Hierarchy of Urban Settlements | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
The Urban System concept was first introduced by Brian J.L. Berry in 1964 through his influential work, "Cities as Systems within Systems of Cities." This concept suggests that urban areas are not isolated entities but are instead interconnected through various relationships with other towns and cities. An urban system can be described as a network of interdependent urban locations.
The idea of urban hierarchy takes into account the differences in population sizes and economic functions between various urban areas. Analyzing urban hierarchy involves ranking cities according to specific criteria, such as population size, economic strength, retail sales, and the number of industrial workers.
Urban settlements can be arranged in a hierarchical order, from top to bottom, based on their population size. This classification is typically done using three main criteria:
- Population size: Larger cities rank higher in the hierarchy, while smaller towns and settlements rank lower.
- Functions performed: Cities that serve more significant economic, political, or cultural functions have a higher rank in the hierarchy than those with fewer such functions.
- Sphere of influence: Cities with a more extensive reach or impact on surrounding areas rank higher in the hierarchy than those with a more limited sphere of influence.
In summary, the Urban System concept highlights the interconnectedness of cities and towns, emphasizing the importance of understanding their relationships within a larger network. The urban hierarchy further clarifies these relationships by ranking urban areas based on factors such as population size, functions performed, and sphere of influence.
Hierarchy Based on Size or Services
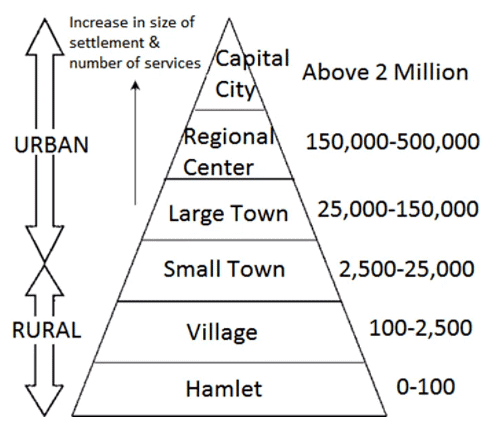
Settlement hierarchy is a system that categorizes various settlements based on their size and the services they offer. This system helps in understanding how settlements progress from rural to semi-urban and ultimately to urban areas.
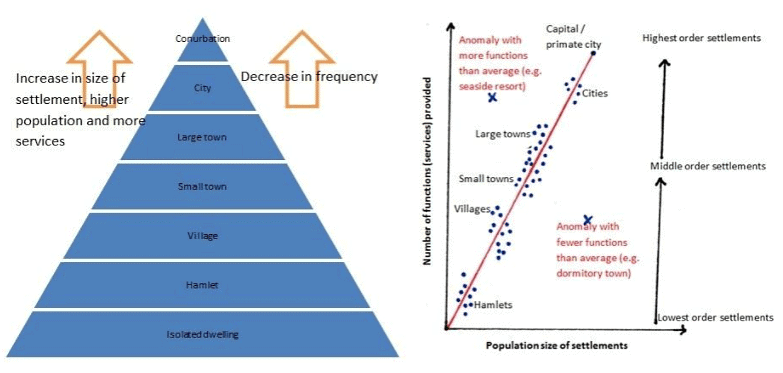
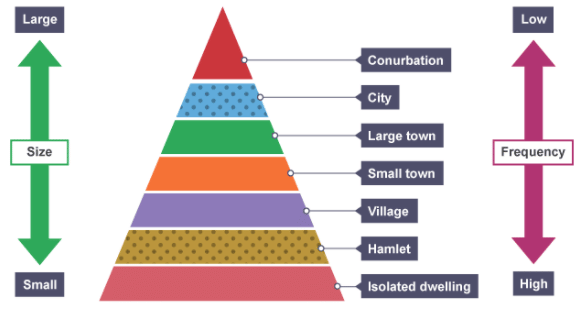
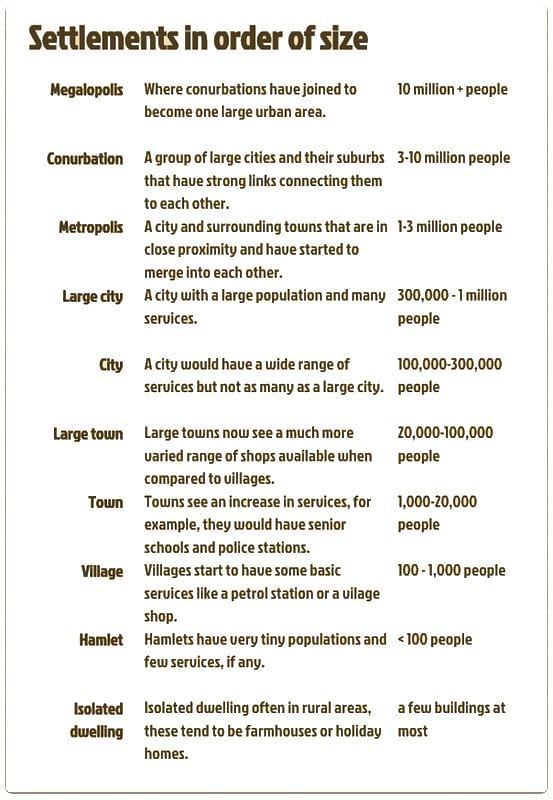
- In the settlement hierarchy, as you go higher in the order, the size of the settlements increases, and the distance between settlements of similar size also grows. For example, there are more conurbations than cities, more cities than towns, and more towns than villages.
- The range of services provided by a settlement is directly proportional to its size. Smaller settlements usually offer basic services such as post offices, doctors, and newsagents, while larger towns, cities, and conurbations provide both low-order and high-order services, including leisure centers, chain stores, and hospitals.
- Furthermore, larger settlements and conurbations have a broader sphere of influence compared to smaller ones. This implies that they attract people from a larger area due to the variety of facilities they provide. For instance, a global city like London has an extensive sphere of influence, whereas a small hamlet or village may only influence its immediate surroundings, spanning just a few kilometers.
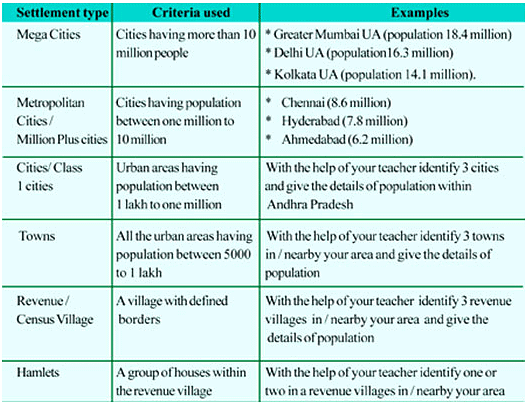
- Polis refers to a thriving village or small town that has recently transformed into an urban center. As Polis continues to grow and develop, it becomes known as Eopolis, signifying its transition into a larger town.
- A Metropolis consists of a central city and its surrounding towns, cities, and conurbations, which are all interconnected through economic and social aspects. These areas are made up of various villages and are strongly linked in terms of functionality.
- Tyrranopolis refers to a city where living conditions deteriorate due to insufficient services and poor civic amenities, causing the quality of life to become miserable for its inhabitants.
- Nekropolis, on the other hand, signifies cities that have been abandoned and turned into 'ghost cities' as a result of deurbanization, where the population shifts away from urban areas.
- A Megalopolis is a continuous chain of urban cities or centers that are closely linked. This phenomenon is commonly seen in countries such as the United States, with examples like the Philadelphia-New York-Boston corridor, as well as in Japan, where six million-plus cities like Tokyo, Osaka, and Kobe form a connected network. In India, there is potential for a Megalopolis to develop between Mumbai and Ahmedabad, incorporating cities like Surat, Vadodara, and Anand.
To gain a deeper understanding of these terminologies and their meanings, it is recommended to read up on rural and urban settlement definitions, as well as consult resources such as "Rupa Made Simple Economic and Social Geography."
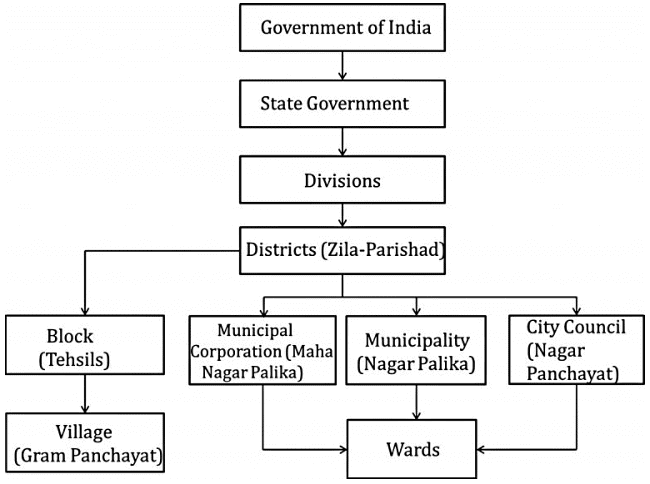
Hierarchy Based on Administrative Regions
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of the urban system highlights the interconnectedness of urban centers and their varying roles in terms of population size, economic functions, and sphere of influence. The urban hierarchy arranges settlements vertically based on these criteria, with larger settlements providing more services and having a broader sphere of influence. As settlements grow and evolve, they can transition through stages such as Polis, Eopolis, Metropolis, Tyrranopolis, Nekropolis, and Megalopolis, reflecting their development and the challenges they may face. Understanding the urban hierarchy and the relationships between settlements is crucial for effective urban planning and the sustainable development of cities and their surrounding areas.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Hierarchy of Urban Settlements
What is an urban system?
An urban system is defined as any network of interdependent urban places, indicating that individual urban centers are linked to each other through various relationships.
What is the urban hierarchy concept?
The urban hierarchy concept considers that urban places vary in population sizes and economic functions. The analysis of urban hierarchy mainly relates to the ranked order of cities based on different criteria such as population size, economic power, retail sales, and the number of industrial workers.
What are the three criteria for classifying the hierarchy of urban settlements?
The three criteria for classifying the hierarchy of urban settlements are the size of the population, functions performed, and the sphere of influence.
What is the difference between low-order and high-order services in urban settlements?
Low-order services are basic services provided by small settlements such as post offices, doctors, and newsagents. High-order services are more advanced services provided by larger towns, cities, and conurbations, such as leisure centers, chain stores, and hospitals.
What is a megalopolis?
A megalopolis is a chain of urban cities or centers that are economically and socially integrated with strong functional linkages. These large-scale urban areas can be found in countries like the USA and Japan, with potential for development in India between Mumbai and Ahmedabad.
|
303 videos|636 docs|252 tests
|
FAQs on Hierarchy of Urban Settlements - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the hierarchy of urban settlements? |  |
| 2. What factors determine the hierarchy of urban settlements? |  |
| 3. How does the hierarchy of urban settlements impact regional development? |  |
| 4. What are the different levels in the hierarchy of urban settlements? |  |
| 5. How does urban planning consider the hierarchy of urban settlements? |  |





















