UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > GC Leong Summary: The Earth & The Universe
GC Leong Summary: The Earth & The Universe | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Exploring the Universe

- Earth’s Own Galaxy-Milky Way (Contains 100000 Million Stars)
- The light from the nearest star travelling at the speed of light i.e. 186,000 miles per second takes something like 4 yrs to reach us.
- 8 minutes- ray of light from the sun to reach the earth
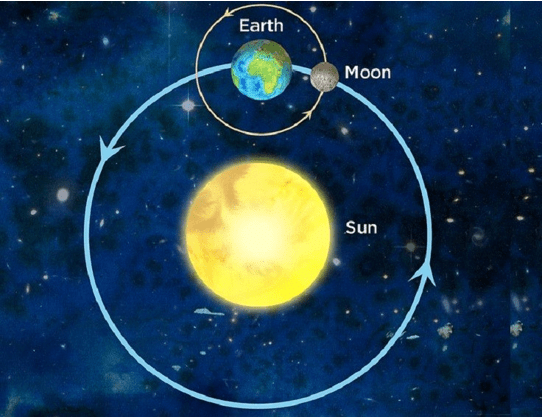
The Solar System

- Comprises Sun and 8 Planets
- Planets revolve round the sun in elliptical orbits.
- Mercury the smallest and closest to the sun
- Venus, twice the distance away from the sun (Next Closest Planet)
- Earth, has life and all living beings we see around us in earth.
- Natural Satellite of Earth-Moon
- 4th Planet-Mars (Dark Patches and have some possibility of some plant life)
- Jupiter-largest planet, made up of many gases like hydrogen, helium and methane (12 Satellites), Surface very cold.
- Saturn-Unique planet (3 rings and 9 satellites), 2nd largest after Jupiter
- 7th Planet-Uranus, another giant planet, 50 times larger than earth, 15 times as heavy (orbits around the sun in a clockwise direction from east to west with five satellites revolving round it).
- Outermost planet- Neptune and pluto, visible with telescopes, result of mathematical calculations.
- Neptune much colder.
Natural Satellite (Moon)

- Moon rotates around the earth in an elliptical orbit as earth rotates around the sun
- Axis of moon is inclined at 58.4 * approx, wrt Plane of ecliptic, as a result distance of moon from earth keeps on changing.
- Only 59 % of moon’s surface is visible from earth at the max Perigee-Nearest point to the moon’s orbit from Earth.
- Apogee- Farthest point to the moon’s orbit from Earth.
- Sidereal Month- Moon completes 1 rotation in 27 days 7 hrs & 43 min approx. With reference to earth
- Synoptic Month- Moon completes 1 rotation in 29 days 12 hrs & 44 min annrox. With reference to sun
Question for GC Leong Summary: The Earth & The UniverseTry yourself: How long does it take for the light from the nearest star to reach us?View Solution
Features of the Earth
1. Shape of Earth
- Oblate spheroid or oblate ellipsoid shape
- Slightly flattering at poles & slightly bulging at equator
- Polar radius approx. 21 km shorter than equatorial radius
2. Axis of Earth
- Earth rotating around an imaginary line running through North Pole & South Pole via its centre.
3. Equator
- Center most parallel, dividing earth into two equal hemispheres namely Northern & Southern hemisphere
- Lying at 0* latitude with L = 40000 Km Approx.
4. Tropic of Cancer
- Parallels at 23.5* north of equator Tropic of Capricorn
- Parallels at 23.5* south of equator
5. Arctic Circle
- Parallels at 66.5* north of Equator
6. Antarctic circle
- Parallels at 66.5* south of Equator
7. Other Features
- Length of latitudes decreases from equator to poles i.e. max. at equator & 0 at poles.
- As earth’s axis is inclined by 23.5* to its orbital plane, therefore 23.5* is max. latitude upto which sunrays can be perpendicular to any place.
- Means all places between Tropic of cancer & Tropic of Capricorn experience vertical rays of sun twice a year but both the tropics only once.
- Tropic of cancer will get vertical sunrays at summer solstice, when Northern hemisphere of earth is at max. inclination from sunrays.
- Tropic of Capricorn will get vertical sunrays at winter solstice, when southern hemisphere of earth is at max. inclination from sunrays.
- Evidences of the Earth’s Sphericity:
(i) Circum navigation of the earth
(ii) The circular horizon
(iii) Ships visibility
(iv) Sunrise and sunset
(v) The Lunar Eclipse
(vi) Planetary bodies are spherical
(vii) Driving poles on level ground on a curved earth
(viii) Aerial Photographs
Rotation of the Earth
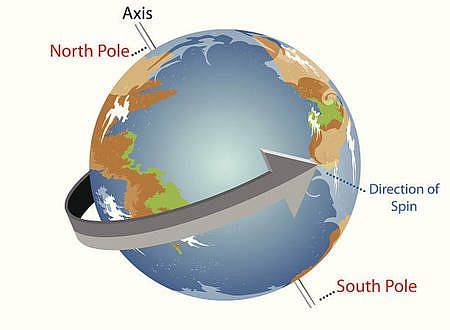
- Earth’s rotate around its own axis from west to east viz. Anticlockwise direction.
- Earth’s rotate around the sun (Elliptical path) from west to east viz. anticlockwise direction.
- Axis of earth rotation is inclined at 66.5* to its plane of elliptic.
- Axis of earth rotation is inclined at 23.5* to perpendicular to the plane of elliptic
- Plane of earths equator to plane of elliptic or earth’s axis to axis of revolution is inclined at 23.5 *
- Velocity of earth’s rotation decreases from equator to poles.
- Correlated with length of the parallels which also decreases from equator to poles
- velocity at equator & 0 velocity at poles
- Weight of body is less at equator & greater at poles
- Because of greater centrifugal force at the equator (mvA2 / r) due to greater velocity at equator.
- Because of higher gravitational force at poles (GMm/r) due to lesser radius of poles than the equator
- The earth moves in space in two distinct ways viz.
- It rotates on its own axis from west to east once in every 24 hours causing day & night.
- It revolves around the sun in an orbit every 365(1/4) days causing the seasons & the year.
- Throughout the revolution of earth around the sun, its axis remains tilted in the same direction.
- Its axis continues to point to same spot in heaven known as Polaris / polestar/ parallelism of axis.
- Polestar -Brightest star in the sky in north direction or northern star.
Eclipses

- Partial or total obstruction of light from a celestial body as it passes through shadow of another celestial body.
- Apparently, eclipse shall occur every month because of revolution of earth around the sun & moon around the earth, but Plane of moon’s orbit around the earth is inclined at 5.9* to the plane of earth’s orbit around the sun.
1. Solar Eclipse
- When moon comes exactly between earth & sun & obstructs a part or whole of the sun then a partial or total eclipse occur.
- Usually at sunrise or sunset at new moon.
2. Lunar Eclipse
- When earth comes exactly between Sun & moon.
- Usually occurs at full moon.
3. Dawn and Twilight
- The brief period between sunrise & full daylight is called dawn & that between sunset & complete darkness is termed as twilight.
- This is caused by the fact that during the periods of dawn & twilight earth receives diffused or refracted light from the sun while it is still below the horizon.
- Since the sun rises & sets in vertical path at the equator, the period during which refracted light is received is short.
- But in temperate latitudes, the rises & sets in oblique path & hence the period of refracted light is longer than that at equator, which is much longer at poles.
Question for GC Leong Summary: The Earth & The UniverseTry yourself: What is the shape of the Earth?View Solution
4. Latitudes
- Angular distance of a place, along meridian on earth’s surface as measured from center.
- Distance between them increases towards the poles.
- Most important lines: The Equator, The tropic of cancer, tropic of Capricorn, arctic circle and Antarctic circle
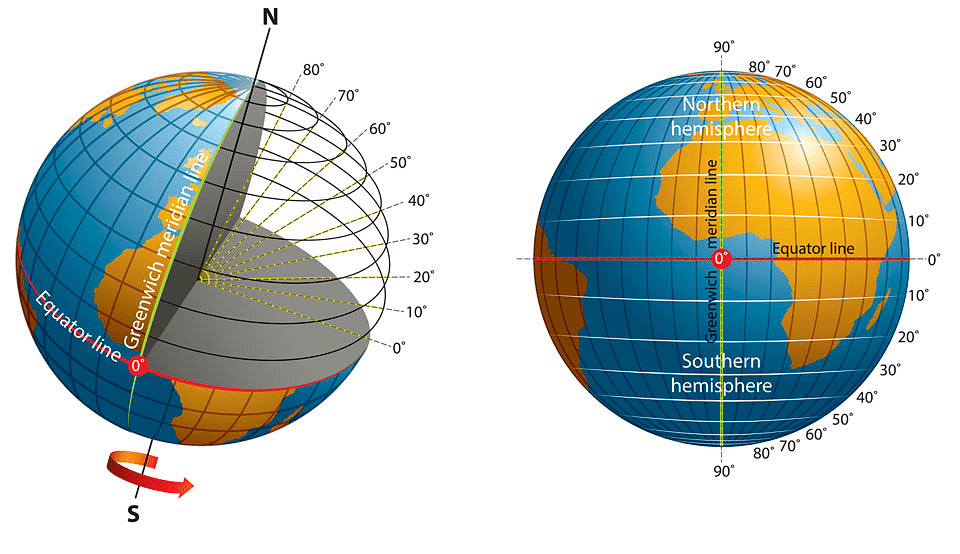
5. Longitudes
- Imaginary lines which joins poles & perpendicular to all parallels.
- Drawn as a semicircle on the globe.
- Also known as meridians.
- Equidistant in nature.
6. Longitudes and Concept of Time
- Since earth rotates west to east places located in the east gain time while those located in the west loose time.
- Generally, 12: 00 noon at a place is considered when sun’s altitude is highest & exactly over the meridian at that place Time at all the places located at particular meridian i.e. north & south will be same, however places located at east & west will have different local time.
7. Standard Time of a Country
- Standard time of a country is local time of a selected longitude crossing through a place in the country of due importance.
- Standard time of India is local time of longitude passing through Allahabad situated at 82.5* East of Prime meridian i.e. Five & half hours ahead of GMT.
- Calendar date is changed by one day when someone crosses international date line.
- Although line is deviated at some places to mark same date at some countries & islands.
- Thumb Rule -Loose 12 hrs west of Prime meridian & gain 12 hrs east of prime meridian.
(i) Greenwich Meridian
- Also known as Prime Meridian or Time Meridian.
- Meridian passing through Royal observatory at Greenwich near London which divides earth in eastern & western hemisphere.
(ii) International Date Line
- Exact opposite to Greenwich meridian at longitude of 180*
(iii) Graticule
- Network of parallels & meridians drawn on the globe.
- Helps to locate a place with given longitudes & latitudes.
(iv) Great Circles
- Imaginary circles which divides the earth into two equal parts & whose center lies at the center of the earth.
- Largest circles that can be drawn on the globe i.e. Equator & all meridians
The altitude of The Sun
1. Solstices
- When sun is at the greatest distance from the equator.
- Its rays falls vertical either at tropic of Cancer or tropic of Capricorn.
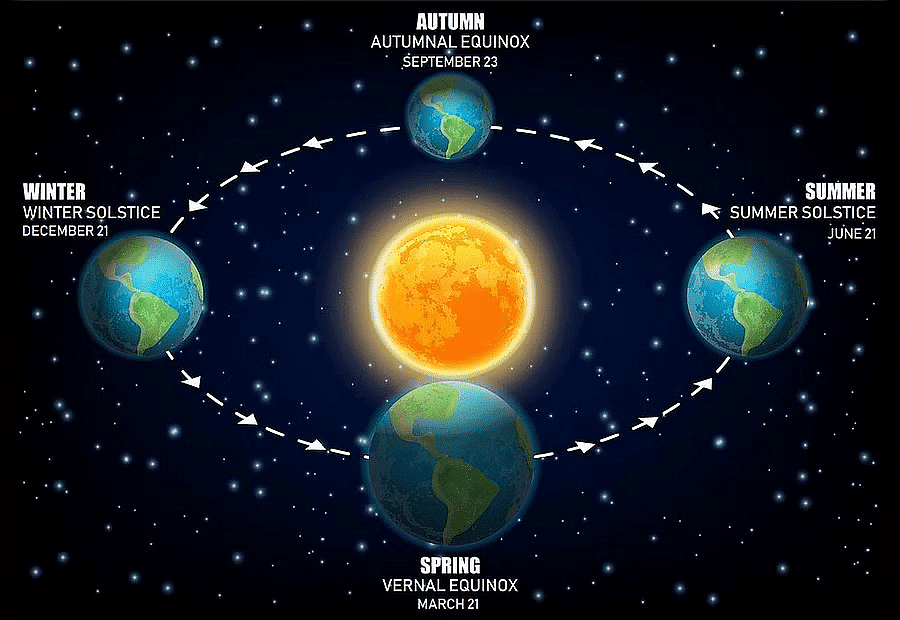
2. Summer Solstice
- Earth’s axis leans at max 23.5* in northern hemisphere towards the sun.
- Sun’s rays fall vertical at Tropic of cancer around 21/22 June.
- This brings summer season in Northern hemisphere.
- With this duration of days starts decreasing.
- Means June 21/June 22 is longest day in Northern hemisphere.
- Daylights of 14 hrs at Tropic of Cancer; 12 hrs at Equator; 10 hrs at Tropic of Capricorn.
- Between Arctic Circle & North Pole day lasts for 24 hours & between Antarctic Circle & South Pole same duration of night lasts.
- At North Pole day last for 6 months & at South Pole night last for 6 month approx.
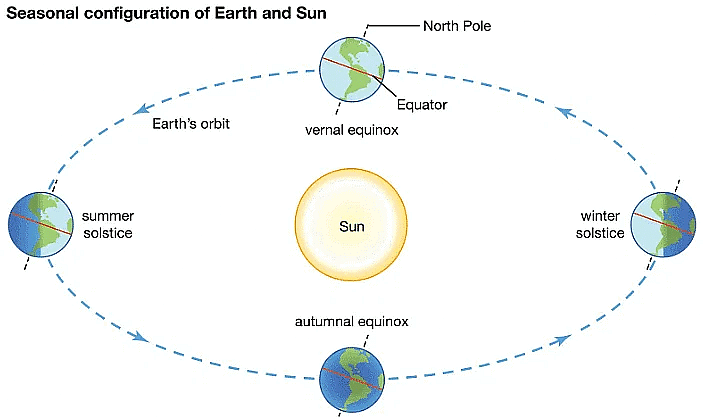
3. Winter Solstice
- Earth’s axis leans at max 23.5* in southern hemisphere towards the sun.
- Sun’s ray falls vertical at Tropic of Capricorn around 21/22 Dec.
- This brings summer season in Southern hemisphere
- With this duration of days starts increasing in Northern hemisphere
- Means Dec 21/June 22 is shortest day in Northern hemisphere
- Daylights of 14 hrs at Tropic of Capricorn; 12 hrs at Equator; 10 hrs at Tropic of Cancer
- Between Antarctic Circle & South Pole day lasts for 24 hours & between Arctic Circle & North Pole same duration of night lasts.
- At South Pole day last for 6 months & at North Pole night last for 6 month approx.
4. Equinoxes
- The sun is vertically overhead at the equator on two days of the year usually on 21 March & 21 September.
- Dates changes because a year is not exactly of 365 days.
- These two days are termed as equinox means on these two days all parts of the world have equal days & nights.
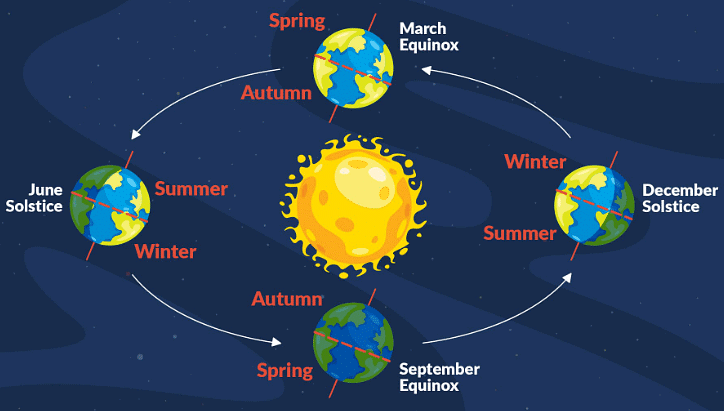
5. Seasonal Changes & their effect on temperature
- In summer, sun is overhead & its sunrays fall almost vertically on the earth, concentrating its heat on a small area;
- Temperature therefore rises & summers are always warm
- In winters, the oblique rays of sun come through atmosphere less directly & have their heat absorbed by atmosphere & water vapour;
- Sun rays fall obliquely & spread over greater area, hence temperature remain low.
- In addition days are longer than nights in summer & more heat is received over longer daylight duration; Nights are shorter & less heat is lost. Hence, there is net gain in total heat received & temperature rises in summer.
- Shorter days & longer nights in winters accounts for reverse effect
- Made up of several concentric layers.
- The outer layer is the earth’s crust-the lithosphere.
- Lithosphere comprises two distinct parts-granite rocks-upper part & lower part-basaltic rocks.
The document GC Leong Summary: The Earth & The Universe | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
180 videos|482 docs|193 tests
|
FAQs on GC Leong Summary: The Earth & The Universe - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the relationship between the Earth and the Universe according to GC Leong? |  |
Ans. GC Leong explains that the Earth is a part of the Universe, which includes all celestial bodies such as planets, stars, galaxies, and other cosmic entities.
| 2. How does the Earth interact with the rest of the Universe as discussed in the article? |  |
Ans. The Earth interacts with the rest of the Universe through various processes such as gravitational forces, electromagnetic radiation, and cosmic events like meteor showers and solar flares.
| 3. What is the significance of studying the Earth and the Universe in geography according to GC Leong? |  |
Ans. GC Leong emphasizes the importance of studying the Earth and the Universe in geography as it helps us understand our place in the cosmos, the interconnectedness of all living beings, and the impact of celestial phenomena on our planet.
| 4. How does the study of the Earth and the Universe contribute to our knowledge of climate change and environmental issues? |  |
Ans. By studying the Earth and the Universe, geographers can better understand the factors influencing climate change, such as solar radiation, greenhouse gas emissions, and natural disasters, leading to more informed environmental policies and conservation efforts.
| 5. What are some key concepts or theories related to the Earth and the Universe that are discussed in GC Leong's work? |  |
Ans. GC Leong explores concepts such as the Big Bang theory, plate tectonics, celestial mechanics, and the formation of galaxies, providing a comprehensive understanding of the Earth's place in the vast expanse of the Universe.
Related Searches