Henry's Law: Effect of Pressure on Solubility of Gases in Liquids | Physical Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Henry's Law |

|
| Factors Affecting the Henry’s Law Constant |

|
| Applications of Henry's Law |

|
| Limitations of Henry's Law |

|
Henry's Law
Henry’s Law gives a quantitative relation between pressure and gas solubility in a liquid. It states that:
The solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas present above the surface of liquid or solution.
The solubility is taken as the mass of the gas dissolved per unit volume of the liquid. Thus, if m is the mass of the gas dissolved per unit volume of the solvent and P is the pressure of the gas in equilibrium with the solution, then
| m ∝ p m = Kp |
where K is the proportionality constant.
When P = 1, m = K, i. e., the solubility of the gas at unit pressure is equal to constant K.

Factors Affecting the Henry’s Law Constant
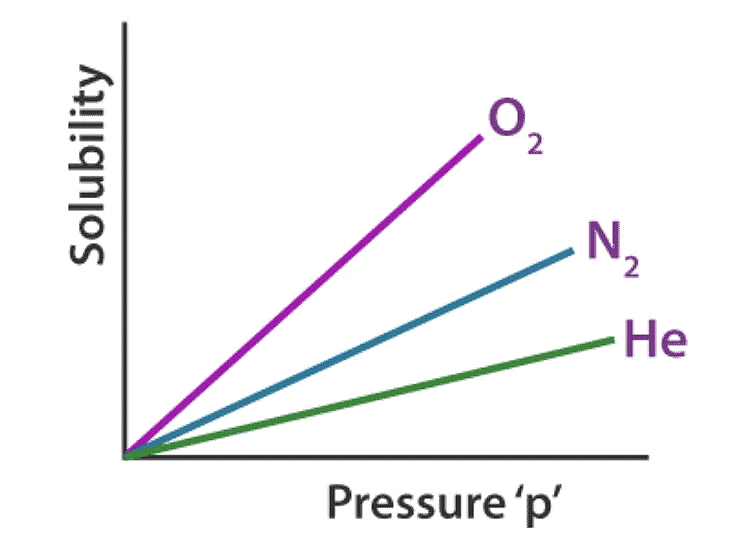
- Nature of the gas: Different gases have varying solubilities in a solvent due to differences in molecular size, polarity, and intermolecular forces. For example, highly polar gases tend to be more soluble in polar solvents compared to nonpolar gases.

- Nature of the solvent: The solvent's polarity and molecular structure influence its ability to dissolve gases. Polar solvents, such as water, favor the dissolution of polar gases, while nonpolar solvents prefer nonpolar gases. Additionally, solvent-solute interactions affect the solubility.
- Temperature: Henry's Law constant is temperature-dependent. Generally, solubility decreases with increasing temperature due to decreased gas solvation in the solvent. However, this relationship can vary depending on the specific solute-solvent system and the enthalpy of solution.
- The units of pressure
Therefore, different gases have different Henry’s laws constant in different solvents, as illustrated graphically above.
Effect of Pressure on Solubility of Gases in Liquids
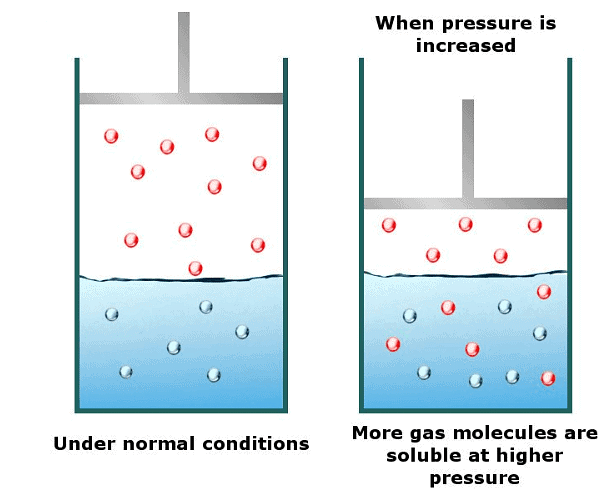
- Solubility of a gas in liquid increases with an increase in pressure and vice versa. That is the solubility of a gas in liquid decreases with a decrease in pressure.

- The solubility of a gas in liquid decreases with an increase in Henry’s Law constant (KH), at a given pressure. This means at a given pressure higher the value of KH (Henry’s Law constant), the lower is the solubility of the gas in a liquid and vice versa.
Example 1. If N2 gas is bubbled through water at 293 K, how many millimoles of N2 gas would dissolve in 1 litre of water? Assume that N2 exerts a partial pressure of 0.987 bar. Given that Henry’s law constant for N2 at 293 K is 76.48 kbar.
Solution.
The solubility of gas is related to the mole fraction in aqueous solution.
The mole fraction of the gas in the solution is calculated by applying Henry’s law.Thus:
x (Nitrogen) = p(nitrogen)/KH = 0.987 bar/76.480 = 1.29 × 10-5
As 1 litre of water contains 55.5 mol of it, therefore if n represents number of moles of N2 in solution,
x (Nitrogen) = n mol/n mol + 55.5 mol = n/55.5 = 1.29 × 10-5
(n in denominator is neglected as it is < < 55.5)
Thus n = 1.29 × 10–5 × 55.5 mol = 7.16 × 10–4 mol
Applications of Henry's Law
- Pepsi and other Carbonated Drinks: Since the solubility of a gas in liquid increases with an increase in pressure, hence increasing the solubility of CO2 in soft drinks and soda water, the bottle is sealed under high pressure.
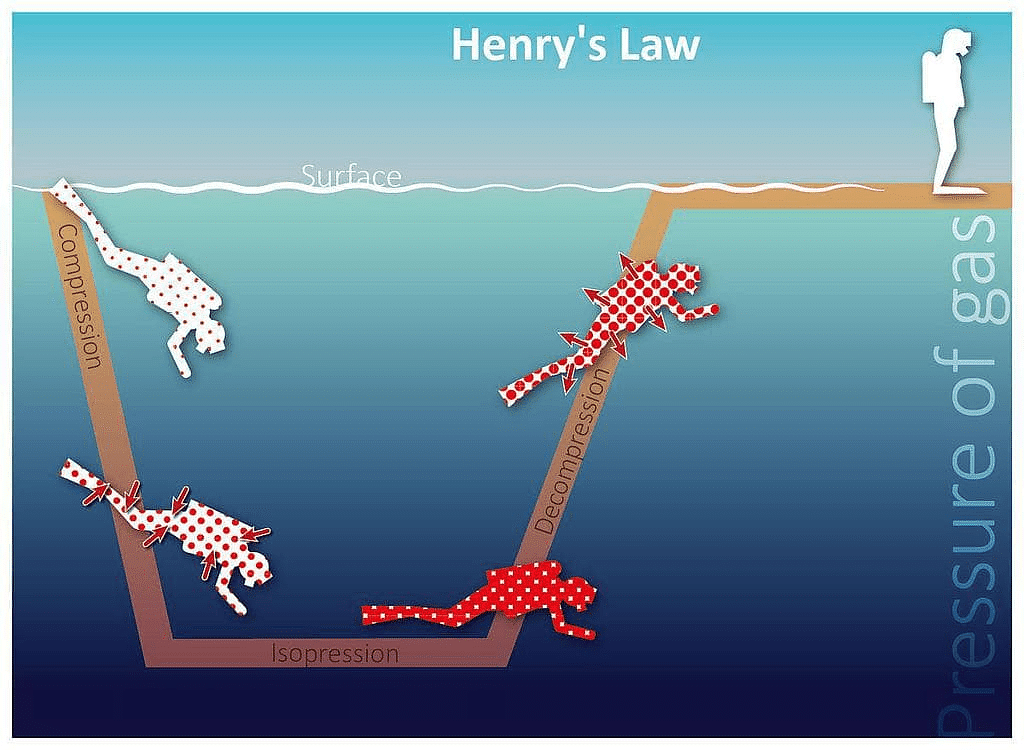
- Scuba divers have to face the problems of bends. When they dive and go deeper in water, pressure gradually increases resulting in an increase in the solubility of atmospheric gases in the blood. Bends is a medical condition which blocks the blood capillaries due to the formation of bubbles of nitrogen in the blood. Bends is very painful and dangerous to live.
When scuba divers come towards the surface of the water they have to face bends. Hence scuba diver uses a tank filled with air diluted with helium (11.7% helium, 56.2% nitrogen and 32.1% oxygen) to avoid bends as well as toxic effects of high concentration of nitrogen in the blood because of increase in pressure underwater and decreasing pressure towards the water surface.
- People, who live at high altitudes and climbers (mountaineers) have to face a problem called anoxia. Anoxia is also a medical condition.
 The partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere decreases with high altitude. A decrease in partial pressure of oxygen leads to a low concentration of oxygen in blood and tissues. Because of low concentration of oxygen people feel short of breath and become weak and unable to think clearly.To avoid the condition of anoxia, mountaineers use oxygen cylinder while climbing to high altitude.
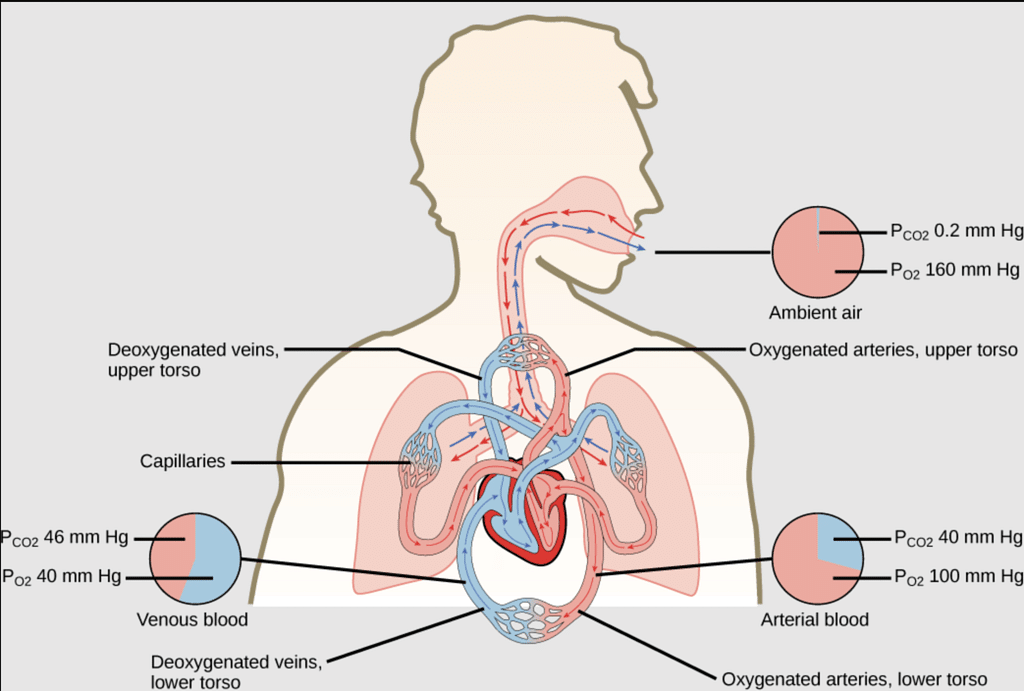
The partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere decreases with high altitude. A decrease in partial pressure of oxygen leads to a low concentration of oxygen in blood and tissues. Because of low concentration of oxygen people feel short of breath and become weak and unable to think clearly.To avoid the condition of anoxia, mountaineers use oxygen cylinder while climbing to high altitude. - Respiration and the Oxygenation of Blood: In the lungs, where oxygen is present in the air with high partial pressure, haemoglobin combines with oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin. In tissues where the partial pressure of oxygen is low, oxyhaemoglobin releases oxygen for utilization in cellular activities.
 Respiration and the Oxygenation of Blood
Respiration and the Oxygenation of Blood
Limitations of Henry's Law
Henry's law holds good if the following conditions are fulfilled:
- The pressure is not too high,
- The temperature is not very low,
- The gas does not chemically combine with the solvent.
Example.2. Calculate the concentration of CO2 in a soft drink that is bottled at partial pressure of CO2 of 4 atm' over the liquid at 25° C. The Henry’ Law constant for CO2 in water at 25 ˚C is 3.1 × 10-2 mol/litre-atm.
Solution.
According to Henry's Law:
S = KP
3.1 × 10-2 × 4 = 0.12 mol litre-1
Try Yourself!
Q.1. At 20° C the solubility of nitrogen gas in water is 0.0150 g/litre when the partial pressure N2 is 580 torr. Find the solubility N2 in H2O at 20°C when its partial pressure is 800 torr.
Ans. 0.0207 g/litre.
|
117 videos|225 docs|239 tests
|
FAQs on Henry's Law: Effect of Pressure on Solubility of Gases in Liquids - Physical Chemistry for NEET
| 1. How does pressure affect the solubility of gases in liquids according to Henry's Law? |  |
| 2. What are the factors that can affect the Henry's Law constant? |  |
| 3. What are some applications of Henry's Law in real life? |  |
| 4. What are the limitations of Henry's Law? |  |
| 5. How can Henry's Law be used to calculate the solubility of a gas in a liquid at a given pressure? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
 The partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere decreases with high altitude. A decrease in partial pressure of oxygen leads to a low concentration of oxygen in blood and tissues. Because of low concentration of oxygen people feel short of breath and become weak and unable to think clearly.To avoid the condition of anoxia, mountaineers use oxygen cylinder while climbing to high altitude.
The partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere decreases with high altitude. A decrease in partial pressure of oxygen leads to a low concentration of oxygen in blood and tissues. Because of low concentration of oxygen people feel short of breath and become weak and unable to think clearly.To avoid the condition of anoxia, mountaineers use oxygen cylinder while climbing to high altitude.