Respiratory Organs & Human Respiratory System | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Introduction
- Oxygen (O2) is used by organisms to break down simple molecules like glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids to obtain energy for various activities.
- During this process, carbon dioxide (CO2), which is harmful, is also produced. This shows that O2 needs to be continuously supplied to cells, while the CO2 produced must be expelled.
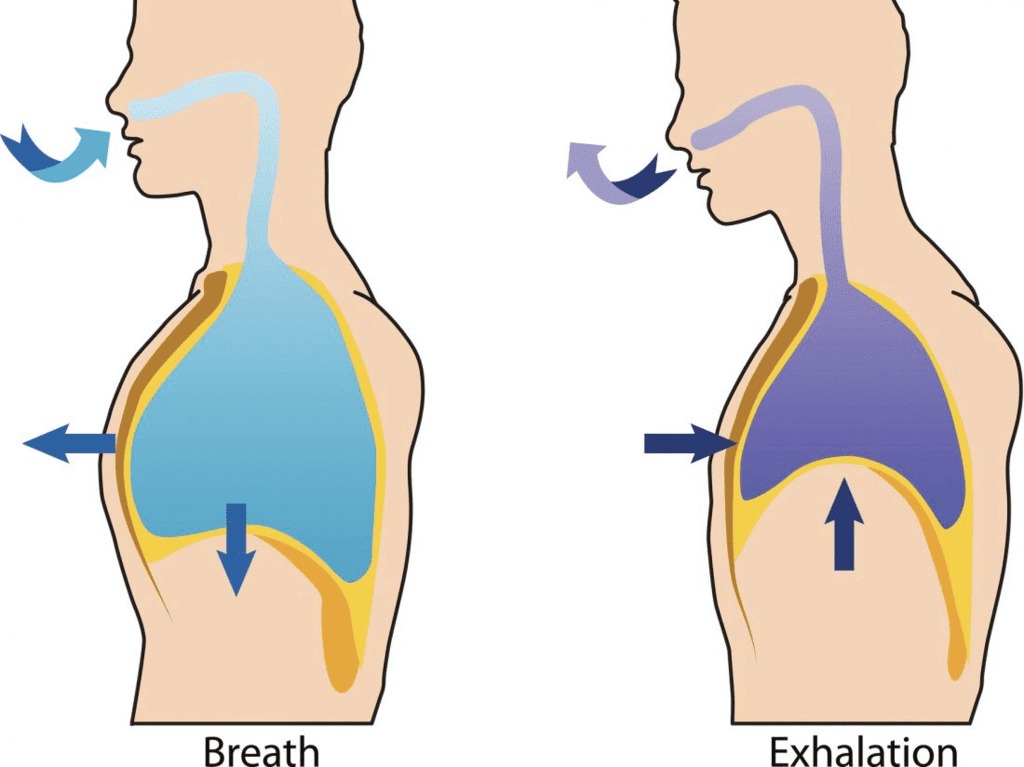
- The exchange of O2 from the atmosphere with CO2 produced by cells is known as breathing or respiration.
- When you place your hands on your chest, you can feel it moving up and down, which is a result of breathing. But how do we breathe?
Respiratory Organs
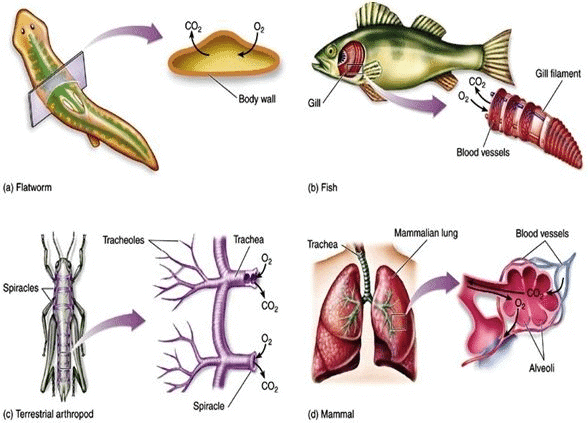
The way animals breathe varies depending on their habitat and level of biological organization. Here’s how different groups of animals carry out gas exchange:- Lower Invertebrates: Animals like sponges, coelenterates, and flatworms exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide through simple diffusion across their entire body surface.
- Earthworms: Earthworms breathe using their moist cuticle, which allows gas exchange.
- Insects: Insects have a network of tubes called tracheal tubes that transport atmospheric air within their bodies.
- Aquatic Arthropods and Molluscs: These animals use specialized vascularized structures called gills for gas exchange in water, a process known as branchial respiration.
- Terrestrial Arthropods and Molluscs: Terrestrial forms of arthropods and molluscs use vascularized bags called lungs for gas exchange, a process known as pulmonary respiration.
Vertebrates:
- Fishes: Fishes breathe using gills, which extract oxygen from water.
- Amphibians: Amphibians like frogs can breathe through their lungs, but they can also respire through their moist skin in a process called cutaneous respiration.
- Reptiles, Birds, and Mammals: All these vertebrate groups primarily use lungs for respiration.
Human Respiratory System
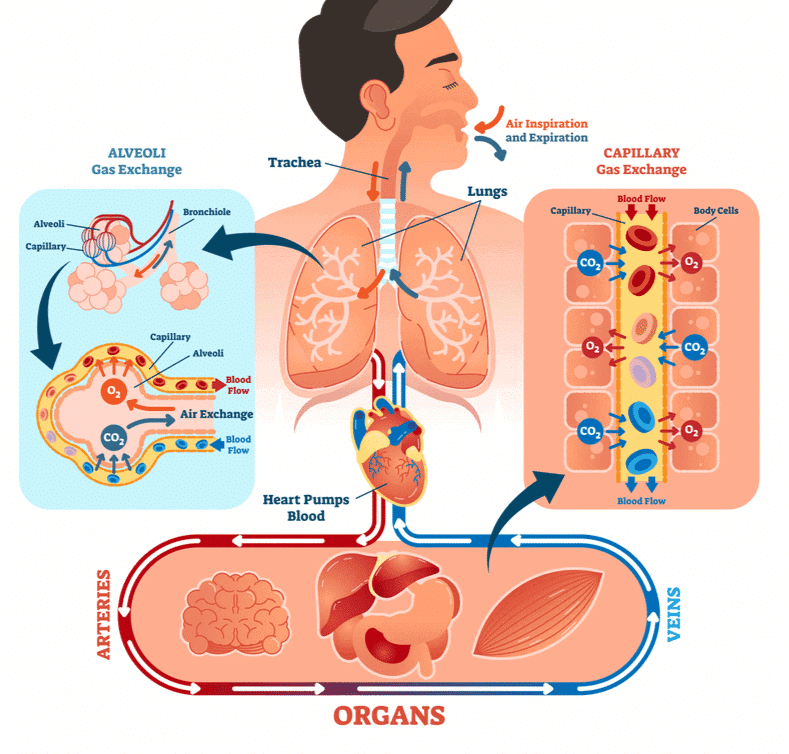
The respiratory system in humans is responsible for the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. It consists of various parts that work together to ensure the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide.1. Structure of the Respiratory System
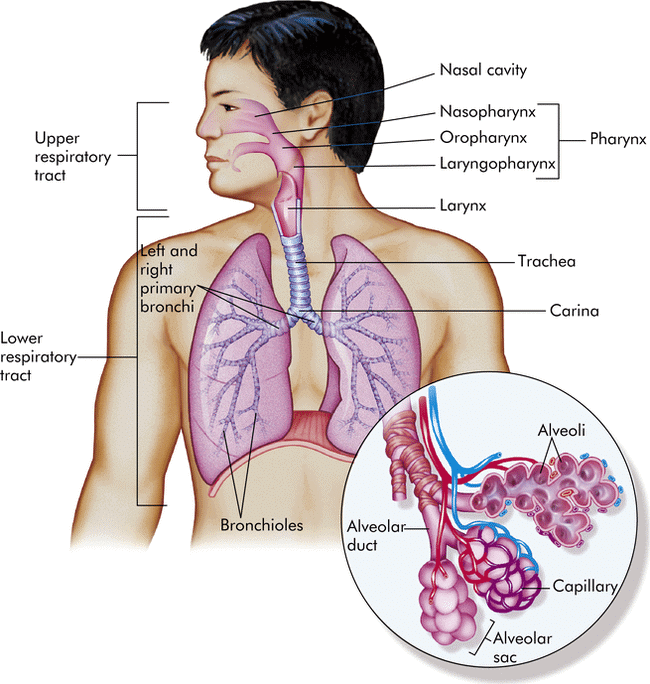
The human respiratory system comprises the following parts:- External Nostrils: These are the openings located above the upper lip, leading to the nasal passage.
- Nasal Chamber: The external nostrils open into the nasal chamber through the nasal passage. This chamber plays a crucial role in filtering and humidifying the air before it enters the lungs.
- Pharynx: The nasal chamber connects to the pharynx, which is a shared passage for food and air. The pharynx is an essential part of the respiratory system as it directs air towards the larynx.
- Larynx: Also known as the voice box, the larynx is a cartilaginous structure that produces sound. During swallowing, a thin elastic flap called the epiglottis covers the glottis (the opening of the larynx) to prevent food from entering the airway.
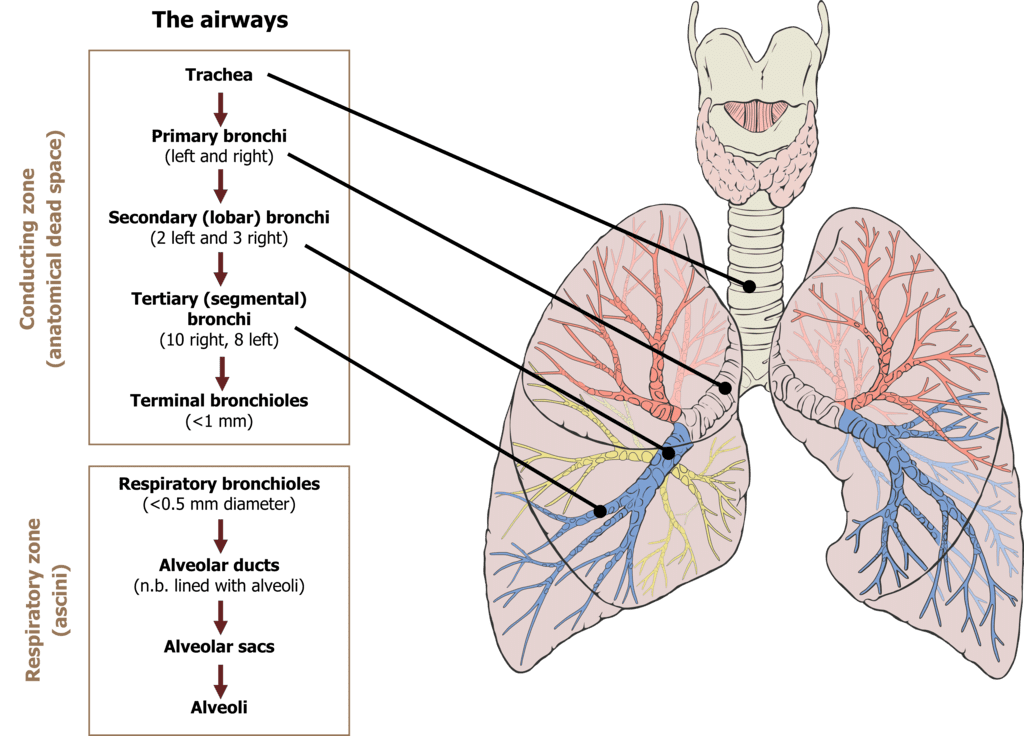
- Trachea: The trachea, or windpipe, is a straight tube that extends into the thoracic cavity. It divides into the right and left primary bronchi at the level of the fifth thoracic vertebra. The trachea and bronchi are supported by incomplete cartilaginous rings, which keep the airways open.
- Bronchi and Bronchioles: The primary bronchi further divide into secondary and tertiary bronchi, which continue to branch into smaller bronchioles. The bronchioles end in terminal bronchioles, which are the last part of the conducting zone.
- Alveoli: Each terminal bronchiole leads to a cluster of alveoli, which are thin-walled, vascularized sacs where gas exchange occurs. The alveoli are the functional units of the respiratory system, providing a large surface area for the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Lungs: Humans have two lungs covered by a double-layered pleura, with pleural fluid between the layers. This fluid reduces friction and allows the lungs to expand and contract smoothly. The outer pleural membrane is attached to the thoracic cavity, while the inner membrane is in contact with the lung surface.
2. Conducting Part vs. Exchange Part
- Conducting Part: This part includes the external nostrils, nasal chamber, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles up to the terminal bronchioles. Its functions include: Transporting atmospheric air to the alveoli, Clearing the air of foreign particles, Humidifying the air & Bringing the air to body temperature.
- Exchange Part: This part consists of the alveoli and their ducts. It is responsible for the actual diffusion of gases (O 2 and CO 2 ) between the blood and the atmospheric air.
3. Thoracic Cavity and Lungs
- The lungs are situated in the thoracic cavity, which is an airtight chamber. The thoracic cavity is bordered by the vertebral column (dorsally), sternum (ventrally), ribs (laterally), and diaphragm (inferiorly).
- The anatomical arrangement of the lungs in the thorax allows any change in the volume of the thoracic cavity to be reflected in the lung (pulmonary) cavity. This arrangement is crucial for breathing, as the pulmonary volume cannot be altered directly.
4. Respiratory Process
(i) Breathing or Pulmonary Ventilation: This involves the inhalation of atmospheric air and the exhalation of carbon dioxide-rich alveolar air.
(ii) Diffusion of Gases: Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse across the alveolar membrane during gas exchange.
(iii) Transport of Gases by Blood: Oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported by the blood to and from the tissues.
(iv) Diffusion between Blood and Tissues: Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the blood and tissues, facilitating cellular respiration.
(v) Utilization of Oxygen by Cells: Cells use oxygen for catabolic reactions, producing carbon dioxide as a byproduct. This process is known as cellular respiration.
|
150 videos|398 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Respiratory Organs & Human Respiratory System - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the main function of the human respiratory system? |  |
| 2. What are the parts of the human respiratory system? |  |
| 3. What are the steps involved in the process of respiration? |  |
| 4. How does respiration occur in the human body? |  |
| 5. Why is respiration essential for human survival? |  |

















