HIV Structure | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
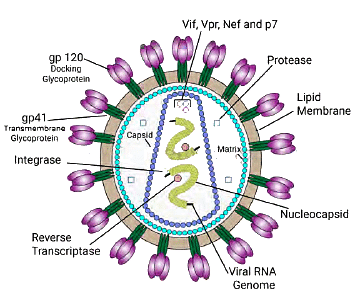
- Lentivirus
- Ranges in size from 80 to 110 nm
- Comprises Envelope and Nucleocapsid
- Envelope features gpl20 and gp41
- Nucleocapsid contains two identical copies of single-stranded RNA (ss) and viral enzymes
- Structural genes include Gag-p24, Pol-RT, protease, Integrase, Env-gpl20, gp-41, along with nonstructural genes Tat, Nef, Vpu, Vpr, Vpx, Rev, Vif
- Serotyping for HIV-1 and HIV-2
- HIV-1 subtypes (M, N, O, P) with M being predominant worldwide
- HIV-2 subtypes (A-H) with Group A being more prevalent

WHO-HIV clinical Staging in Adults
Clinical Stage 1:
- Asymptomatic
- Persistent generalized lymphadenopathy
Clinical Stage 2:
- Moderate unexplained weight loss (<10% of presumed or measured body weight)
- Recurrent respiratory tract infections (sinusitis, tonsillitis, otitis media, pharyngitis)
- Herpes zoster
- Angular cheilitis
- Recurrent oral ulceration
- Papular pruritic eruption
- Fungal nail infections
- Seborrheic dermatitis
Clinical Stage 3:
- Unexplained severe weight loss (>10% of presumed or measured body weight)
- Unexplained chronic diarrhea for longer than 1 month
- Unexplained persistent fever (intermittent or constant for longer than 1 month)
- Persistent oral candidiasis
- Oral hairy leukoplakia
- Pulmonary tuberculosis
- Severe bacterial infections (such as pneumonia, empyema, pyomyositis, bone or joint infection, meningitis, bacteremia)
- Acute necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis, gingivitis, or periodontitis
- Unexplained anemia (<8 g/dl), neutropenia (<0.5 x 109/L), and/or chronic thrombocytopenia (<50 x 109/L)
Clinical Stage 4:
- HIV wasting syndrome
- Pneumocystis (jirovecii) pneumonia
- Recurrent severe bacterial pneumonia
- Chronic herpes simplex infection (orolabial, genital, or anorectal for more than 1 month's duration or visceral at any site)
- Esophageal candidiasis (or candidiasis of trachea, bronchi, or lungs)
- Extra-pulmonary tuberculosis
- Kaposi sarcoma
- Cytomegalovirus infection (retinitis or infection of other organs)
- Central nervous system toxoplasmosis
- HIV encephalopathy
- Extra-pulmonary cryptococcosis, including meningitis
- Disseminated non-tuberculous mycobacterial infection
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- Chronic cryptosporidiosis
- Chronic isosporiasis
- Disseminated mycosis (extra-pulmonary histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis)
- Lymphoma (cerebral or B-cell non-Hodgkin)
- Symptomatic HIV-associated nephropathy or cardiomyopathy
- Recurrent septicemia (including non-typhoid Salmonella)
- Invasive cervical carcinoma
- Atypical disseminated leishmaniasis
HIV -Modes of Transmission

Lab Diagnosis of HIV


Serological Diagnosis

Serological Diagnosis of HIV


Serologic Tests in the Diagnosis of HIV-1 or HIV-2 Infection.
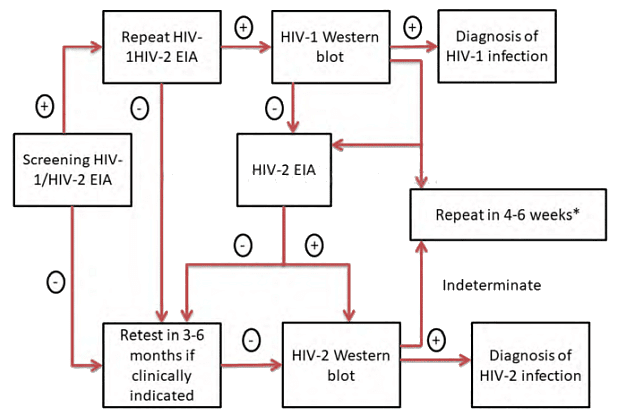
NACO Testing Strategy for HIV Diagnosis
In resource-poor countries, confirming HIV screening test results through PCR or western blot is impractical due to the expense and limited availability of these assays. The National AIDS Control Organization (NACO) in India has devised a strategic plan for HIV diagnosis.
- Depending on the specific situation or condition for which the test is conducted, a positive result from the initial screening test should either be accepted as is or confirmed by one or two additional screening tests.
- The first screening test should prioritize high sensitivity, while the second and third screening tests should prioritize high specificity.
- The three screening tests should employ different principles or different antigens, and it is essential not to reuse the same kit.
- Supplemental or confirmatory tests should be reserved for cases where the screening test(s) yield equivocal or intermediate results.

There are four strategic plans/algorithms outlined by NACO:
1. Strategy I:
- Applied to blood donors in blood banks.
- Involves a single test.
2. Strategy II (a):
- Implemented for seroprevalence or epidemiological purposes.
- Requires two tests.
3. Strategy II (b):
- Utilized for the diagnosis of HIV/AIDS in symptomatic patients.
- Involves two tests.
4. Strategy III:
- Employed for the diagnosis of asymptomatic HIV patients, antenatal screening, and screening of patients awaiting surgeries.
- Involves three tests.
Strategy I
Use test of high sensitivity

A blood unit that tests positive should be discarded. In the event that the donor has consented to be notified of their result, it becomes a diagnostic matter, requiring the use of strategies II and III following appropriate counseling. The donor should then be referred to an Integrated Counseling and Testing Center (ICTC) for result confirmation.
Strategy II A
Used in Sentinel surveillance

Strategy II B
Used for diagnosis in symptomatic patients

Strategy III
Used for diagnosis in asymptomatic patients
Test 1-High sensitivity Test 2 and 3-High specificity

If results remain negative despite repeated testing, conduct PCR testing (if facilities are available) and refer the case to the National Viral Reference Laboratory (NVRL)
Dermatological Manifestations of HIV
More than 90% of individuals with HIV infection experience dermatologic issues.
Non-Neoplastic:
- Seborrheic dermatitis is observed in 50% of HIV patients and is exacerbated by concurrent Pityrosporum infection, a yeastlike fungus.
- Folliculitis is present in nearly 20% of HIV cases.
- Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis manifests as multiple urticarial perifollicular papules that may merge into plaque-like lesions, accompanied by elevated serum IgE levels.
- Prurigo nodularis (PN) is a skin condition characterized by hard, itchy nodules.
- Norwegian scabies is a severe form with hyperkeratotic psoriasiform lesions.
- Guttate psoriasis transforms preexisting psoriasis and becomes refractory to treatment.
- Reactivation of Herpes Zoster is observed in 10-20% of HIV patients, with clinical manifestations indicative of immunologic compromise but less severe than in other immunodeficient conditions.
- Recurrent reactivation of Herpes simplex infection presents as beefy red lesions, intensely painful, and often occurring high in the gluteal cleft.
- Diffuse skin eruptions due to molluscum contagiosum.
- Cutaneous drug reactions, including erythroderma, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis, as reactions to drugs such as sulfa drugs, nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, abacavir, amprenavir, darunavir, fosamprenavir, and tipranavir.
Neoplastic:
- Kaposi's Sarcoma: The initial lesion may appear on the skin, oral mucosa, or sun-exposed areas, particularly following trauma (Koebner phenomenon).

HIV-Repeats
- Describe the mode of transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus and outline preventive measures to curb its spread (1994).
- Explore the various modes of HIV/AIDS transmission prevalent in India (1997).
- Provide details on drug treatment, including names, doses, and toxicity, for managing HIV infection (2003).
- Identify common dermatological lesions associated with AIDS (2006).
- Enumerate significant parasitic and fungal opportunistic infections occurring during HIV infection. Discuss current strategies for HIV testing, monitoring progress, and briefly outline recommended treatment (2011).
- Delve into the laboratory diagnosis of AIDS (2012).
- Provide a detailed account of the laboratory diagnosis of AIDS (2016).
- Name two opportunistic fungal and two parasitic agents causing infections in an HIV patient. Describe the laboratory diagnosis of one of them (2017).
- Discuss the strategic plans formulated by NACO for diagnosing individuals exhibiting AIDS-indicative symptoms (2018).
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on HIV Structure - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is WHO-HIV clinical staging in adults? |  |
| 2. What are the modes of transmission for HIV? |  |
| 3. How is HIV diagnosed through serological testing? |  |
| 4. What is NACO's testing strategy for HIV diagnosis? |  |
| 5. What are the dermatological manifestations of HIV? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















