History, Art and Culture: October 2024 Current Affairs | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
Lal Bahadur Shastri Jayanti

Why in News?
Lal Bahadur Shastri, revered as one of India's most esteemed leaders, is commemorated annually on October 2nd, marking his birth anniversary. Known for his humility, integrity, and decisive leadership during pivotal moments in Indian history, this day serves as a tribute to his life and his significant contributions to the country. The occasion encourages reflection on the values he exemplified and his lasting influence on India's socio-political framework.
Lal Bahadur Shastri Jayanti 2024
- Shastri was born on October 2, 1904, in Mughalsarai, Uttar Pradesh. His legacy is tied closely to his leadership during the Indo-Pak War of 1965, during which he famously coined the slogan "Jai Jawan Jai Kisan," emphasizing the vital roles of both the armed forces and farmers in building a robust and self-reliant nation. His initiatives laid the groundwork for the Green Revolution and the White Revolution, profoundly impacting India's agricultural and defense sectors. Lal Bahadur Shastri Jayanti is a day to honor his legacy, his life, and his contributions to India's growth and unity.
- Characterized by simplicity and steadfast integrity, Shastri lived a modest life, even in his role as Prime Minister, prioritizing the nation's needs over personal gains. His upbringing in a humble family, losing his father early, instilled a deep sense of patriotism and respect for education. Influenced by Mahatma Gandhi's principles of non-violence and simplicity, Shastri opted to drop his surname as a statement against the caste system, earning his title "Shastri" after graduating with a degree in philosophy from Kashi Vidyapeeth.
Lal Bahadur Shastri Biography
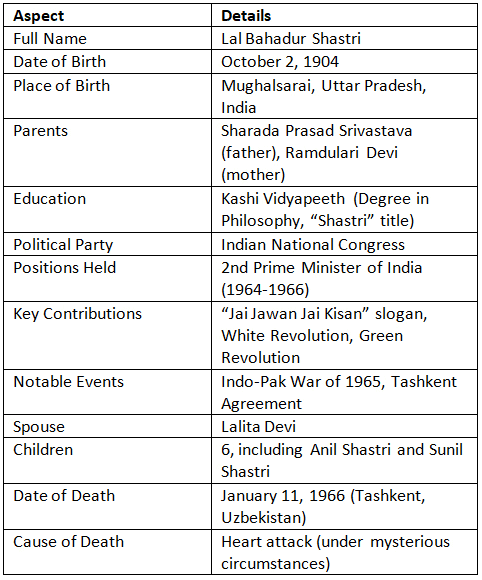
120th Birth Anniversary of Shri Lal Bahadur Shastri
- Shastri's birth anniversary coincides with Mahatma Gandhi's, which adds to its significance in India.
- The year 2024 marks the 120thanniversary of his birth, and various events, speeches, and cultural programs will be organized nationwide to celebrate his principles and the invaluable service he rendered to the nation.
Lal Bahadur Shastri Education
- Shastri completed his education at Kashi Vidyapeeth and was deeply involved in the Indian independence movement, inspired by Gandhian ideology.
- His political career began with the Indian National Congress, where he actively participated in key movements like the Non-Cooperation Movement and the Salt Satyagraha, facing imprisonment for his dedication.
Lal Bahadur Shastri’s Entry into Politics
- Post-independence, Shastri held various ministerial roles in Uttar Pradesh, eventually becoming Prime Minister after Nehru's death in 1964. His leadership during the challenging Madras anti-Hindi agitation of 1965 and his economic policies, including the White Revolution and the Green Revolution, showcased his commitment to India's progress. Shastri's famous slogan "Jai Jawan Jai Kisan" resonated with the public, highlighting the importance of both soldiers and farmers in the nation's development.
- Shastri's foreign policy maintained India's non-alignment stance while fostering strong ties with the Soviet Union, especially after the Sino-Indian War of 1962. His proactive approach led to the Tashkent Agreement, which aimed to establish peace between India and Pakistan following the Indo-Pak War of 1965.
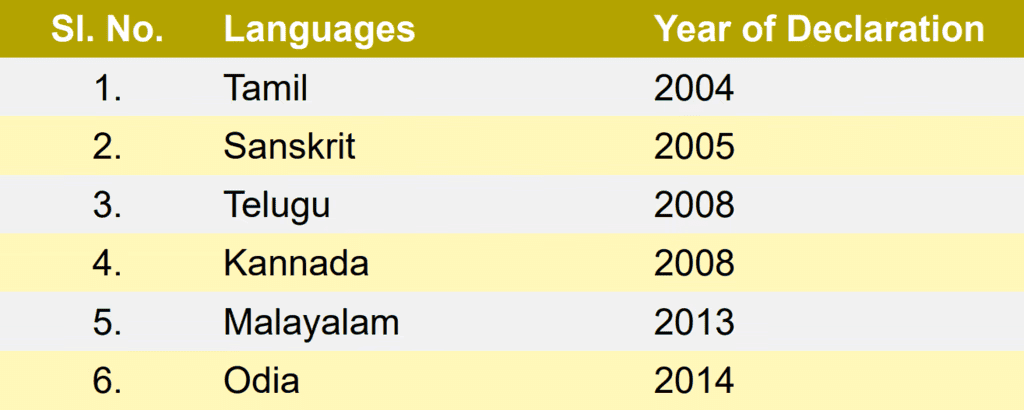
5 New Classical Languages and Change in Criteria

Why in news?
The Union Cabinet has approved the recognition of five additional languages as "classical," thereby expanding the list of culturally significant languages in the country. In addition to the existing six languages, Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese, and Bengali have been added to this esteemed category.
What is a Classical Language?
About
- The Indian government initiated the designation of languages as "Classical Languages" in 2004 to acknowledge and safeguard their ancient heritage.
- India now recognizes 11 classical languages that act as custodians of the nation’s rich cultural legacy, capturing vital historical and cultural milestones for their communities.
- Classical languages are characterized by a significant historical background, rich literary traditions, and unique cultural heritage.
Significance
- These languages are crucial for the intellectual and cultural development of their regions.
- Their literature provides deep insights into various fields such as literature, philosophy, and religion.
Criteria
- The criteria for declaring languages as classical were revised in 2005 and again in 2024 based on recommendations from Linguistic Experts Committees (LEC) under the Sahitya Akademi.
- The revised criteria established in 2005 include:
- High Antiquity: The language must have early texts and a recorded history spanning between 1,500 to 2,000 years.
- Ancient Literature: There should be a body of ancient literature or texts that are deemed valuable heritage by successive generations.
- Knowledge Texts: The language must possess an original literary tradition that is not borrowed from other speech communities.
- Distinct Evolution: The classical language and its literature must be distinct from modern forms, which may include a significant discontinuity from its later versions or derivatives.
- In 2024, the criteria were updated, particularly replacing the previous "Knowledge Texts" criterion with a broader definition emphasizing the existence of prose texts in addition to poetry, alongside epigraphical and inscriptional evidence.
Benefits
- Languages recognized as 'classical' are entitled to various governmental benefits aimed at promoting their study and preservation.
- Two prestigious international awards are conferred annually to scholars for their significant contributions to the research, teaching, or promotion of classical Indian languages:
- The Presidential Award of Certificate of Honour.
- The Maharshi Badrayan Samman Award.
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) provides support for establishing Professional Chairs in central universities and research institutions focusing on classical Indian languages.
- To protect and promote these linguistic treasures, the government has set up the Center of Excellence for Studies in Classical Languages at the Central Institute of Indian Languages (CIIL) in Mysore.
What are the Other Provisions to Promote Language?
- Eighth Schedule: This schedule aims to promote the progressive use, enrichment, and advancement of languages and includes 22 languages such as Assamese, Bengali, Hindi, Kannada, and others.
- Article 344(1): This article allows for the establishment of a Commission by the President after five years from the Constitution's commencement to enhance the use of Hindi.
- Article 351: It mandates the Union to promote the spread of the Hindi language.
- Other Efforts to Promote Languages:
- Project ASMITA: This initiative aims to publish 22,000 books in various Indian languages over five years.
- New Education Policy (NEP): The NEP seeks to transform Sanskrit universities into multi-disciplinary institutions.
- Central Sanskrit Universities Bill, 2019: This legislation grants central status to three deemed Sanskrit universities, enhancing their academic stature and outreach.
Raja Ravi Varma

Why in News?
The first true copy of the painting Indulekha by Raja Ravi Varma will be unveiled at the Kilimanoor Palace, Kerala, where the eminent artist was born in 1848, on the occasion of his 176th birth anniversary celebrations.
About Raja Ravi Varma
- Raja Ravi Varma was a prominent Indian painter, renowned as one of the greatest figures in Indian art history.
- He was born as Ravi Varma Koil Thampuran in Kilimanoor Palace, located in the former princely state of Travancore (Thiruvithankur) in Kerala.
- His artwork primarily focused on themes from the Puranas (ancient mythological texts) and major Indian epics, including the Mahabharata and Ramayana.
- In addition to mythological subjects, Varma created numerous portraits of both Indian and British individuals during his time in India.
- It is estimated that he produced around 7,000 paintings before his death at the age of 58.
- Some of his most acclaimed works include:
- Damayanti Talking to a Swan
- Shakuntala Looking for Dushyanta
- Nair Lady Adorning Her Hair
- Shantanu Matsyagandha
Features of his work
- Prior to Raja Ravi Varma’s contributions, Indian paintings were heavily influenced by Persian and Mughal styles.
- He was the first Indian artist to incorporate Western techniques of perspective and composition into Indian art, adapting these methods to local subjects, styles, and themes.
- His works exemplify a successful blend of European academic art with an Indian sensibility and iconography.
- Varma was among the early Indian artists to utilize oil paints and excel in lithographic reproduction of his artworks.
- He made his paintings accessible to a broader audience by producing affordable lithographs, significantly expanding his influence as a public figure and artist.
- His artwork often depicted mythological figures and Indian royalty in a realistic manner, challenging and redefining traditional artistic conventions.
Recognitions
- Raja Ravi Varma gained significant recognition after winning an award for his paintings at an exhibition in Vienna in 1873.
- His works were also showcased at the World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago in 1893, where he was honored with two gold medals.
- In 1904, Viceroy Lord Curzon, representing the King Emperor, awarded him the Kaisar-i-Hind Gold Medal, marking the first official recognition of him as "Raja Ravi Varma."
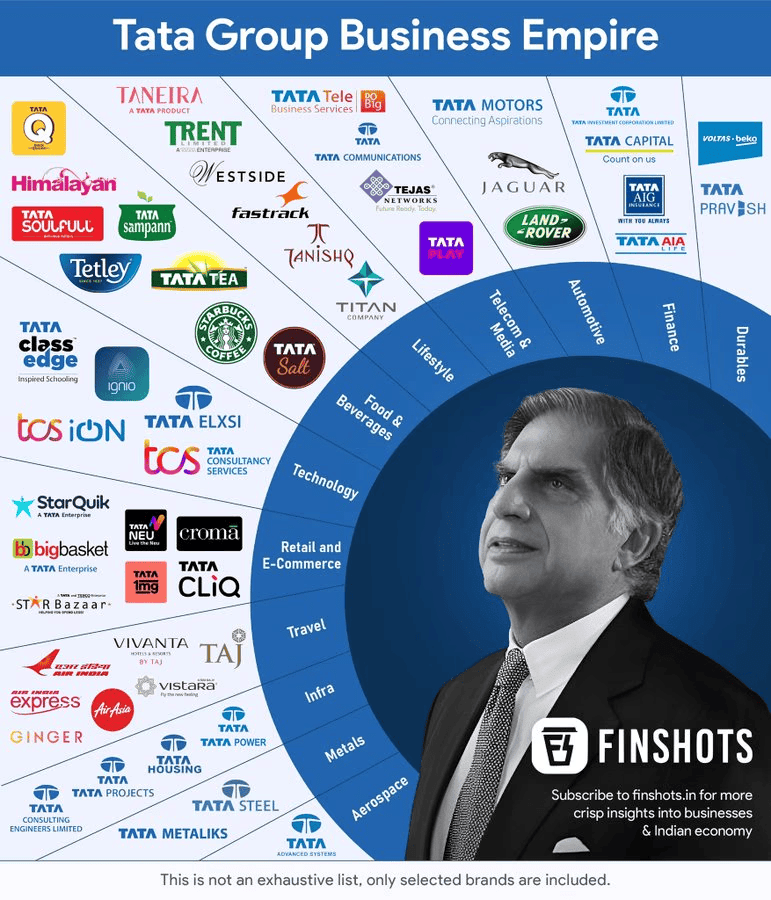
Contributions and Legacy of Ratan Tata

Why in news?
Recently, Ratan Naval Tata, the former chairman of Tata Group who became a symbol of India's economic resurgence in the 21st century, passed away at a Mumbai hospital at the age of 86.
Who was Ratan Tata?
About
- Ratan Naval Tata was a prominent Indian businessman and former chairman of Tata Group, which is one of India's largest conglomerates.
- He was honored with the Padma Bhushan in 2000 and the Padma Vibhushan in 2008.
- Tata graduated in architecture from Cornell University and returned to India in 1962 to join the Tata Group, founded by his great-grandfather, Jamsetji Tata.
- Known for his calm demeanor, he led a relatively modest lifestyle and was actively involved in philanthropic efforts.
- Ratan Tata was regarded as a visionary leader and a compassionate figure, earning respect in both business and social sectors.
Achievements
- Under his leadership, Tata Group transformed into a global powerhouse, with ventures across various industries including steel, automobiles, software, and telecommunications.
- Early in his career, Tata worked with several Tata companies, revitalizing entities such as Tata Motors (previously known as Telco) and Tata Steel.
- He took over as chairman of Tata Group in 1991, succeeding J.R.D. Tata.
- Implemented notable organizational reforms, such as introducing retirement ages and promoting young talent to senior positions.
Received numerous awards, including
- Assam Baibhav by the Government of Assam in 2021.
- Honorary Officer of the Order of Australia from King Charles III in 2023.
- Honorary Doctor of Science from IIT Bombay in 2008.
- Honorary Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the British Empire (GBE) from Queen Elizabeth II in 2014.
- Honorary Citizen Award from the Government of Singapore in 2008.
Contributions
- In 1996, Tata established Tata Teleservices and later took Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) public in 2004, seizing the opportunities presented by the IT boom.
- His leadership was marked by significant international acquisitions, such as:
- The acquisition of Tetley Tea in 2000.
- Acquisition of VSNL (Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited) in 2002.
- The purchase of Corus Steel in 2007, one of the largest takeovers by an Indian firm.
- Acquisition of Jaguar and Land Rover from Ford.
- Played a crucial role in Tata Group's acquisition of Air India from the government in January 2022.
- He also introduced the Tata Nano, a low-cost car aimed at making affordable transportation accessible to the Indian population.
- After stepping down from active leadership, Tata became a notable investor in Indian startups, supporting ventures like:
- Paytm
- Ola Electric
- Urban Company
Napoleon’s Ambition with India and his Rule
Why in news?
Napoleon Bonaparte's strong interest in India was driven by his desire to weaken British dominance in the region. His influence extended beyond India, impacting European, American, and African politics.
What was Napoleon’s Ambition with India (Orient)?
- Oriental World: The term "Oriental" describes the Eastern world from a European viewpoint, covering regions and cultures east of Europe, primarily Asia, including nations like China, Japan, Indonesia, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- Napoleon’s Interest in the Orient: Fascinated by the Orient from an early age, Napoleon drew inspiration from Alexander the Great's conquests in Asia. His specific interest in India emerged around 1798 during his Egyptian campaign, aimed at threatening Britain and disrupting its increasing trade with India. Despite suffering a significant defeat in Egypt and the death of Tipu Sultan in 1799, he continued to pursue strategies to challenge British authority in India amid the territorial conflicts involving major European colonial powers like Britain, Russia, and France.
- Partners of Napoleon for Invasion of India:
- Russia: After his defeat in Egypt, Russian Tsar Paul I approached Napoleon during the "Great Game," a geopolitical contest between Britain and Russia for control of Asian territories. In 1801, the Tsar secretly proposed a joint invasion of India to expel the British and divide the territory. However, Napoleon declined, and Paul I later abandoned the plan after his assassination.
- Persia (Iran): Recognizing Persia's strategic significance as a bridge between Europe and India, Napoleon sought to engage with Persian Shah Fath Ali. In response, Britain negotiated a treaty with Persia in 1801, preventing French influence and allowing Persia to attack Afghanistan if it threatened India. Following Russia's annexation of Georgian territory claimed by Persia in 1801, Napoleon secured the Treaty of Finkenstein with Persia, promising military support against Russia and requiring Persia to sever ties with Britain.
What are the Key Facts About Napoleon Bonaparte?
Personal Life
- Born in 1769 on Corsica, Napoleon became a lieutenant in artillery at 16.
- He joined the army during the French Revolution and later crowned himself Emperor of France.
Role of Napoleon
- France: During the Revolutionary Wars, he emerged as a prominent military commander, leading significant campaigns in Italy and Egypt.
- Overthrow of Directory: He played a key role in the 1799 coup d'état that ended the Directory, paving the way for the Consulate where he held power as First Consul.
- Napoleonic Wars (1803-1815): As Emperor from 1804, he expanded French control across Europe through military campaigns, centralizing power and modernizing administration, education, taxation, and infrastructure.
- Establishment of the Napoleonic Code: Introduced in 1804, this legal framework emphasized equality before the law and individual rights, influencing legal systems worldwide.
- Continental System: Napoleon aimed to economically weaken Britain by imposing a trade blockade, but the results were mixed, adversely affecting France’s economy.
- Modernisation of France: His reforms significantly modernized French society, including advancements in education, banking, and infrastructure, leaving a lasting legacy.
Europe
- Establishment of the Continental System (1806): This strategic blockade aimed to isolate Britain by cutting off trade with continental Europe, intending to make Europe self-sufficient.
- Peninsular War (1808): Napoleon compelled Portugal to adhere to the Continental System, deposing the Spanish king and igniting nationalist sentiments in Spain.
- Growth of Nationalism and Resistance: His actions, especially in Spain, intensified nationalist movements across Europe, leading to widespread resistance and contributing to the collapse of his empire.
Out of Europe
Egyptian Campaign (1798-1801): Napoleon sought to diminish British influence in the Middle East and India by controlling Egypt but ultimately failed after initial victories.
Role in the Americas:
- Louisiana Purchase (1803): Napoleon sold the Louisiana Territory to the United States, doubling its size and funding his military campaigns.
- Haiti and the Caribbean: Napoleon aimed to regain control over Haiti but failed after a slave rebellion led to its independence in 1804.
How Napoleon’s Policy led to his Downfall?
The Decline of the Empire:
- Failed Russian Invasion (1812): Napoleon's invasion was disastrous due to Russia's scorched-earth tactics and harsh winter, resulting in massive losses for his army.
- The Sixth Coalition War (1813-1814): In response to his failed campaign, European powers formed the Sixth Coalition, leading to a significant defeat at the Battle of Leipzig.
- First Abdication and Exile to Elba (1814): Facing defeat, he abdicated in April 1814 and was exiled to Elba, where he attempted administrative reforms.
- Defeat at the Battle of Waterloo (1815): His final effort to restore his empire culminated in defeat at Waterloo, ending his rule.
- Second Abdication and Exile to Saint Helena: After his defeat, he was exiled to Saint Helena, where he lived under British supervision until his death.
- Historians note that despite his downfall, Napoleon's legacy persists through his legal reforms and military strategies, significantly shaping European politics and governance in the 19th century.
Mains Question
Q: Discuss Napoleon Bonaparte's policies and reforms shape modern nation-states in the 19th century?
Birth Anniversary of Dr APJ Abdul Kalam

Why in news?
Recently, President Droupadi Murmu honoured former President Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam on his birth anniversary.
What are the Key Facts of Dr APJ Abdul Kalam?
About
- Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam was born on October 15, 1931, in Rameswaram, Tamil Nadu.
- He earned the title "Missile Man of India" due to his significant contributions to missile development.
- He served as India’s 11th President from 2002 to 2007, completing a full term.
Awards Received
- He was a recipient of several prestigious civilian awards including:
- Padma Bhushan (1981)
- Padma Vibhushan (1990)
- Bharat Ratna (1997), the highest civilian award in India.
- Dr. Kalam held honorary doctorates from 48 universities and institutions both in India and worldwide.
Literary Works
- Wings of Fire
- India 2020 - A Vision for the New Millennium
- My Journey
- Ignited Minds - Unleashing the Power Within India
- Indomitable Spirit
Contributions
- Pioneer in Fiberglass Technology: Dr. Kalam was instrumental in advancing fiberglass technology, leading a youthful team at ISRO.
- Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV-3): As Project Director, he was crucial in developing India's first indigenous satellite launch vehicle, which successfully launched the Rohini satellite into orbit in July 1980. This achievement marked India's entry into the elite Space Club.
- Indigenous Guided Missiles:
- He was the Chief Executive of the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- Dr. Kalam led the efforts to weaponize strategic missile systems and oversaw the Pokhran-II nuclear tests in collaboration with the Department of Atomic Energy.
- He witnessed India's first nuclear test, Smiling Buddha, and directed Project Devil and Project Valiant, which focused on developing ballistic missiles using technology from the successful SLV program.
- Technology Vision 2020: In 1998, Dr. Kalam proposed a national plan called Technology Vision 2020, aimed at transforming India from a developing to a developed nation within two decades.
- Medical and Healthcare: In partnership with cardiologist B. Soma Raju, Dr. Kalam developed the affordable 'Kalam-Raju Stent' for treating coronary heart disease, thus enhancing healthcare accessibility.
Copper Plates Discovered from Vijayanagara Kingdom

Why in news?
Recently, a collection of copper plate inscriptions featuring two leaves from the 16th Century CE was discovered at the Sri Singeeswarar temple in Mappedu village, Tiruvallur district of Tamil Nadu. The two leaves of the copper plates were strung together using a ring featuring the seal of the Vijayanagara Kingdom. The inscriptions detail a village donation to Brahmins by the Raja of Chandragiri and are written in Sanskrit and the Nandinagari script, engraved in 1513 during the reign of King Krishnadevaraya.
Who was King Krishandevaraya?

- Reign of Krishnadevaraya: Ruled the Kingdom of Vijayanagar from 1509 to 1529 AD. Succeeded by Achyuta Raya in 1530 and later by Sada Siva Raya in 1542.
- Titles: Known by various titles, including "Kannadaraya" and "Kannada Rajya Ramaramana." He is recognized as one of the greatest statesmen in Indian history and a significant ruler of medieval South India.
- Literary Contributions: An eminent scholar, he authored works such as Madalasa Charita, Satyavedu Parinaya, and Amuktamalkyada. Proficient in multiple languages, he supported poets writing in Sanskrit, Telugu, Tamil, and Kannada.
- Patronage of Learning and Literature: His court included the Ashtadiggajas, eight prominent scholars, including Allasani Peddana, known as the Andhra-kavitapitamaha, and Kannada poet Thimmanna who completed the Kannada Mahabharatha at Krishnadevaraya's behest.
- Cultural Development: Played a vital role in nurturing the Carnatic musical tradition and encouraged classical dance forms such as Bharatanatyam and Kuchipudi.
- Infrastructural Development: Credited with constructing fine temples and adding impressive gopurams to many significant south Indian temples. Founded a suburban township called Nagalapuram after his mother.
What are the Key Facts of the Vijayanagar Empire?
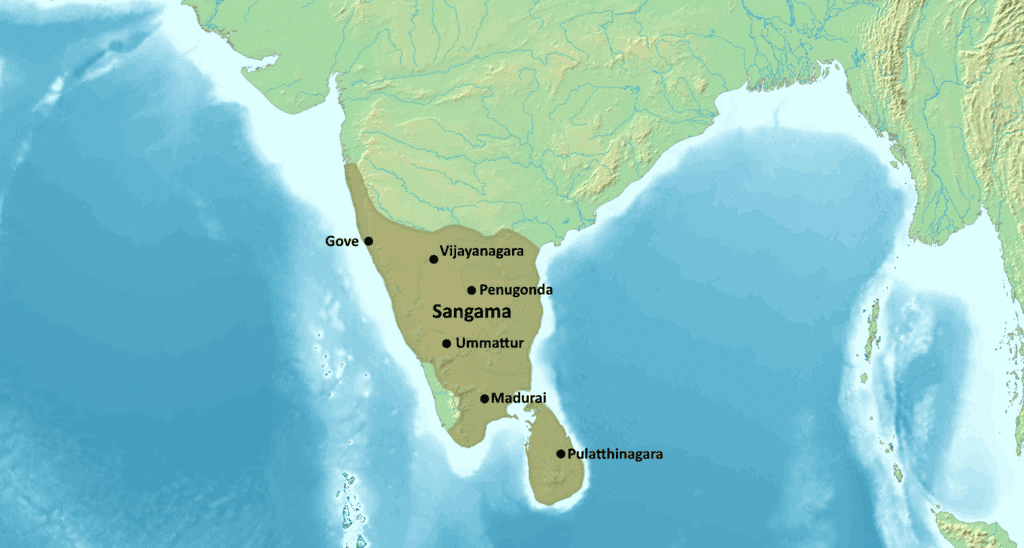
- Foundation and Duration of the Empire: Established in the Deccan region from 1336 onwards by Harihara and Bukka Raya, with Hampi declared a World Heritage site by UNESCO in 1986. Ruled by four major dynasties: Sangama, Saluva, Tuluva, and Aravidu, it lasted until around 1660.
- Portuguese Relations: In around 1510, the Portuguese captured Goa with support from the Vijayanagara Empire. They supplied the empire with guns and Arabian horses while the empire exported goods like cotton, rice, and spices.
- Cultural and Architectural Flourishing: The empire reached its zenith during Krishna Deva Raya's reign, characterized by notable monuments such as the Hazara Rama temple and Krishna temple, showcasing remarkable architecture.
- Dominance in Southern India: For over two centuries, the Vijayanagara Empire was the dominant power in southern India and served as a defense against invasions from the Turkic Sultanates of the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
- Tussle with the Deccan Sultanates and Mughals: The empire's foundation was partly a response to the weakening of the Delhi Sultanate. It frequently clashed with the Bahmani Sultanate and engaged in territorial conflicts driven by resource competition.
- Area of Rule under Vijayanagar: At its peak, the empire covered vast areas of southern India, including parts of modern Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Telangana.
- Decline and Fall: The decisive defeat at the Battle of Talikota in 1565 by the allied Deccan sultanates marked a turning point leading to the empire's decline.
Mains Question
Q: Discuss the socio-economic and cultural contributions of the Vijayanagara Empire to southern India. How did these contributions influence subsequent Indian history?
Revival of National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM)
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Ministry of Culture has announced plans to revive and relaunch the National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM).
What are the Key Points of the Revived NMM?
Key Points of the Revived NMM
- The Union Ministry of Culture intends to establish an autonomous body under its jurisdiction specifically for the NMM.
- Currently, the NMM operates as part of the Indira Gandhi National Centre for Arts.
Achievements of NMM
- Since its inception in 2003, metadata for 52 lakh manuscripts has been compiled, with over 3 lakh titles digitized.
- Of these, one-third have been made available online, although only around 70,000 out of the 1.3 lakh uploaded manuscripts are accessible to the public.
Concerns
- A large number of manuscripts are owned privately, limiting public access as owners have little incentive to share.
Future Roadmap
- The plan includes establishing university chairs internationally that focus on ancient Indian studies.
- There are suggestions to involve legal experts in Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs) to address issues regarding the sale of manuscripts abroad and private ownership.
- There is a strong emphasis on preserving lesser-known scripts and those that are not Brahmi.
Key Facts About NMM
- About: The NMM is an initiative aimed at preserving and documenting India's extensive collection of manuscripts.
- Launch: It was initiated to uncover, document, conserve, and promote India's vast manuscript heritage.
- Implementing Bodies: The Department of Culture oversees the implementation of the mission, while the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA) acts as the nodal agency.
- Objectives: The mission is focused on conserving manuscripts and disseminating the knowledge contained within them, adhering to its motto of "conserving the past for the future."
- Scope and Collection: India is estimated to have around five million manuscripts, potentially the largest collection globally, with approximately 70% written in Sanskrit.
155th Mahatma Gandhi Jayanti

Why in News?
Gandhi Jayanti 2024 will be observed worldwide on October 2nd. Continue reading to learn about the 155th anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi Jayanti 2024 and the International Day of Non-Violence 2024.
Gandhi Jayanti 2024
- Gandhi Jayanti, celebrated annually on October 2, honors the birth of Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, widely known as Mahatma Gandhi or the Father of the Nation. Gandhi Jayanti 2024 will mark his 155th birth anniversary, a significant event not only for India but around the world.
- This day is dedicated to remembering Mahatma Gandhi's life and legacy, with his principles of non-violence, truth, and social justice holding particular importance as the world confronts issues like terrorism and other forms of violence.
Mahatma Gandhi Birth Anniversary 2024
- Gandhi Jayanti 2024, observed on October 2, will honor Mahatma Gandhi’s crucial role in leading India toward independence from British rule. His non-violent strategy, known as Satyagraha, brought together people of different communities and faiths, establishing him as a key figure in the freedom struggle.
- The 2024 anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi’s birth is also recognized as the International Day of Non-Violence, underscoring his worldwide impact. On this day, events across India and globally will include prayer gatherings, tributes at Raj Ghat in New Delhi, and discussions on Gandhian values.
Gandhi Jayanti 2024: Biography of Mahatma Gandhi
Gandhi’s transformation from a lawyer in London to a leader of the global non-violence movement is a powerful story, illustrating the evolution of political thought and activism. His life exemplifies how a single person can shape history and inspire future generations.
Mahatma Gandhi Biography – Overview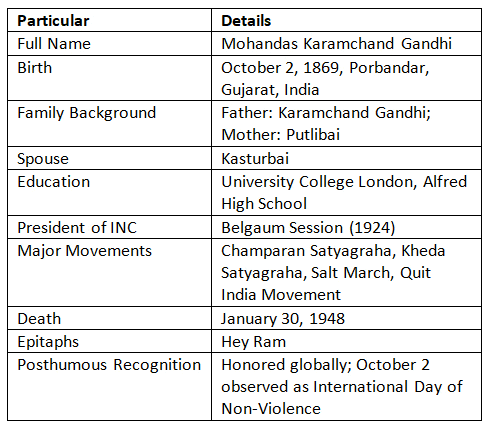
Gandhi’s Formative Years: Early Life and Education
- Mohandas Gandhi was born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, a coastal town in Gujarat, India, into a Hindu Modh Baniya family. His father, Karamchand Gandhi, held the position of Diwan (Chief Minister) of Porbandar, while his mother, Putlibai, was a devoutly religious woman whose spiritual practices greatly influenced Gandhi.
- Raised in a strict but loving household, Gandhi was taught the values of honesty and simplicity from an early age. At 13, he married Kasturbai in 1882. In 1888, he went to London to study law at the Inner Temple, one of the city’s four law colleges. Although initially uneasy with Western customs, he gradually adapted, and his time in England exposed him to a range of intellectual and ethical ideas that deeply shaped his perspective.
Gandhi’s Time in London
- Although Gandhi faced challenges adapting to Western life, his time in London provided him with valuable insights into European socio-political structures. He engaged with the works of philosophers like Tolstoy and John Ruskin, whose ideas on nonviolence and simple living deeply impacted him.
- Ruskin’s Unto This Last was especially influential, inspiring Gandhi’s ideal of Sarvodaya, or the welfare of all. These intellectual influences laid the foundation for his principles of Satyagraha—an unwavering commitment to truth and nonviolent resistance.
The South African Chapter: A Fight Against Racism
- After completing his legal studies, Gandhi traveled to South Africa in 1893 to handle a legal case for Dada Abdullah Jhave. This journey marked a pivotal period in his life, as he encountered institutional racism for the first time. A defining incident occurred when he was forcibly removed from a train in Pietermaritzburg for refusing to vacate a “whites-only” compartment.
- This experience of discrimination sparked Gandhi’s commitment to fighting for justice and dignity for the oppressed. His first campaign of nonviolent resistance focused on securing rights for Indian immigrants, who faced harsh working conditions and discriminatory laws. In 1894, he established the ‘Natal Indian Congress,’ launched Indian Opinion in 1903, and founded the ‘Phoenix Settlement’ in 1904.
- Gandhi’s approach of nonviolent resistance in South Africa laid the groundwork for future movements in India, transforming South Africa into a testing ground for strategies he would later use to oppose British colonialism.
Return to India: Leading the Freedom Struggle
In 1915, Gandhi returned to India, bringing with him the principles of nonviolent civil disobedience. He soon became involved in the freedom movement, advocating for the rights of India’s poorest communities. His focus was on addressing their hardships and exposing injustices, such as excessive taxes and exploitative British policies.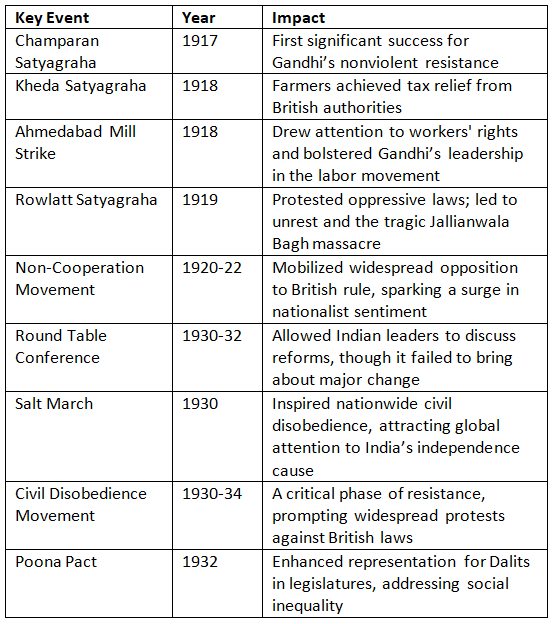
The Quit India Movement: The Final Struggle for Freedom
- In 1942, Gandhi initiated the Quit India Movement, demanding an immediate end to British rule and marking the final major phase of India’s fight for independence. His call for widespread civil disobedience led to mass protests, strikes, and demonstrations across the nation.
- The slogan “Do or Die” struck a chord, inspiring a nationwide push for freedom. Although the movement was suppressed, it weakened British authority and amplified the call for independence. By 1947, these collective efforts culminated in India’s independence, leaving a legacy of courage and unity.
- Gandhi was affectionately honored with titles like “Mahatma,” meaning “Great Soul,” bestowed by Rabindranath Tagore, and “Father of the Nation,” by Subhash Chandra Bose, reflecting the immense respect for his leadership.
The Final Years and Legacy of Gandhi
- As India neared independence, tensions between Hindus and Muslims escalated, ultimately leading to the partition of India in 1947. Deeply disturbed by the violence that followed, Gandhi traveled extensively to promote peace and reconciliation.
- Sadly, on January 30, 1948, Gandhi was assassinated by Nathuram Godse, a tragedy that sent shockwaves across India and the world. His death marked an irreplaceable loss for those who believed in his vision of nonviolence and communal harmony.
- However, Gandhi’s legacy as a champion of nonviolence and civil rights continues to inspire global movements for justice and equality. Figures like Martin Luther King Jr. and Nelson Mandela drew from his principles to advance their own causes.
Relevance of Mahatma Gandhi’s Ideas in Present Times
Gandhi Jayanti 2024 serves as a reminder that Mahatma Gandhi’s ideas are still profoundly relevant today. His principles of non-violence (Ahimsa), truth (Satya), self-reliance (Swadeshi), and sustainable living offer valuable lessons for addressing modern challenges.
- Non-violence: In today’s world, plagued by global conflicts, terrorism, and political unrest, Gandhi’s commitment to resolving conflicts without violence remains a crucial lesson for contemporary leaders.
- Truth and Integrity: Gandhi’s dedication to truth is especially relevant now, as misinformation and fake news continue to spread widely.
- Swadeshi and Self-reliance: With initiatives like Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India), Gandhi’s focus on local production and self-sufficiency is gaining renewed importance, resonating with modern economic policies.
- Sustainable Living: In the face of climate change and environmental challenges, Gandhi’s advocacy for simple living and sustainable resource use provides timely and effective solutions.
International Day of Non-Violence 2024
- Since 2007, October 2 has been recognized globally as the International Day of Non-Violence, as declared by the United Nations. The purpose of this day is to "spread the message of non-violence through education and public awareness."
- In 2024, this observance holds even more significance due to increasing global tensions, wars, and civil unrest in various regions. Events and discussions held around the world on this day will center on efforts for peace-building, conflict resolution, and promoting a culture of dialogue over warfare.
Shyamji Krishna Varma

Why in News?
Prime Minister Modi honored revolutionary freedom fighter Shyamji Krishna Varma on the occasion of his 95th birth anniversary.
About
Shyamji Krishna Varma was born on October 4, 1857, in Gujarat. He was an Indian revolutionary, lawyer, and journalist. To advance the cause of Indian nationalism and independence, he founded several key institutions in London, including:
- The Indian Home Rule Society
- The India House
- The Indian Sociologist (a journal to promote nationalist ideas).
Legacy
- Shyamji Krishna Varma was the first president of the Bombay Arya Samaj and was significantly influenced by Dayanand Saraswati.
- He played a crucial role in inspiring Indian revolutionaries, including Veer Savarkar, who was also connected to India House in London.
- Additionally, Varma served as the Divan (Prime Minister) for several princely states in India.
International Abhidhamma Divas

Why in News?
The Prime Minister took part in the celebration of International Abhidhamma Divas and the recognition of Pali as a classical language.
What is Abhidhamma?
- Abhidhamma, meaning "Higher Teaching" or "Special Teaching" in Pali, is one of the three main sections of the Tripitaka (Abhidhamma Pitaka) in Theravada Buddhism. It provides a systematic and analytical study of the mind and matter, offering a deeper exploration of Buddhist philosophy beyond the Sutta Pitaka.
- The Abhidhamma examines mental states, consciousness, and psychological processes, establishing a framework for understanding reality. It is recognized for its specialized vocabulary in Pali, including terms such as:
- Chitta (consciousness)
- Chetasika (mental factors)
- Rupa (materiality)
- Nibbana (final liberation).
- The Abhidhamma Pitaka consists of seven treatises, with Pannhana being particularly important for its analysis of causal relationships. Traditionally, it is believed that the Buddha taught the Abhidhamma to the gods in the Tavatimsa heaven, later passing on these teachings to his disciple Sariputta.
About International Abhidhamma Divas
- International Abhidhamma Divas is celebrated on Ashwin Purnima (the full moon), marking the Buddha’s descent from the Tavatimsa-devaloka (a celestial realm) to Sankassiya (Sankisa Basantapur, UP). This day also signifies the end of the 3-month rain retreat, known as Varsavasa or Vasa, during which monks stay in one place for meditation and prayer.
- The celebration includes Dhamma discourses, academic sessions, and exhibitions that connect ancient Buddhist wisdom with modern spiritual practices. The event is hosted at Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi, and organized by the Ministry of Culture in collaboration with the International Buddhist Confederation (IBC).
Teachings of Abhidhamma
The Abhidhamma offers a detailed framework for understanding the mind, matter, and existence. It addresses complex concepts such as birth, death, and mental phenomena with precision and abstract reasoning.
The Abhidhamma is known for its analytical approach, including:
- Categorizing mental states and emotions.
- Explaining causal relationships that determine both mental and material phenomena.
Its teachings cover various topics, such as:
- Moral and mental states.
- Aggregates (components of existence).
- Causal links.
- The path to enlightenment.
Historical Background and Significance
- Abhidhamma Divas commemorates the day when Lord Buddha returned to earth after imparting the Abhidhamma teachings in the Tavatimsa realm.
- This event is historically significant, marked by the Ashokan Elephant Pillar at Sankassiya. The celebration coincides with the conclusion of the Rainy Retreat (Vassa), a period of monastic seclusion, and the Pavarana festival, a time for mutual reflection and reconciliation among monks.
Classical Status to Pali Language
- In 2024, Pali was granted the status of a Classical Language by the Indian government, highlighting its cultural and historical importance. Pali is the ancient language in which much of Buddhist canonical literature, including the Tipitaka, is written. This recognition was made alongside other languages such as Marathi, Prakrit, Assamese, and Bengali.
- Pali's significance stems from its role as the medium for conveying Buddha’s teachings, particularly through the Sutta Pitaka, Vinaya Pitaka, and Abhidhamma Pitaka.
- The Tipitaka consists of:
- Vinaya Pitaka: Ethical guidelines for monks and nuns.
- Sutta Pitaka: Buddha’s discourses and teachings.
- Abhidhamma Pitaka: In-depth analysis of mental and physical phenomena.
- Additionally, Pali has a rich tradition of commentaries, such as Atthasalini and Sammohavinodani, which help in understanding complex Abhidhamma concepts.
|
201 videos|1016 docs|2274 tests
|
















