Important Places of Ancient India, History, UPSC | Additional Study Material for UPSC PDF Download
Important Places of Ancient India
(1) Ahichhatra—in Bareilly distt of U.P. excavated by K.N. Dikshit a site of continuous habitation since prehistoric and historical period.
Its pottery studies have led to evolution of systematic study of cultures based on pottery. Became important during Harsha’s time. During Mahajanapada period Ahichhatra served as the seat of power of Panchala Kingdom.
(2) Madhyanika—This school of philosophy was developed by Nagarjuna. Also it is known as ‘Sunya vada’. It was very much popular during Vikramaditya (Gupta Dynasty).
(3) Atranjikhera—associated with painted grey were culture of later Vedic times. Excavation reveals settlements for one to three centuries, without any predecessors. People lived in mud brick homes erected on wooden poles. This site has yielded the proof of Iron use in 8th century B.C. Also a place of large vedic sacrifice as corroborated by the findings of cattle bones in huge amounts.
(4) Madurai—Pandyan capital in southern India. Here 3rd Sangama was held which led to compilations of Tolkappiyam, the Tamil grammar. It was an important trade and manufacturing centre.
(5) Ayodhya—Associated with Rama legend formed part of the Koshala Mahajanpada. Excavated evidence do not attest settlement before 8th C B.C.
(6) Nagarjun Konda—In Krishna Valley. Site of Neolithic settlements that were vibrant.
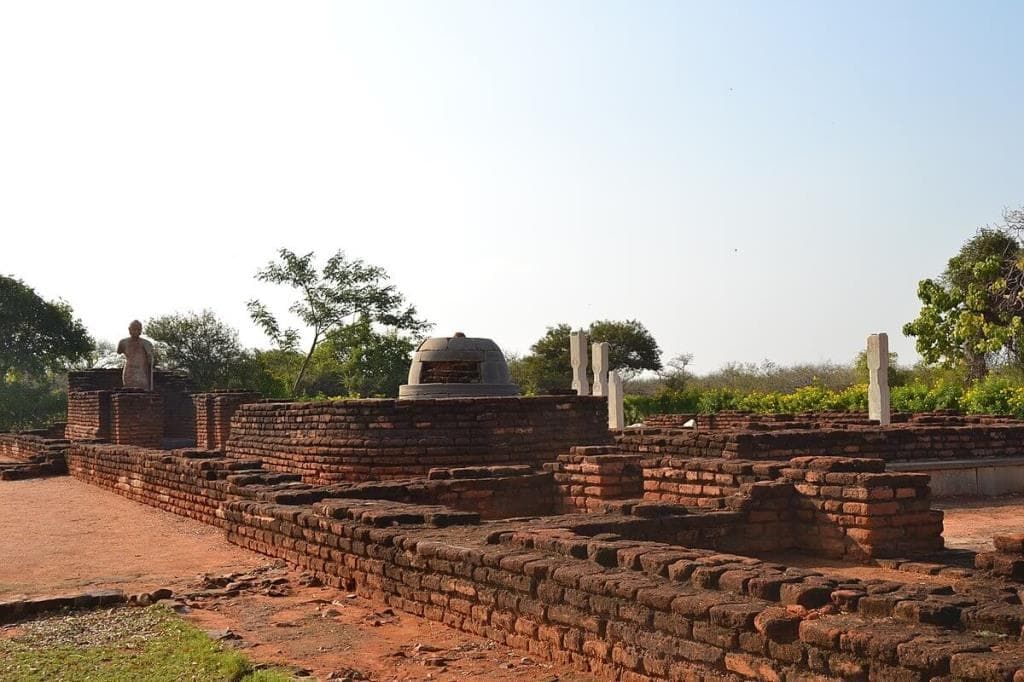 Nagarjun Konda
Nagarjun Konda
It had trading contacts with outside. A Buddhist stupa of early centuries A.D. Beginning of architectural style under the Ikshavakus anticipated later Nagara style of north India.
(7) Brahmagiri—In Karnataka maintained continuity of cultural heritage from Neolithic to Megalithic. Site of one of the two minor Rock Edicts of Asoka, which points to Asoka becoming a monk after two and half years of his conversion to Buddhism.
(8) Paithan—Pratisthan—at the mouth of river Godavari in the Aurangabad district of Maharashtra, the capital of Satavahana kings. It lied on route to South India from North India.
(9) Burzahom—in Kashmir valley near Srinagar. Associated with neolithic settlement, famous for pit dwellers stone (axe) and bones as weapons and practised fishing.
(10) Assam—capital of Kama-rupa situated on the banks of Brahmaputra. Its ruler was Bhaskarvarman an ally of Harsha and had trading and cultural contacts with China.
(11) Puskalvati—modern Char-sadda on river Kabul in Afghanistan city. A gold coin with goddess Lakshmi holding a lotus, discovered. Remained under Greeks, Shakas and Kushans, and was important link of Indian trade with central Asia and China.

(12) Dhauli—(Tosali), near Bhubaneswar in Orissa, seat of Mauryan provincial governor. Fourteenth Major Rock Edict of Asoka, located have the list of conquered people and Asoka’s policies regarding them.
(13) Sanchi—in Madhya Pradesh famous for Buddhist stupas and Asoka’s Minor pillar edicts. Inscriptions of Satavahanas and Guptas found here. It’s ancient name Kaknodbota, the land of tribal prople Kakar, which was captured by Samudragupta.
(14) Dwarka—associated with Krishna legend. It is in Saurashtra on the coast of Arabian sea. Myth had it that ancient city was submerged in sea. Excavations carried out under S.R. Rao revealed tools dating back to Harappan times.
(15) Sarnath—near Varanasi, Budha delivered his first sermon at deer park-Dharma chakra pravartana’. Asokan pillar out of which the lion capital was adopted as the state emblem for India, is here.

Important centre for art. Gupta’s plastic art reached its zenith. Famous sculpture are Buddha seated in preaching mood.
(16) Hastinapur—situated along the bank of Ganges. Important town during the 6th C B.C. associated with Mahabharata legend. Excavation reveal settlements not before 9th C B.C. and urban features not before 7th C B.C.
(17) Surparaka—port town known to Periplus and Ptolemy. Foreign trade was important. But lost its importance to Broach in Ist C A.D. It was 40 miles north of Bombay. Also, known as Sopara.
(18) Kalibangan—in Rajasthan, Neolithic, Pre-Harappan, Harappan and even post Harappan phases of culture found here. Plough field discovered of Harappan time. It was an important town during Harappans.
(19) Tamralipti—on East Coast near Calcutta. Important trade centre for trade with south east Asian countries and sea route to China.
(20) Kanchipuram—Sacred pilgrimage centre for Hindus important for Jainas also captured by Samundra Gupta. Rose to prominence under Pallavas in 7th C AD. Famous for Kalaishnatha temple, which crystallized the Dravida style of architecture and paintings.
(21) Tanjore—seat of Imperial Chola since 9th C AD. After Vijay Nagars fall it became a Nayaka Kingdom. Famous for the temples.The Brihadeshwara or Raja Rajeswara temple famous for sculpture and paintings.
(22) Kapilvastu—principality town in Nepal Terai wherd Buddha was born, prosperous town during Buddha’s time. Important pilgrimage centre for Bhuddhist. Asoka visited it during his Dharma Yatras.
(23) Thaneswar—near Kuruk-shetra in Haryana capital of Pushyabhuti dynasty to which Harsha belonged. It was an important centre for trade. Attacked by Mahmud Gazani in 1014 AD.
(24) Karnasuvarna—region in East India, parts of Bihar, Bengal, Orissa ruled by Sasanka, the Shaivite King in early 7th C A.D. Harsha captured in 619 A.D.
(25) Vaisali—in Bihar, important town in 6th C A.D. 2nd Buddhist Council was held here, seat of Lichchhavi power. Annexed by Ajatshatru.
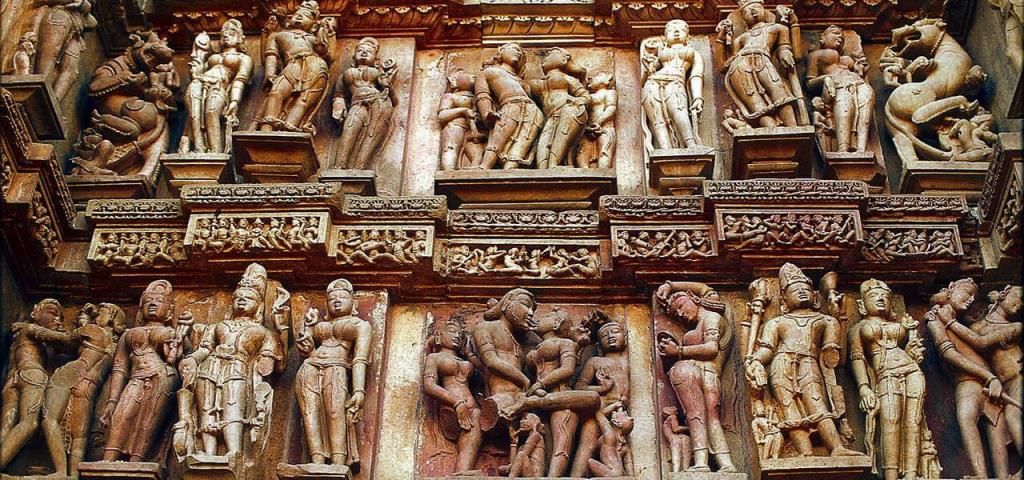
(26) Khajuraho—world famous for its erotic sculptures. Chandellas patronized this cultural centre and built Mahadeva temple. It is in Madhya Pradesh.
(27) Vatapi— Badami—base of Chalukyan power and its capital destroyed by Narasimha Verman in 642 A.D. when he defeated and killed Pulkesian.
(28) Lothal—important town during Harappan civilization, port town dockyard found here. Traces of horse bones found here.
(39) Vengi—in Andhra Pradesh joined Samudra Gupta’s empire as a tribute paying state capital of eastern Chalukyas. Its fertile soil was the bone of contention between Chalukyas and the Pallavas.
(30) Aihole—the place is situated near Badami. It is famous for its rock cut temples in Chalukyan style. Famous for its eulogical inscription of Chalukyan king “Pulakeshin II”, written by court poet “Ravi Kirti”.
(31) Amaravati—situated near modern Vijayawada. It is famous for Buddhist stupas. It was the centre of art during Satvahanas rule. It was an important centre of trade with Burma and Indonesia.
(32) Anurudhapur—capital city of Srilanka. Asoka sent his brother Mahinder as a Buddhist missionary to this place. The place was burnt later by Chola king Rajendra I.
(33) Badami—the place is also known as Vatapi. Situated in modern Bijapur district, the place was founded by Pulakeshin I and later became the capital of western Chalukyas. Famous for its cave temple dedicated to Lord Vishnu.
(34) Bhagwanpura—an important site of later vedic period. Excavation reveals a forty room mud house which throws light on family structure during vedic period.
(35) Girnar—it was situated near Junagadh in Gujarat. Pushyagupta, a Mauryan Governor built famous Sudershan lake here. Famous inscription in chaste Sanskrit, issued by Saka ruler ‘Rudradaman’ was found here.
(36) Kausambi—it was an important port town of late Vedic period. It was the seat of authority of Vatsa kingdom. The place is famous for Asokan pillar and Kushanas inscriptions.
(37) Kusinagara—it is situated in the modern Deoria district of U.P. It was the capital of Mallas during ancient period. The place is famous for Buddha’s parinirvana. Asoka built a stone stupa to commemorate Buddha parinirvana.
(38) Kot Diji—an important Harrapan sites. Famous for remains of Indus valley civilization which helps to reconstruct the history of the period.
(39) Lumbini—situated in Teria plains of southern Nepal. The place is famous as the birth place of Buddha. Asokan pillar inscription is found here.
(40) Mahabalipuram—this port city was founded by the Pallava king “Narasimhavarman.” It was the chief centre of Pallava art. The place is famous for seven Rath temple, shore temple and a few other temples.
(41) Nalanda—the place is situated in South Bihar. It was the most famous centre for Buddhist learning. Most important excavation is the University complex. It remained in flourishing condition during the ancient period.
(42) Pratisthana—the place was situated on the mouth of the river Godavari in the Aurangabad distt. of Maharashtra. It was the capital of Satavahana kingdom. It had an important trade route, linking it with Sravasti.
(43) Purushpura—modern Peshawar. It was the capital of Kushana ruler, Kanishka. It was a famous centre of Gandhara art. Kanishka built a monastery and a stupa here.
(44) Rajagriha—it was the first capital of Magadhan empire during 6 th. Century B.C. It is surrounded by hills which made it impregnable during the period. The first Buddhist council was held here.
(45) Sravasti—modern Sahet—Mahet on the border of Gonda and Bahraich distt. of U.P. It was a famous trade centre in ancient period. It was the capital of Kosala kingdom. Later it served as the provincial headquarter of Gupta kings.
(46) Sravanabelogola—the place is situated in the Hasan distt. of modern Karnatka. It is famous for its monolithic statue of Gomateshwara which had been erected in 980 A.D. by Chamunda Rai, the chief minister of Ganga king Rachmal.
(47) Sultanganj—situated in modern day Bihar. A very important Pala-Bronze centre where from famous Bronze Buddha has been found.
(48) Surkotada—situated in Gujarat. It was one of the most famous site of Indus valley civilization. It had a citadel and a lower town. The place is famous for horse remain.
(49) Takshsila: during ancient time, it was important place of learning. Famous as a centre of trade and commerce. Had many trade routes.
 Takshshila(50) Vidisa—modern Besnagar. It is in east Malwa. It was a part of the Shunga empire. It was famous for its ivory workers. It is famous for its Garuda pillar inscription, erected by a Greek ambassador, Helliodorus in memory of Lord
Takshshila(50) Vidisa—modern Besnagar. It is in east Malwa. It was a part of the Shunga empire. It was famous for its ivory workers. It is famous for its Garuda pillar inscription, erected by a Greek ambassador, Helliodorus in memory of Lord
Vishnu.
(51) Valabhi—it was another famous seat of Buddhist learning. Its high standard of learning attracted even the foreigners. It is here only the final settlements of the Jainas Canonical texts took place in 5th century A.D.
(52) Alamgirpur—the place is situated in Meerut district of U.P. It was one of the famous site of urban Indus valley civilization. Excavation reveals the place as in flourishing condition during the period of Harappan culture.
(53) Aharara—the place is famous for Asokan inscription. It was a trading centre during ancient period.
(54) Aphsad—situated in M.P., the place was famous for its trade and commerce.
(55) Ratnagiri—it was known as Brahamagiri also. The place is situated in South India and during ancient period it was famous for minor rock edict of Asoka.
|
20 videos|561 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on Important Places of Ancient India, History, UPSC - Additional Study Material for UPSC
| 1. What are some important places in ancient India? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Indus Valley Civilization? |  |
| 3. What is the historical importance of Nalanda? |  |
| 4. Which city served as the capital of the Maurya and Gupta empires? |  |
| 5. What is the historical significance of Varanasi? |  |
|
20 videos|561 docs|160 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|


















