GST Important Points | Legal Reasoning for CLAT PDF Download
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a value-added tax (VAT) levied on most goods and services sold for domestic consumption. The GST is paid by consumers, but it is remitted to the government by the businesses selling the goods and services.
What Is Direct Tax?
- Direct Tax is defined as a type of tax where the impact and incidence of the tax fall on the same entity. So, the payment direct taxes cannot be passed on to a different individual or a different entity. The organization or individual upon which this type of tax is levied is responsible for its payment. The most common examples of direct taxes in India are income tax, corporation tax, property tax and gift tax.
Various Types of Direct Taxes:
- Income tax
- corporate tax
- Wealth tax
- Gift tax
- Estate duty
- Expenditure tax
- Fringe Benefit Tax
What is Indirect Tax?
- People are subject to an indirect tax when they use products and services. A person’s income is not directly taxed when they pay indirect taxes. However, in addition to the actual cost of the goods or services the seller paid for, he must pay the tax. In general, sellers who pass the tax on to the final customer are subject to indirect tax.
- There is a distinction between the person bearing the burden and the person paying the tax in indirect taxes. These taxes must be paid to the government by the sellers (e.g., manufacturers and retailers). However, businesses pass on the cost of paying the tax to you because they sell items to consumers.
- For instance, assume you are eating at a restaurant. Your total amount plus GST will be shown on the bill (Indirect tax). For example,
The total bill is ₹2500,
and the GST rate is 5%.
Then you must pay a total of 2500+125=₹2625.
This ₹125 is the indirect tax the service provider passes you.
Various Types of Indirect Taxes:
- Service tax
- Excise duty
- Value added tax
- Custom duty
- Securities Transaction Tax(STT)
- Stamp Duty
- Entertainment tax
GST – Goods and Services Tax in India
Launch:
GST Bill Passed on Date:
The bill was passed by the Rajah Sabha on 3 August 2016, and the amended bill was passed by the Lok Sabha on 8 August 2016. The bill, after ratification by the States, received assent from President Pranab Mukherjee on 8 September 2016, and was notified in The Gazette of India on the same date.
The GST was launched at midnight on 1 July 2017 by the President of India, Pranab Mukherjee, and the Prime Minister of India Narendra Modi.
101 Amendment of GST:
Addition of articles 246A, 269A, 279A. Deletion of Article 268A .Amendment of articles 248, 249, 250, 268, 269, 270, 271, 286, 366, 368, 6 Schedule, 7 Schedule.
What is GST?
GST (Goods and Services Tax) is the indirect tax reform of India. GST is a single tax on the supply of goods and services. It is a destination based tax. GST has subsumed taxes like Central Excise Law, Service Tax Law, VAT, Entry Tax, Ontario, etc. GST is one of the biggest indirect tax in the country. GST is expected to bring together state economies and improve overall economic growth of the nation.
GST is a comprehensive indirect tax levy on manufacture, sale and consumption of goods as well as services at the national level. It will replace all indirect taxes levied on goods and services by states and Central. Businesses are required to obtain a GST Identification Number in every state they are registered.
There are around 160 countries in the world that have GST in place. GST is a destination based taxed where the tax is collected by the State where goods are consumed. GST has been implemented in India from July 1, 2017 and it has adopted the Dual GST model in which both States and Central levies tax on Goods or Services or both.
- SGST – State GST, collected by the State Govt.
- CGST – Central GST, collected by the Central Govt.
- IGST – Integrated GST, collected by the Central Govt.
- UTGST – Union territory GST, collected by union territory government
Advantages of GST
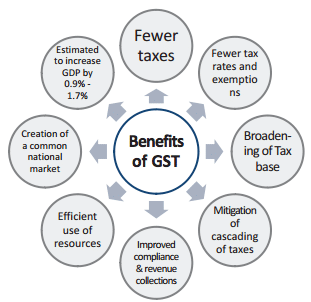
- Helps Maintain Equity
- Indirect taxes are very equitable. The tax depends on the cost of the goods. The higher the price of the goods the more can be the indirect taxes involved. Thus, the people who can purchase high-priced goods pay higher indirect taxes.
- Easy to Pay/Collect
- Indirect taxes are easy to pay for both taxpayers and the authorities. For the tax-payers: While making payment of direct taxes, you need to file an income tax return statement, though it can be done by yourself, it generally requires a Chartered Accountant. But in case of Indirect Taxes, there is no such need as it is paid when you purchase a good.
- For Authorities: It is easier to collect for the authorities. This is because the taxes are collected in the shop, factories themselves.
Convenient
- While calculating the income, there are 5 heads to go through. It should include all the earnings you have made; this is the reason why people evade income tax. But indirect taxes provide you convenience as these are collected on point of sales, i.e., when you purchase.
Limit Harmful Consumption
- Commodities that are harmful to our health such as tobacco, wine, etc include the highest indirect tax. This makes them highly expensive. The high cost of goods helps limit their consumption.
Has a Broader Scope
- Indirect taxes are levied on a range of products and services. It is not the case that some brands incur taxes and some don’t. Also, unlike direct taxes, where it is a one-time payment that is high, indirect taxes are paid as and when you purchase and are much smaller in amount.
Disadvantages of GST
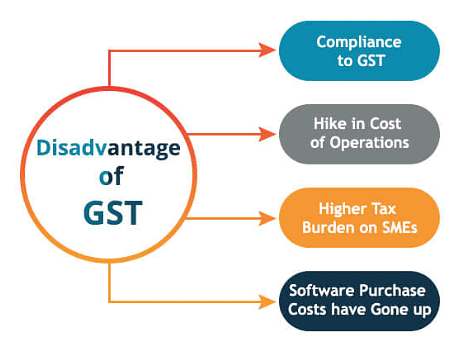
- Can be Regressive
- Regression is a state which pushes a country backward. Indirect taxes are regressive as they are the same for the commodities. Thus, it doesn’t matter you are rich or poor, you pay the same tax. Thus, if you have a lower income, a larger proportion will go towards indirect tax, making your income even lesser.
- Can be Inflationary
- If the indirect taxes are increased by the government, the sellers will add higher charges to their products, this will increase the prices of goods. Thus, it can lead to inflation.
- Discourage Industries
- Indirect taxes when are levied on the raw materials, will make them costly, this can discourage the industry owners to make the product. This can also affect the competitiveness of the market.
- Unpredictable Revenue
- The indirect tax collection is not fixed. It depends on the purchase of goods and services. Thus the government cannot be certain of how much revenue will come through the indirect tax.
Impact of GST on Indian Economy:
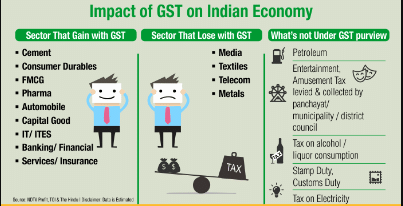
GST offers several benefits to our economy. Here are some key advantages:
- Create unified common national market for India, giving a boost to Foreign investment and “Make in India” campaign
- Boost export and manufacturing activity and leading to substantive economic growth
- Help in poverty eradication by generating more employment
- Uniform SGST and IGST rates to reduce the incentive for tax evasion
Impact of GST on Consumers:
GST is also beneficial for consumers. Here is how it impacts the Indian consumers:
- Simpler Tax system
- Reduction in prices of goods & services due to elimination of cascading
- Uniform prices throughout the country
- Transparency in taxation system
- Increase in employment opportunities
Impact of GST on Traders:
GST is also has some positive impact on traders. Let’s see how it affects the traders:
- Reduction in multiplicity of taxes
- Mitigation of cascading/ double taxation through input tax credit
- More efficient neutralization of taxes especially for exports
- Development of common national market
- Simpler tax regime and Fewer rates and exemptions
GST Rates in 2024
The following are some of the changes that were made-
Railways Goods and Parts under Chapter 86:
- Old GST Rate: 12%
- New GST Rate: 18%
Pens:
- Old GST Rate: 12%
- New GST Rate: 18%
Metal Concentrates and Ores:
- Old GST Rate: 5%
- New GST Rate: 18%
Certain Renewable Energy Devices:
- Old GST Rate: 5%
- New GST Rate: 12%
Recorded Media Reproduction and Print:
- Old GST Rate: 12%
- New GST Rate: 18%
Broadcasting, Sound Recordings, and Licensing:
- Old GST Rate: 12%
- New GST Rate: 18%
Printed Material:
- Old GST Rate: 12%
- New GST Rate: 18%
Packing Containers and Boxes:
- Old GST Rate: 12%
- New GST Rate: 18%
Scrap and Polyurethanes:
- Old GST Rate: 5%
- New GST Rate: 18%
As per the recently held GST Council on 22 June 2024, the following GST rates were announced-
A uniform rate for all types of milk cans:
- Old Rate: –
- New Rate: 12%
A uniform IGST rate applies to imports of aircraft tool kits:
- Old Rate: –
- New Rate: 5%
Carton boxes and cases:
- Old Rate: 18%
- New Rate: 12%
All types of solar cookers:
- Old Rate: 5%
- New Rate: 12%
A uniform rate for all types of sprinklers:
- Old Rate: –
- New Rate: 12%
Indian Railways – Platform tickets:
- Old Rate: –
- New Rate: Exempt
Indian Railways – Facility of retiring rooms/waiting rooms:
- Old Rate: –
- New Rate: Exempt
Indian Railways – Cloak room services:
- Old Rate: –
- New Rate: Exempt
Indian Railways – Battery operated car services:
- Old Rate: –
- New Rate: Exempt
Hostel accommodation service under certain conditions:
- Old Rate: –
- New Rate: Exempt
Decrease in the GST Rates
If vehicles are equipped with retrofitting kits for disabled people:
- Old GST Rate: Applicability
- New GST Rate: 5%
Keytruda for cancer:
- Old GST Rate: 12%
- New GST Rate: 5%
IGST is levied on goods sold at the Indo-Bangladesh border:
- Old GST Rate: Applicability
- New GST Rate: NIL
Kinds of GST Rates and Structures in India
The primary GST slabs for regular taxpayers are currently 0% (nil-rated), 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. There are a few GST rates that are less commonly used, such as 3% and 0.25%.
Furthermore, the taxable composition persons are required to pay General Service Tax at lower or nominal rates such as 1.5%, 5%, or 6% on their turnover. TDS and TCS are also concepts under GST, with rates of 2% and 1%, respectively.
These are the total IGST rates for interstate supplies or the sum of CGST and SGST for intrastate supplies. To calculate the GST amounts on a tax invoice, multiply the GST rates by the assessable value of the supply.
Furthermore, in addition to the above GST rates, the GST law imposes a cess on the sale of certain items such as cigarettes, tobacco, aerated water, gasoline, and motor vehicles, with rates ranging from 1% to 204%.
- Milk: 0%
- Eggs: 0%
- Curd: 0%
- Lassi: 0%
- Kajal: 0%
- Education Services: 0%
- Health Services: 0%
- Children's Drawing & Coloring Books: 0%
- Unpacked Foodgrains: 0%
- Unpacked Paneer: 0%
- Gur: 0%
- Unbranded Natural Honey: 0%
- Fresh Vegetables: 0%
- Salt: 0%
- Unbranded Atta: 0%
- Unbranded Maida: 0%
- Besan: 0%
- Prasad: 0%
- Palmyra Jaggery: 0%
- Phool Bhari Jhadoo: 0%
- Sugar: 5%
- Tea: 5%
- Packed Paneer: 5%
- Coal: 5%
- Edible Oils: 5%
- Raisin: 5%
- Domestic LPG: 5%
- Roasted Coffee Beans: 5%
- PDS Kerosene: 5%
- Skimmed Milk Powder: 5%
- Cashew Nuts: 5%
- Footwear (< Rs.500): 5%
- Milk Food for Babies: 5%
- Apparels (< Rs.1000): 5%
- Fabric: 5%
- Coir Mats, Matting & Floor Covering: 5%
- Spices: 5%
- Agarbatti: 5%
- Coal: 5%
- Mishti/Mithai (Indian Sweets): 5%
- Life-saving Drugs: 5%
- Coffee (except instant): 5%
- Butter: 12%
- Ghee: 12%
- Computers: 12%
- Processed Food: 12%
- Almonds: 12%
- Mobiles: 12%
- Fruit Juice: 12%
- Preparations of Vegetables, Nuts, Fruits, or other parts: 12%
- Packed Coconut Water: 12%
- Umbrella: 12%
- Hair Oil: 18%
- Capital Goods: 18%
- Toothpaste: 18%
- Industrial Intermediaries: 18%
- Soap: 18%
- Ice-cream: 18%
- Pasta: 18%
- Toiletries: 18%
- Corn Flakes: 18%
- Soups: 18%
- Computers: 18%
- Printers: 18%
- Small Cars (+1% or 3% cess): 28%
- High-end Motorcycles (+15% cess): 28%
- Consumer Durables (e.g., AC and Fridge): 28%
- Beedis (not included here): 28%
- Luxury & Sin Items (e.g., BMWs, cigarettes, and aerated drinks) (+15% cess): 28%
HSN and SAC System
- All of the goods and services transacted in the country are classified under the HSN code system or the SAC code system under GST. Goods are classified using the HSN Code, while services are classified using the SAC Code.
- GST rates have been set in five slabs based on the HSN or SAC code, namely NIL, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
HSN System
- The World Customs Organization developed the HSN code, or Harmonized System Nomenclature code number, as an internationally accepted commodity description and coding system. More than 200 countries use the HSN code as the basis for their customs tariffs.
- Currently, over 98% of international trade merchandise is classified using the HSN code. With the HSN code serving as a universal classification for goods, the Government has decided to use the HSN code for GST classification and levy.
- The current version used in international trade transactions is the HSN Code 2017 Edition. Prior to the implementation of the HSN Code-2017 Edition, all international trade transactions used the HSN Code-2012 Edition. The HSN Codes are divided into sections and chapters, and each chapter contains the Harmonized System's six-digit codes.
SAC System
The Service Tax Department of India developed the SAC Code, or Services Accounting Code, as a classification system for services. The General Service Tax rates for services are fixed in 5 slabs using the SAC code, namely 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. If a service is not GST exempt or the GST rates are not provided, the default GST rate for services of 18% will apply.
|
65 videos|182 docs|38 tests
|
FAQs on GST Important Points - Legal Reasoning for CLAT
| 1. What are the key differences between direct tax and indirect tax? |  |
| 2. What are the main types of direct taxes? |  |
| 3. What is GST and how does it work in India? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of implementing GST in India? |  |
| 5. How has GST impacted consumers and traders in India? |  |





















