Global e-Business | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
- Communication technologies have advanced significantly since the last decade of the twentieth century, accelerating the process of globalization. Currently, most nations are well-prepared for the electronic economy and the establishment of e-business infrastructure. It's crucial for different countries to formulate specialized e-business strategies that leverage their unique capabilities, resources, and geographic positions. There's a need for diverse models to construct e-business infrastructure and engage in global e-commerce.
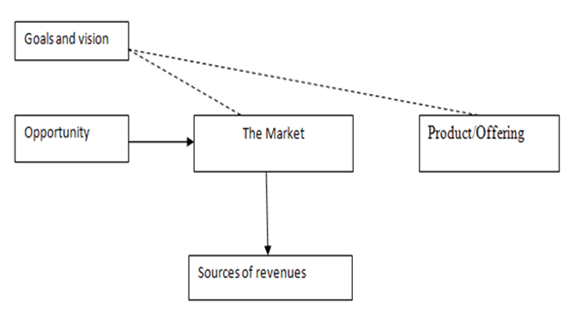
- The growth of global e-business is rapid, with several trillion dollars exchanged annually over the internet. Companies need to evaluate global markets and expand their online presence not only in developed countries but also in emerging economies like China, Brazil, and India to harness the potential of global e-business technology. Companies can either proactively seize global e-business opportunities and benefit from e-commerce or adopt a protective approach against new global competition that poses a threat to their business.
- As e-business becomes more widespread, domestic businesses will increasingly feel the pressure of international competition. E-business provides companies with a platform to compete on a universal level, intensifying the competition in the global market.
Internet as a Game-Changer:
- The combination of telecommunications and computer technology led to the creation of the internet.
- It's a significant development in business, often seen as an example of ecological business growth.
Internet's Impact:
- The internet has become a crucial technology, drawing attention from academics, entrepreneurs, businesses, and investors.
- E-commerce, conducted through the internet, is transforming the business environment and causing significant changes.
Information Age Transformation:
- The information age, marked by the rise of the internet, has forced companies to rethink their organizational models for managing business.
Organizational Ecology:
- Organizational ecologists, like Hannan and Freeman, have emphasized that environmental pressures strongly influence how successful an organization is in terms of its structure, function, and overall strategy.
E-commerce Growth:
- Examining the growth of e-commerce on the internet provides a unique opportunity to understand how a business sector evolves rapidly.
- Internet technology, including e-commerce, offers global companies the chance to create distinct strategic advantages.
Global E-commerce Definition:
- Global e-commerce involves using electronic networks to reach global markets.
- It encompasses various types of transactions like business-to-business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C), consumer-to-consumer (C2C), business-to-government (B2G), and other mixed forms of transactions.
Theoretical Research on Global E Business
Impact of Globalization on Business Strategies:
- Traditionally, globalization led companies to expand and sell the same product with similar strategies worldwide.
- With internet advancements, organizations can now successfully sell globally by adapting their websites to be accessible to diverse customers.
Website Localization Essentials:
- To make a website effective globally, it needs to be adapted linguistically, racially, and in various other ways for a global audience.
- Localization involves considering factors like language, design, culture, customs, symbols, currency, and more in web design.
Evolution of Localization Industry:
- Within a decade, an industry has emerged to help companies design localized multilingual websites and software for diverse cultures.
- This industry also assists companies in navigating international challenges related to legal and logistical issues.
E-commerce and Organizational Change:
- Global e-commerce, influenced by the internet, has led to organizational changes in how businesses operate.
- The paper by Singh, Alhorr, and Kim introduces the concept of "adaptive strategies" in international e-commerce, addressing the debate between localization and standardization.
Cultural Congruency in Websites:
- Vyncke and Brengman's study reviews the impact of cultural congruency on the efficacy of international websites.
- It explores whether creating culturally harmonious websites is essential for successfully reaching diverse target countries.
Information Ecology Perspective:
- Zhu and Thatcher study global e-commerce development from an information ecology viewpoint.
- Their research highlights the influence of national information ecology on a country's e-commerce adoption at different stages of development.
Institutional Theory and E-commerce:
- Martinez and Williams analyze e-commerce development in different nations based on economic institutional theory and entrepreneurship theory.
- Their findings support the idea that strong legal, political, and socio-economic institutions positively influence a country's access to e-commerce technologies.
Importance of Website Localization:
- Research suggests that companies must develop localized international websites to effectively communicate and sell to online viewers globally.
- Website localization involves adapting websites to meet the linguistic, cultural, and other requirements of the target market.
Global E-business Strategic Factor Markets:
- The web provides access to global resources through international e-business strategic factor markets.
- These markets offer information-rich, knowledge-oriented, and intangible resources, categorized into internet-based, alliance-based, and location-based strategic factor markets.
 Global online business environment
Global online business environmentBain & Company's findings over the past three years revealed a doubling of digital purchases from overseas, indicating a rising demand for foreign products. Interestingly, while the desire for international goods is evident, Chinese consumers still prefer a local e-commerce experience. To effectively compete in this dynamic market, companies are advised to localize aspects such as payment methods, currency support, and marketing campaigns to align with local preferences. In the realm of global e-business, firms employ diverse transaction approaches, including hierarchical forms, market forms, and hybrid forms. In the hybrid model, companies establish long-term partnerships and joint ventures with local firms, allowing them to navigate the global market successfully. The key to the success of globally competing firms lies in their ability to adapt and address local market nuances effectively.
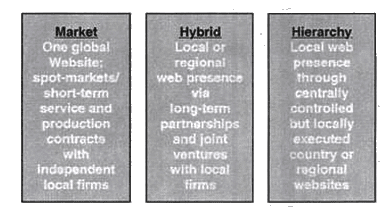 Continuum of market and hierarchy
Continuum of market and hierarchy
Benefits of E-business Strategy:
- E-business strategies help companies develop cost-effective communication and marketing plans.
- Having an online presence becomes central to communication and marketing efforts in an upgraded e-business environment.
Web Presence and Global Access:
- E-business provides companies with a vital web presence, allowing them to communicate and market effectively.
- The internet offers powerful ways to access global markets and precisely target customers.
Lower Initial Investment:
- Adopting e-business is advantageous for entrepreneurs as the initial investment is typically lower than traditional business models.
- It makes communication and transactions faster and more cost-effective through email and online ordering systems.
Changing International Selling Trends:
- Global e-business has transformed the way companies sell internationally.
- Challenges in global e-business are linked to cultural, economic, infrastructure, and political regulatory factors.
Challenges in Global E-business:
- Challenges include cultural barriers, language differences, shopping habits, and the use of credit cards.
- Organizations face difficulties in web localization efforts, geopolitical uncertainties, and a lack of professionally trained workforce.
Online Challenges for International Sales:
- Managing multiple languages, local currency transactions, customer support, shipping, legal issues, and technical aspects are challenges in international e-commerce.
- Compliance with complex regulations for global trade management is crucial for financial success.
Strategies for Global E-business Success:
- The web benefits the industry, and companies launch e-business processes to attract international customers and increase sales.
- Successful global e-business expansion requires organizations to understand and replicate processes for effective website globalization management.
Global Dynamic Capabilities:
- Global dynamic capabilities help companies adapt internal processes to respond effectively to the global business environment.
- To attract a global audience, e-businesses need strategies for exploring new markets, utilizing social media, and creating valuable content.
Internet Strategies for Consumer Reach:
- Utilizing the internet for strategies like selling discounted stock and exploring new target markets is advisable.
- Building a global audience involves using social media and content to establish healthy relationships with consumers worldwide.
FAQs on Global e-Business - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is global e-business? |  |
| 2. How does global e-business impact traditional brick-and-mortar businesses? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of global e-business? |  |
| 4. What are the challenges faced by global e-businesses? |  |
| 5. How can businesses overcome the challenges of global e-business? |  |

















