GMAT Integrated Reasoning Preparation Tips to achieve a perfect score PDF Download
The Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) is an essential part of the admissions process for many top business and management programs in the United States. It is a rigorous computer-adaptive exam that measures a student's aptitude in writing, analytical and quantitative reasoning. One of the toughest sections of the GMAT is the Integrated Reasoning (IR) section, which tests a student's ability to analyze data and make decisions presented in multiple formats, such as tables, charts, and graphs. For Integrated reasoning, the general consensus is that a score of 6 and above is good. Getting a score of 6 would translate to 67 percentile, while 7 would mean 82 and a perfect 8 would be 93. So, how do you achieve this score? This article will give you the key prep tips and resources to help you reach your desired score.
GMAT Integrated Reasoning Important Highlights
GMAT Integrated Reasoning Preparation Tips
- Make it a habit to Read the question carefully and make sure you understand what is being asked before attempting to answer. By taking the time to read and understand the question, you can more effectively evaluate the data presented in the question and draw the appropriate conclusion. This will help you to better synthesize the information you need to answer the question correctly.
- Familiarize yourself with the different types of questions asked in the integrated reasoning section: Graphics Interpretation, Multi-Source Reasoning, Two-Part Analysis, and table analysis. Being aware of the general layout of these problems would mean that you won’t get caught by surprise on exam day.
- Learn how to eliminate options to narrow down your choices. What you need to do is think logically and analyze all the options before making a decision. Remember that this process doesn’t work for all questions, but it can be instrumental in reducing the time taken for the questions it does work in.
- Develop the skill of identifying relations between different sets of data. Many questions in the Integrated Reasoning section require you to identify the relation between the data provided. Practice tests for Integrated reasoning by EduRev is a great resource for developing the said skill.
- Practice with real GMAT questions to get a feel for the type of questions asked. It is important to simulate the same time constraints as that in the actual GMAT exam. You can use EduRev’s Practice questions and Mock tests, as they put test takers under time constraints, thus helping students develop time management skills.
- Focus on the key points of the question. When approaching a problem, it is important to focus on the key points of the question in order to make the most informed decision. This means considering all aspects of the question, including the context, potential implications, and any relevant data that can help inform the decision. Once all the necessary information has been gathered, the decision-maker should use this information to guide their decision-making process.
- Make double-checking your answers a habit. By double-checking your work, you can identify any errors or gaps in your reasoning and make appropriate corrections. Additionally, double-checking your work helps to reinforce the concepts and principles you have used in order to solve the problem, making it easier to apply them in the future
- Practice time management: The 12 "questions" in Integrated reasoning actually consist of multiple parts, meaning that if you don't answer all parts of a single question correctly, you won't get any points for that question. Although 30 minutes for 12 questions seems like a lot of time, but when you look at them as 36 questions, the time allotted for each part is significantly less. This calls for proper time management. With regards to time management, all you need to do is have a plan for how to approach each question which ensures that you efficiently work through the material and answer all questions within the allotted time.
How to approach Multi-Source Reasoning Questions
Multi-Source Reasoning questions in the GMAT Integrated Reasoning section present information from multiple sources, such as a graph, table, and written passage, which must be used to answer the question. These types of questions are designed to test a candidate's ability to analyze and interpret data from multiple sources and in various formats. Examples of Multi-Source Reasoning questions include:
- Analyzing a graph and a table to determine a trend or pattern.
- Comparing and contrasting information from a written passage and a chart.
- Using a table and a graph to answer a series of related questions.
- Reading a passage and interpreting a chart to make inferences about the information presented.
- Using multiple tables and charts to answer a question about a specific scenario.
Sample Multi-Source Reasoning Question( from Practice Test: Multi Reasoning Problems - 2 by EduRev)
Directions: Consider each of the following statements. Does the information in the three emails support the inference as stated?
Email - 1
Sent from a coffee shop regional manager to the branch manager.
9:14am - We're considering changing the prices of our lattes to compete with some of the local mom-and-pop stores. The nearby competition charges $2.50 for their large-size lattes. That is much cheaper than I had thought, and explains why we've been losing customers since our current large latte price is $4.00 without any additional syrups, i believe that if we change our price to $3.00. well be able to lure back our old customers and prevent any more of our current regulars from leaving.
Email-2
Sent from the branch manager to the regional manager.
2:06pm - I agree thata price-change may be our best bet to keep our current customers happy. However, $3.00 is a big decrease, and I'd suggest we drop the price to $3.75. If we go below $3.50 we will not be able to remain profitable.Email-3
Sent from the regional manager to the branch manager.
$3:46pm - $3.75 still puts ourcoffee more than $1 over our competitor's price. However,we offer syrups which the competition does not. If we charge $3.50 and include one free syrup, we'll be able to lure customer's back and stay within profitability.
Here’s how you should approach Multi-Source Reasoning questions.
- Read the question properly: More emphasis should be put on this step, as these questions contain the most amount of text, and it can be easy to get lost in excess of information.
- Go over the data swiftly and then examine the question. Doing this will help you save time as you will be aware of the exact location of the data.
- Manage time: There are three pages of information and numerous questions on the same subject making it time-consuming. When attempting these questions, remember to go over all the details, while also being on the lookout for time.
- Keep track of Important information: When looking at three different tabs, it is important that you note the important information mentioned in each of the three tabs so that answering these questions is made easier.
- Summarise the information: It is recommended that you divide your scratchpad into three parts, and summarise important information from each of these parts so that your path to the answer is smoother.
- Don’t rush to the answer: It is very common for students to go directly to the question if they find the slightest of clues to the question. It is recommended that you don't stop reading the passage. It's possible that more information could be available further in the text that would influence the answers you give.
How to approach Table Analysis Questions
Table analysis questions in the GMAT Integrated Reasoning section require the candidate to analyze and interpret data presented in a table format. These types of questions are designed to test a candidate's ability to understand and manipulate data in a table format, and to make inferences and deductions based on the information presented. Examples of table analysis questions include:
- Identifying the relationship between two variables in a table.
- Determining the total or average value of a specific category or data set.
- Comparing and contrasting data across multiple rows or columns in a table.
- Reading a table and interpreting a chart to make inferences about the information presented.
- Using multiple tables to answer a question about a specific scenario.
Sample table analysis question (From table analysis Solved Examples by EduRev)
Ques 1. National Account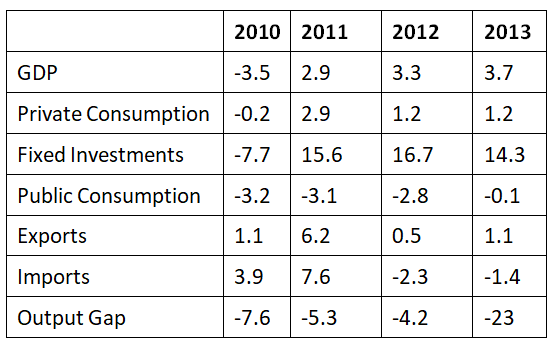
Labor Market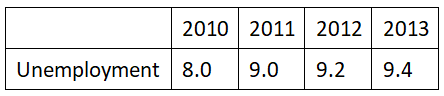
Price and Wages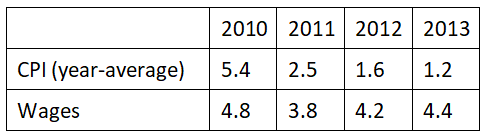
External Balances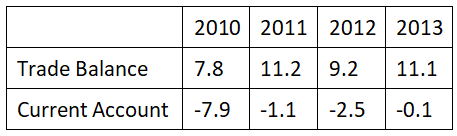
The unemployment in Iceland has generally decreased over the years
Option:
1. Yes
2. No
Ans: No
Here’s how you should approach table analysis questions:
- Understand the question: Read the question carefully and make sure you understand what information is being asked for.
- Take note of units of measurement: Make sure you understand the units of measurement used in the table, as this may affect your calculations and understanding of the data.
- Look for patterns: This can include recognizing trends, looking for anomalies, and comparing the values in different columns. It can also help to look for relationships between different columns and to identify possible causes or explanations for the data
- Take notes: Take notes as you read through the information in the table. This will help you remember key details and make it easier to compare and contrast the information from different rows or columns.
- Use the process of elimination: Eliminate answer choices that are clearly incorrect. This will help you focus on the remaining choices and increase your chances of selecting the correct answer.
- Make use of the sorting feature: The sorting feature is there to help you find the information you need to answer the questions quickly and accurately, so it is important to use it to its fullest potential. This is helpful in finding information of relevance.
How to approach Graphics Interpretation Questions
Graphics Interpretation questions in the GMAT Integrated Reasoning section require the candidate to analyze and interpret charts, graphs, tables, and other visual data. These types of questions are designed to test a candidate's ability to understand and manipulate data presented in a visual format and to make inferences and deductions based on the information presented. Examples of Graphic Interpretation questions include:
- Identifying the relationship between two variables in a graph.
- Determining the total or average value of a specific category or data set based on a chart.
- Comparing and contrasting data across multiple data sets in a graph.
- Reading a graph and interpreting a chart to make inferences about the information presented.
- Using multiple graphs to answer a question about a specific scenario.
Sample Graphics Interpretation question (From Graphics Interpretation Solved Examples by EduRev)
1. The graph below shows the different commuting options chosen by commuters in the Farview City metropolitan region in 1995 and in 2005.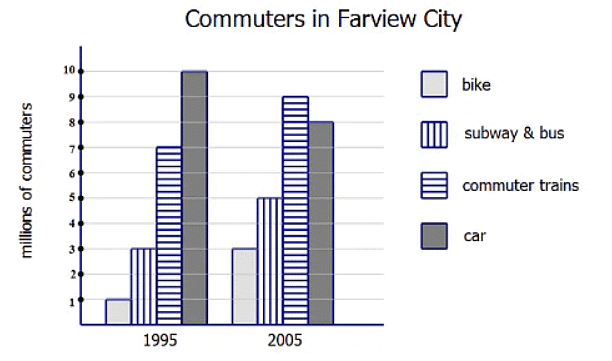
The commuting mode whose ridership increased by approximately 29% from 1995 to 2005 is __________.
(a) bike
(b) Subway and bus
(c) commuter train
(d) car
Ans: commuter train
Here’s how you should approach Graphics Interpretation Questions:
- Read the question properly: Read the question carefully and make sure you understand what information is being asked for. Try not to get lost in unnecessary details.
- Identify the chart type: Identify the type of graph presented (e.g. bar chart, line chart, scatter plot, pie chart, etc) and understand how to interpret the information presented in that type of graph.
- Remember to take the units into account: It is better to double-check the units used in the question before attempting to solve it, to avoid any potential errors. Taking a few moments to check the units can save you time in the long run.
- Identify the relationship between the data provided: You must hone the skill of making meaningful connections between the data that has been presented. This may involve examining the data for patterns, trends, and other correlations that can provide insights and inform decision-making. Developing the ability to recognize and interpret these relationships is essential for utilizing data to its fullest potential.
- Be mindful of the scales: Be mindful of the scales used in the graph and how they may affect your interpretation of the data. For example, if a graph has a wide scale, the differences between data points may appear small, even if they are significant. Conversely, if a graph has a narrow scale, the differences between data points may appear large, even if they are small.
- Work Backwards: Sometimes it can be useful to take a look at the options first, as the answer choices might provide insight into what type of calculation must be done and how precise the answer must be. (number of significant digits)
How to approach Two-Part Analysis Questions
Two-Part Analysis questions in the GMAT Integrated Reasoning section present two related prompts, and the candidate must answer both prompts to complete the question. These types of questions are designed to test a candidate's ability to analyze and interpret data from multiple sources and in various formats, as well as the ability to understand the relationship between different pieces of information. Examples of Two-Part Analysis questions include:
- Analyzing a graph and a table to determine a trend or pattern, and then using that information to answer a related question.
- Reading a passage and interpreting a chart to make inferences about the information presented, and then answering a related question.
- Using a table and a graph to answer a series of related questions.
- Comparing and contrasting information from a written passage and a chart, and then using that information to answer a related question.
- Using multiple tables and charts to answer a set of related questions about a specific scenario.
Sample Two-Part Analysis question (From Two-Part Analysis Solved Examples by EduRev)
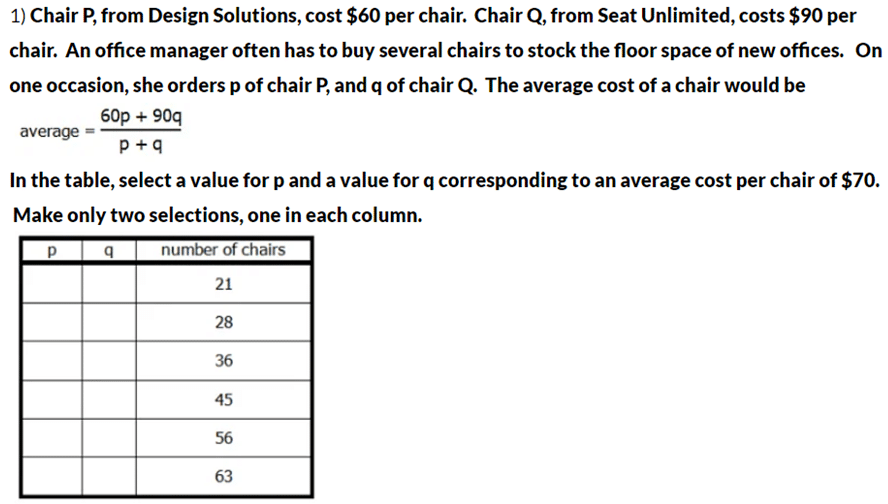
Two-part Analysis questions can be of three types:
- Quant Type Questions
- Critical Reasoning Type Questions
- Follow the Rules Type Questions
Here’s how you should approach Two-Part analysis questions:
- Thoroughly review the data provided: Be sure to thoroughly review both the verbal and numerical information provided in the question. Even if you have expertise in the topic, do not let that affect your response. Only base your answer on the data given in the question, It is important that you don’t base your answer solely on the column headings, instead, review the data provided properly.
- Identify the Question type: Examine the question for numbers or algebraic expressions to identify whether it is a quantitative type question. Additionally, look for words such as infer, conclude, assume, etc. in the question statement to determine if it is a critical reasoning type question.
- For the critical and quant types of questions, it is important to read the information in the passage carefully.
- For questions related to rules, summarize the rules given in the text.
- For critical reasoning questions, identify the premises and the conclusion that is drawn from them
- Identify the relationship between the two prompts: The test taker has to analyze both prompts and identify how the information from one prompt relates to the information from the other prompt. This can involve finding similarities or differences between the two prompts, or determining the cause and effect between them
- If the tasks are inter-dependent, look for an appropriate approach to link the answers, such as a system of equations for quant-type questions
- If the tasks are independent, tackle the simpler one first
- Take notes: Take notes as you read through the information in the prompts. This will help you remember key details and make it easier to compare and contrast the information from different prompts, and you won’t have to go back to the question over and over again.
- Review the answer choices: Sometimes the answer choices can give away the dependency of the tasks, i.e. If the given tasks are independent or dependent.
Tips for GMAT Exam Day
One recurring tip you will notice is to manage stress and rest on the day before the exam. Taking a good night’s sleep is a great way of managing stress and resting your body. Don’t try to cram topics on the day before the exam, because it can end up bringing more harm than good.
Some other things to keep in mind for the exam day are:
- Monitor your time closely: Since the Integrated Reasoning section is a timed section, it is a good idea to allot a specific amount of time to each question.
- Allot adequate time for each question type: Allocate time equally for studying table analysis, Graphics Interpretation, Two-Part Analysis, and Multi-Source Reasoning questions.
- Read the instructions carefully: Make sure you understand what the question is asking and what information is given before you begin answering.
- Take the optional 8-minute break: It's better to take a break and come back to the Integrated section with a fresh mindset after you’ve attempted the previous section.
- Use the Calculator provided: An online basic calculator is provided for only the Integrated Reasoning section of the GMAT exam. You should make use of this calculator to decrease the time spent on calculations.
- Pay attention to the measurement units: When reading the question, pay attention to the measurement units used, as any mistake made in the units you use can end up giving a wrong answer.
How to prepare for GMAT Integrated Reasoning using EduRev Infinity
EduRev Infinity Package for GMAT is a comprehensive package designed to help you get the most out of your GMAT Exam preparation. This package has been designed to provide you with access to hundreds of videos, documents and tests to help you prepare effectively and efficiently for the GMAT exam at an affordable price.
You can use the EduRev Infinity pack to help prepare for the Integrated Reasoning Section of the GMAT exam. The EduRev Infinity pack for GMAT preparation includes explanations of key topics and important tips on how to prepare for the Integrated Reasoning Section. In the pack, you’ll find detailed video explanations, practice questions, mock tests for Reading Comprehension, Critical Reasoning, and Sentence Correction, detailed notes, and much more.
- How to prepare for Integrated Reasoning
- How to attempt IR for GMAT?
- Graph Interpretation
- Table Analysis
- Practice Questions: Integrated Reasoning
- Data Interpretation
- Pie Chart
- Scatter Plot Graph
- Multi Reasoning Problems
- Mock Tests: Integrated Reasoning
- Series Based Problems
- Bar Graph
- Two-Part Analysis
- Data Comparison
- Crash Course: Integrated Reasoning
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) related to GMAT Integrated Reasoning
Is GMAT Integrated Reasoning Tough?
GMAT IR questions are often considered to be among the most difficult on the exam. This is because they require a deep understanding of a variety of concepts and require you to think critically and apply your knowledge in an unfamiliar context. GMAT IR questions often require you to draw inferences from a set of facts and identify trends or relationships among those facts.
Is GMAT Integrated Reasoning score included in the overall score?
No, GMAT IR score is not included in total GMAT score. The GMAT score is composed of three sections: Verbal, Quantitative, and Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA). The GMAT IR score is a separate section and is not included in the total GMAT score
Is GMAT Integrated Reasoning computer-adaptive?
No, the Integrated Reasoning section of the GMAT exam is not Computer adaptive.The IR section is scored separately from the Verbal and Quantitative sections, but the questions are not adjusted based on the student's performance.
Also read: More About Computer Adaptive Test
How is the GMAT exam Integrated Reasoning section scored?
The GMAT Integrated Reasoning section is scored on a scale of 1-8, with 8 being the highest score. The score is based on the number of questions answered correctly because it is not a computer-adaptive section.
Is integrated reasoning important in GMAT?
The Integrated Reasoning section of the GMAT is not included in the total score. But some universities can refer to the score you receive in this section during the admission process, so, the IR section isn’t important for your GMAT score, but it can end up being important for your admissions.
What is a good score for Integrated Reasoning?
A good score for the GMAT Integrated Reasoning section would be a 6 or higher. The score universities consider “good” can vary, but generally speaking, an IR score of 6 is considered respectable.
Do colleges care about Integrated reasoning?
As the IR score isn’t included in the final GMAT score, its importance to your admission depends on the college or graduate business program. Some programs may place more emphasis on the Integrated Reasoning section, while others may not consider it as heavily. It's best to check with the specific program or school you're applying to.














