Genetic Engineering Technique: Gene Transfer | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Gene Transfer? |

|
| Steps Involved in Gene Transfer |

|
| Methods for Gene Transfer |

|
| Achievements of Genetic Engineering |

|
What is Gene Transfer?
Gene transfer is a technique where new DNA is added to the cells of a living organism. This can be done by using carriers like plasmids or modified viruses, such as advanced adeno-associated virus (AAV9) vectors widely adopted by 2025. The new DNA can be added to the cells outside the organism and then put back into the organism, or it can be directly added to the cells inside the organism using cutting-edge tools like CRISPR-Cas12 and base editing systems for precise genetic modifications.
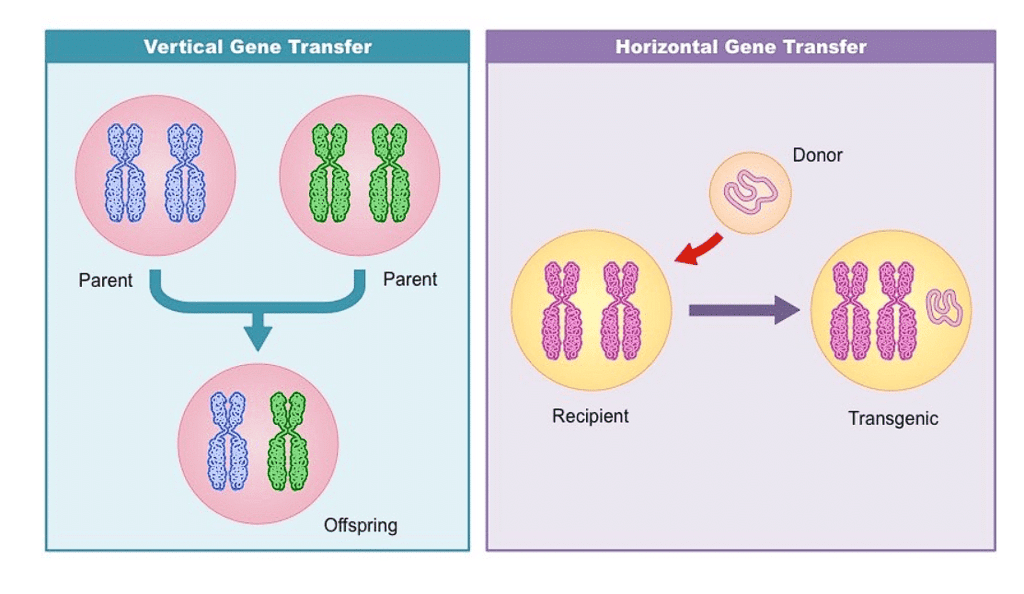 Types of Gene Transfer
Types of Gene Transfer
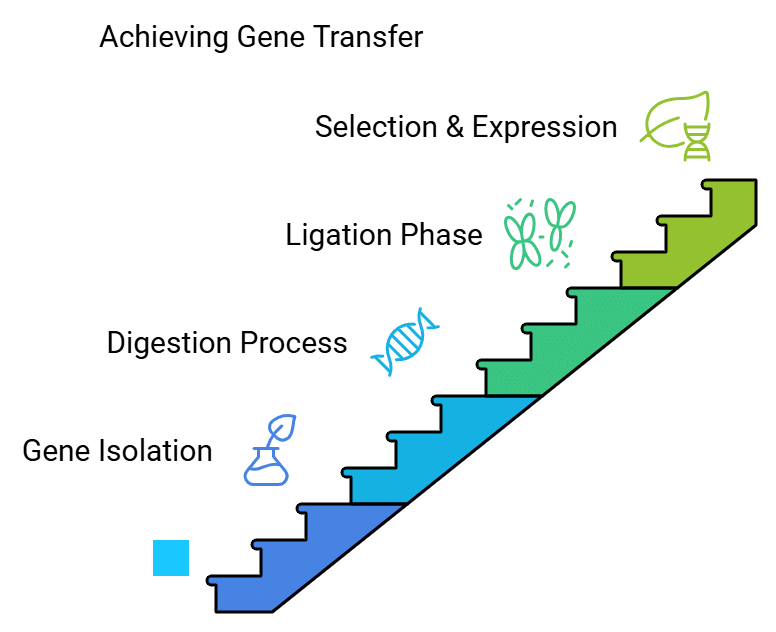
Steps Involved in Gene Transfer
The process of gene transfer can be summarized in four key steps, enhanced by 2025 technologies like CRISPR and next-generation sequencing (NGS):
(a) Isolation of gene and vector (by PCR or advanced CRISPR-based extraction methods)
(b) Digestion of gene and vector (by restriction endonuclease or precise CRISPR-Cas systems)
(c) Ligation of gene and vector (by DNA ligase or CRISPR-mediated integration techniques)
(d) Selection and expression of transgenic construct, now using sophisticated markers like fluorescent proteins
Methods for Gene Transfer
There are two methods of gene transfer, both significantly evolved by 2025 with modern biotechnology advancements:
(a) Indirect or Vector-Mediated Gene Transfer
Indirect or vector-mediated gene transfer in plants involves the use of a plasmid vector. One widely employed vector for plant transformation is the Ti-plasmid found in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, though by 2025, synthetic CRISPR-based vectors are also prevalent.
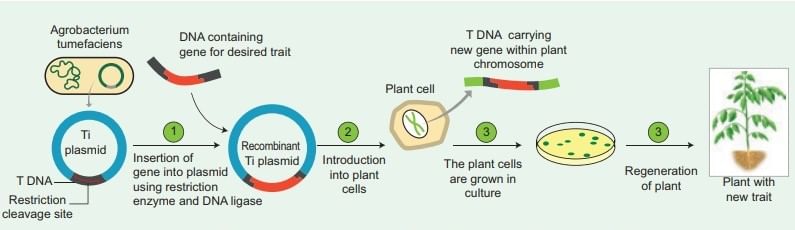 Agrobacterium-mediated Gene Transfer
Agrobacterium-mediated Gene Transfer
- This bacterium carries a relatively large plasmid called the Ti plasmid (which stands for Tumor-inducing plasmid). A specific portion of this plasmid, known as T-DNA (Transfer DNA), is integrated into the plant genome within infected cells, leading to the development of plant tumors, or crown galls, now harnessed for precise gene insertion.
- Due to its inherent ability to naturally transfer the T-DNA region from its plasmid into the plant genome upon infecting wounded plant cells, Agrobacterium tumefaciens is often referred to as nature’s genetic engineer for plants, a role enhanced by 2025 synthetic biology tools.
- The foreign gene (e.g., Bt gene for insect resistance) and plant selection marker gene, usually an antibiotic gene like npt II which confers resistance to antibiotic kanamycin, are cloned in the T-DNA region of Ti-plasmid in place of unwanted DNA sequences, with 2025 advancements using fluorescent markers for efficiency.
(b) Direct or Vectorless Gene Transfer Method
In the direct gene transfer methods, the foreign gene of interest is delivered into the host plant without the help of a vector. The following are some of the common methods of direct gene transfer in plants, updated with 2025 techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 delivery via nanoparticles.
The various methods of direct gene transfer are:
(i) Chemical Method
Use chemicals like polyethylene glycol and polyvinyl alcohol to help plant cells take in foreign DNA, now optimized with CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins (RNPs).
Start with plant protoplasts (cells without cell walls) in a magnesium-rich medium, enhanced for efficiency.
Add plasmid DNA with the desired gene. Use polyethylene glycol, maintain pH at 8, and briefly heat protoplasts. Cool them on ice to boost DNA uptake, a process refined by 2025 protocols.
Allow incubation for DNA integration. Later, reduce polyethylene glycol and increase calcium ions for better transformation efficiency, leveraging modern biochemical insights.
(ii) Electroporation
A pulse of high voltage is applied to protoplasts, cells, or tissues which makes transient pores in the plasma membrane through which uptake of foreign DNA occurs, now optimized for stem cells and CRISPR delivery.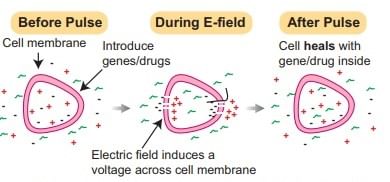
(iii) Biolistic Gun
Foreign DNA is attached to tiny gold or tungsten particles, typically measuring 1-3 µm. These particles are then shot onto the target tissue or cells using a device known as a gene gun, micro projectile gun, or shotgun, enhanced by 2025 with nanoparticles for CRISPR delivery. After bombardment, the treated cells or tissues are grown in a specific medium to encourage the development of plants from the modified cells, a process now more precise.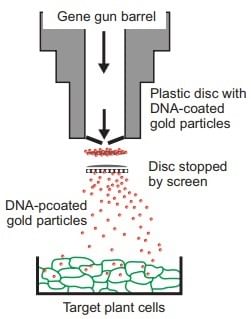 Gene Gun
Gene Gun
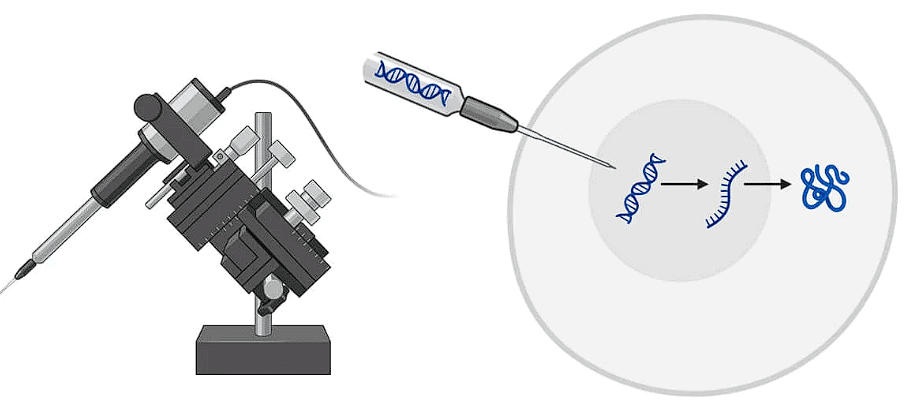
(iv) Microinjection
The DNA is directly injected into the nucleus using fine tipped glass needle or micro pipette to transform plant cells, now used for CRISPR-Cas9 delivery in embryos. The protoplasts are immobilised on a solid support (agarose on a microscopic slide) or held with a holding pipette under suction.
 Microinjection
Microinjection
(v) Lipofection
Artificial phospholipid vesicles called liposomes are valuable for transferring genes. They enable the transfer of genes or DNA from the liposome into the vacuole of a plant, with 2025 advancements favoring lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for mRNA and CRISPR delivery.
Achievements of Genetic Engineering
DNA recombinant technology or genetic engineering provides great benefits for the advancement of science and society, revolutionized by 2025 with tools like CRISPR and synthetic biology.
1. Gene Therapy:
A new system of medicine gene therapy, may develop to treat hereditary diseases such as haemophilia. – It is the technique for curing genetic disease by replacing a "Faulty Gene" with a normal healthy functional gene, with CRISPR-based therapies approved by 2025 for sickle cell disease.- The first gene therapy used in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) patient paved the way for modern CRISPR treatments.
- About 25% of an infant with SCID disorder lack the enzyme adenosine deaminase (ADA) – ADA enzyme involved in purine metabolism, now editable with CRISPR-Cas9.
- These patients have no functioning T & B lymphocytes, a condition now treatable with advanced gene editing.
- The affected child of SCID develops recurrent infection early in life because they have no immune response against invading pathogen, mitigated by 2025 therapies.
- The ideal approach would be to give the patient a functioning ADA by gene therapy, now a reality with CRISPR precision.
- Thus, the genetic disorder can be overcome by introducing a specific gene, enhancing patient outcomes significantly.
2. Bacteria
as "Living Factories" for synthesizing vitamins, hormones, and antibodies, expanded by 2025 to include biofuels and biologics.- Human insulin (Humulin) was the first genetically engineered product produced by an American firm Eli Lilly – 5th July 1983, now followed by complex biologics via synthetic biology.
- Charles Weismann of the University of Zurich obtained interferon through recombinant E.coli (1980), a technique refined with CRISPR by 2025.
- Microbes have been engineered to produce Human Growth Hormone (HGH) for curing dwarfism, now optimized with modern gene editing.
- Vaccines are produced by genetic engineering e.g., for Hepatitis-B and Herpes virus, with mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 prominent by 2025.
- Nitrogen fixation genes may be transferred from bacteria to the major food crops to boost food production without using expensive fertilizers, achieved with CRISPR in 2025 crops like rice.
- Transgenic plant obtained through recombinant DNA technology. The first transgenic plant was tobacco, followed by CRISPR-edited varieties by 2025.
 Tobacco
Tobacco
- It contains a resistant gene against weedicide (Glycophosate), a trait expanded in later CRISPR-edited plants.
- The first transgenic animal was a mouse containing the gene for growth hormone, followed by advanced models by 2025.
- The first introduced transgenic crop in India (2002) is Bt-cotton, succeeded by CRISPR-edited rice in 2025.
- It is resistant for boll worm (Helicoverpa armigera - Larva of insect), a trait now complemented by multi-trait edits.
- It is formed by the transfer of a pest-resistant gene from Bacillus thuringiensis (bt-2 gene encoding Bt–toxin), enhanced with CRISPR precision.
- Bacillus thuringiensis produces a toxic protein called crystal protein (Cry-Protein); this protein is toxic for the larva of a certain insect, with synthetic biology expanding its applications.
 Cry-protein
Cry-protein
- This protein kills the insect by inhibiting ion transport in the mid-gut (bt 2 genes is called cry-gene) – In pollution control, microbes have been engineered to break up the crude oil spills, now using advanced synthetic strains.
- Dr Ananda Mohan Chakraborty introduced plasmid from different strains into a single cell of pseudomonas putida. The result was a new genetically engineered bacterium that would clean oil spills called "Superbug" (oil eating bug), a concept expanded by 2025 bioremediation tech.
3. Medical Diagnosis of Disease
- Recombinant DNA technology is one of the important tools for the diagnosis of several diseases. The diagnostic technique involves the construction of probes consisting of short segments of single-stranded DNA attached to a radioactive or fluorescent marker, now enhanced with CRISPR-Cas12.
- Such probes are used to identify infections agents such as Salmonella (cause food poisoning), Staphylococcus (pus-forming bacterium), hepatitis virus, HIV; muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis and so on, with rapid detection by 2025 standards.
- Recombinant DNA technology can also be employed to predict the inheritance of genetic disorders from carrier parents. The chances of birth of an affected child can be predicted by testing the DNA of repetitive prospective genetic disorder carrier parents, aided by NGS and AI by 2025.
Application
of Recombinant DNA Products
Application of Genetically Engineered Microbes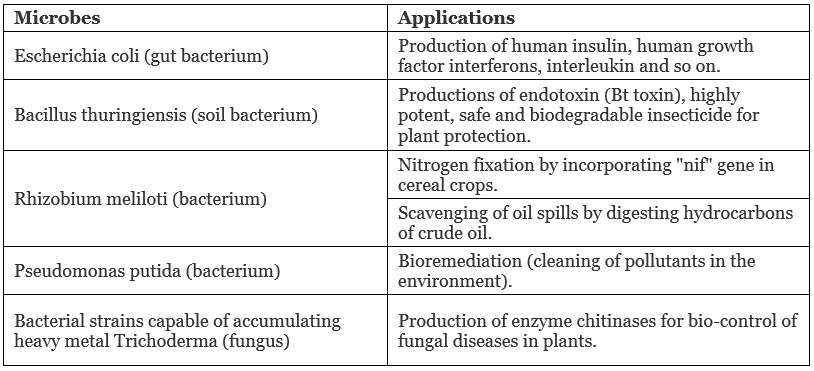
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Genetic Engineering Technique: Gene Transfer - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is gene transfer and why is it important in genetic engineering? |  |
| 2. What are the main steps involved in the gene transfer process? |  |
| 3. What methods are commonly used for gene transfer? |  |
| 4. What are some significant achievements of genetic engineering through gene transfer? |  |
| 5. How has gene transfer technology impacted agriculture and medicine? |  |
















