decisions on aggregate planning. They are involved in determining employee levels, inventory levels, and capacity allocation.
- On an operational level, operations management focuses on lower-level planning and control, where managers and their subordinates make decisions regarding scheduling, sequencing, loading, and work assignments. In the current landscape, operations managers must possess advanced knowledge of operational technology and industry-specific technical expertise, along with interpersonal skills and a broad understanding of other functional areas within the organization. Effective communication, team motivation, project management, and the ability to work in multidisciplinary teams are essential skills for operations managers.
The objective of Operations Management
- The primary goal of operations management is to deliver excellent customer service while efficiently utilizing resources. The operational system aims to provide products or services that meet customer specifications in terms of cost and timeliness. Thus, the fundamental objective is to deliver the right product or service at the right price and at the right time to satisfy customer needs.
- Another primary objective is the optimal utilization of resources to meet customer needs. Operations management primarily focuses on maximizing resource efficiency and minimizing waste or underutilization. Resource utilization is measured by factors such as the proportion of available time utilized, space utilization, and activity levels, which reflect the extent to which resources' potential or capacity is utilized. This goal is commonly referred to as the objective of resource utilization.
Methods of Operations Management
- Operations managers are involved in two main areas of activities. The first involves designing operations systems, while the second entails planning and controlling operations (Dilworth, 1992). Designing operations systems encompasses a wide range of tasks, including crucial decisions that directly impact an organization's competitiveness, costs, sales, and profits, such as facility location decisions for manufacturing or services.
- Factors influencing facility location decisions can be categorized into three types. Subsequently, decisions on facility layout and operational process layout are key components of operations system design. Different operations, varying conditions, and objectives necessitate alternative process layout approaches.
Conclusion
Operations management is the process through which goods and services are developed. It involves decision-making related to the production process to ensure that resulting goods and services meet specified requirements, are produced in the required quantities and within the necessary schedule, and at minimal cost. Theoretical studies highlight that operational management begins with business plans and strategies based on product and service demands.
FAQs on Fundamentals of Operations Management - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the fundamental concept of operations management? |  |
| 2. What are the responsibilities of operations managers? |  |
| 3. How does planning contribute to operations management? |  |
| 4. What are behavior models in operations management? |  |
| 5. What is the objective of operations management? |  |





















