Important Crop Diseases Caused by Bacteria | Botany Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Bacterial Diseases
Bacterial diseases affecting vegetable crops, with additional resources listed at the end of the page that provide detailed information on identifying symptoms and managing these bacterial diseases. It is crucial to involve a plant diagnostics laboratory to confirm the pathogen responsible for any crop diseases, ensuring proper disease management.
Bacterial diseases can have a significant impact on vegetable crops, and they typically enter plant tissue through wounds or natural openings. These wounds can result from various factors, including insect damage, other pathogens, and mechanical damage during agricultural operations like pruning and harvesting.
The activity of bacteria and the development of diseases depend on conducive environmental factors. Bacteria can multiply rapidly under certain conditions, including:
- High humidity
- Crowded plant spacing
- Poor air circulation
- Plant stress due to factors like over-watering, under-watering, or irregular watering
- Soil health issues
- Nutrient imbalances
Bacterial pathogens can persist in the soil, crop debris, seeds, and other plant parts. Weeds can serve as reservoirs for bacterial diseases, and these pathogens can spread through infected seeds, plant materials, crop residues, water splashes, wind-driven rain, and contaminated equipment and hands of workers. Overhead irrigation methods can contribute to the spread of bacterial diseases.
The development of bacterial diseases is influenced by weather conditions. Some bacterial diseases thrive in warm, wet weather, while others prefer cool, wet conditions. Hot, dry conditions may halt disease development but can exacerbate symptoms once a plant is already infected. For example, bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum may show symptoms under such conditions.
In some cases, bacterial ooze may be visible on diseased plant tissue, but symptoms of bacterial diseases can sometimes be mistaken for those caused by fungal diseases. Therefore, it is essential to have diseased tissue examined in a plant diagnostics laboratory to accurately identify the pathogen causing the disease.
Different strains or pathovars of bacterial diseases can affect various types of vegetable crops or cause different diseases in the same crop. For instance, Xanthomonas campestris pv. vitians affects lettuce, while X. campestris pv. cucurbitae affects cucurbits. Similarly, in beans, different pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae (e.g., pv. syringae and pv. phaseolicola) cause distinct diseases.
Common Bacterial Diseases and Crops Affected
Some examples of common bacterial diseases of vegetable crops are provided in the table below with some typical symptoms.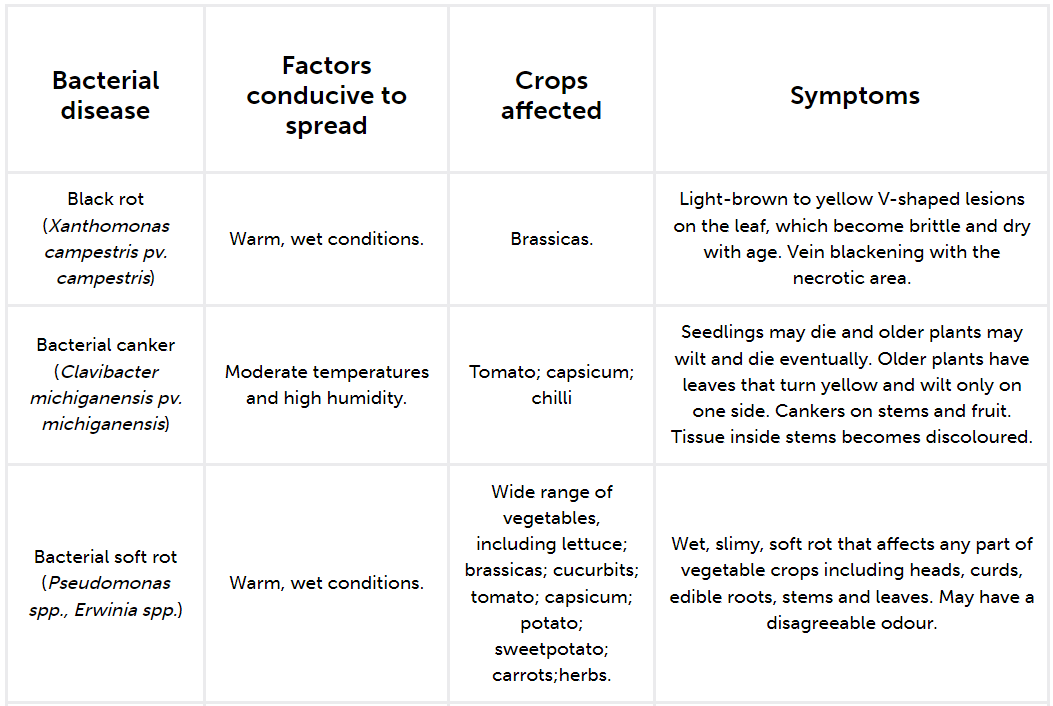


Other bacterial diseases of vegetables include:
- Peppery leaf spot – Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola (brassicas)
- Varnish spot – Pseudomonas spp. (lettuce)
- Corky root – Rhizomonas suberifaciens (lettuce);
- Angular leaf spot – P. syringae pv. lachrymans (cucurbits);
- Bacterial pith necrosis – Pseudomonas corrugata and other bacteria (tomatoes);
- Common bacterial blight – Xanthomonas campestris pv. phaseoli (beans)
- Halo blight – Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola (beans)
- Black leg – Erwinia carotovora pv. atroseptica (potatoes).
Management
Managing bacterial diseases in vegetable crops involves strategies aimed at promoting the growth of host plants while targeting vulnerable stages in the pathogen's lifecycle to prevent or restrict its development.
Key methods for managing bacterial diseases in vegetables include:
- Exclusion or Eradication of the Pathogen:
- Implement quarantine measures to exclude or eradicate the pathogen from your growing area.
- Use pathogen-tested seeds and propagated materials to reduce the risk of introducing the disease.
- Use of Clean Transplants:
- Utilize disease-free transplants or seedlings to start your crop.
- Regular Monitoring and Predictive Models:
- Monitor your crops regularly for signs of disease.
- Use predictive models to anticipate disease outbreaks and take preventive measures.
- Pathogen Reduction by Crop Rotation:
- Employ crop rotation practices to reduce pathogen levels in the soil.
- Weed and Residue Management:
- Remove weeds and incorporate crop residues that can harbor the disease, reducing potential sources of infection.
- Host Plant Protection:
- Choose plant varieties that are resistant to the specific bacterial disease when available.
- Minimize Mechanical Damage and Insect Pest Damage:
- Handle crops with care to minimize mechanical damage.
- Manage insect pests that can create wounds that provide entry points for bacteria.
- Optimal Working Conditions:
- Avoid working in the crops when they are wet, as this can facilitate disease spread.
- Bactericidal Sprays:
- Apply registered bactericides when weather conditions favor disease development to prevent infection.
- Chemical Resistance Management:
- Understand chemical resistance and practice the rotation of chemical groups to prevent the development of resistance in bacterial populations.
- Isolation and Destruction of Infected Plants:
- If plants are already infected, isolate and destroy them.
- Prune infected leaves, but minimize excessive handling of diseased plants.
- In cases of systemic infections that have spread throughout the plant, consider destroying the entire plant, typically through burning or burying.
- Proper Transport and Storage:
- Use correct temperatures and packaging conditions during transport and storage to prevent the spread of the disease.
- Implementing these management strategies can help reduce the impact of bacterial diseases on vegetable crops, safeguard plant health, and promote successful crop production.
|
179 videos|140 docs
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















