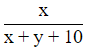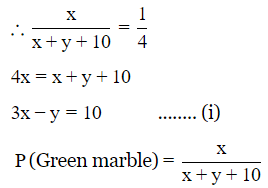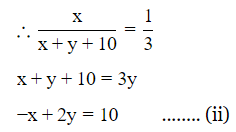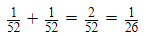Q1: From a set of 17 cards numbered 1 to 17 one is drawn at random. The probability that it is divisible by 3 or 5 is
(a) 8/17
(b) 5/17
(c) 6/17
(d) 7/17
Ans: d
The numbers less than or equal to 17 which are divisible by 3 are 3,6,9,12,15.
Similarly, the numbers less than or equal to 17 which are divisible by 5 are 5,10,15.
Numbers less than or equal to 17 which are divisible by both 3 and 5 are 1.
Hence, total 5 + 3−1 = 7 numbers are divisible by 3 or 5.
Total number of cards = 17
So probability is equal to = 7/17
The correct option is D.
Q2: The probability of selecting a green marble at random from a jar that contains only green, white and yellow marbles is 1/4. The probability of selecting a white marble at random from the same jar is 1/3. If this jar contains 10 yellow marbles. What is the total number of marbles in the jar?
(a) 20
(b) 24
(c) 35
(d) 40
Ans: (b)
P(Green marble) = 1/4
P(white marble) = 1/3
Let number of green marble $$= x$$
and number of white marble = y
So, P(Green marble) = 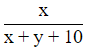
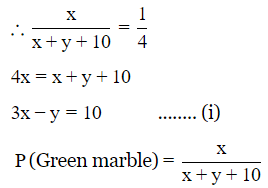
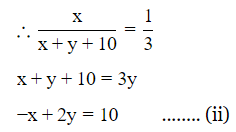
Multiply equation (i) by (ii)
6x − 2y = 20
−x + 2y = 10
5x = 30
x = 6
substitute x = 6 in equation (i)
3 × 6 − y = 10
y = 8
So, total number of marbles = x + y + 10
= 6 + 8 + 10
= 24
Q3: From a pack of 52 playing cards, face cards and tens are removed and kept aside then a card is drawn at random from the remaining cards. If
A : The event that the card drawn is an ace
H : The event that the card drawn is a heart
S : The event that the card drawn is a spade
then which of the following holds?
(a) 9P(A) = 4P(H)
(b) P(S) = 4P(A∩H)
(c) 3P(H) = 3P(A∪S)
(d) None of these
Ans: (a, c, d)
Given from a pack of 52 cards, face cards and tens are removed.
⇒ Total no. of remaining cards = 52−(12+4) = 36 cards
A: The event that the card drawn is an ace, P(A) = 4/36 = 1/9
H: The event that the card drawn is an Heart, P(H)= 9/36 = 1/4
S: The event that the card drawn is a Spade, P(S)= 9/36 = 1/4
and P(A∩S)= 1/36 (Since only 1 card exist which is spade and ace)
P(A ∪ S) = P(A) + P(S)−P(A ∩ S) = 1/9 + 1/4 − 1/36 (since P(A ∩ S) = 1/36) = 1/3
⇒ 9P(A) = 4P(H) = 3P(A ∪ S) = 1 and 9P(A ∩ S) = P(H)
Q4: From a well shuffled standard pack of 52 playing cards, one card is drawn. What is the probability that it is either a King of hearts or a Queen of diamonds.
(a) 1/2
(b) 1/4
(c) 1/8
(d) 1/26
Ans: (d)
No. of Kings of heart = 1, No. of Queen of diamonds =1
Probability of king of hearts or queen of diamonds = 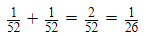
Q5: Two dice are thrown at the same time and the product of numbers appearing on them is noted. Find the probability that the product is a prime number.
Ans: Total no.of possible outcomes = 62 = 36
i.e. (1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(1,5),(1,6)
(2,1),(2,2),(2,3),(2,4),(2,5),(2,6)
(3,1),(3,2),(3,3),(3,4),(3,5),(3,6)
(4,1),(4,2),(4,3),(4,4),(4,5),(4,6)
(5,1),(5,2),(5,3),(5,4),(5,5),(5,6)
(6,1),(6,2),(6,3),(6,4),(6,5),(6,6)
Out of these,product of outcomes that would be prime would be (1,2),(1,3),(1,5),(2,1),(3,1),(5,1).
Probability = 6/36 = 1/6.
Q6: What is the probability that a number selected from numbers 1,2,3,...,30, is a prime number, when each of the given numbers is equally likely to be selected?
(a) 1/2
(b) 1/4
(c) 2/3
(d) 1/3
Ans: (d)
Total numbers: 30
Total prime numbers: 10→{2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29}
Required Probability: