Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Impulse
Impulse | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Impulse
- When an unbalanced force acts on an object's mass, its momentum undergoes alteration.
- The impulse exerted by a force equals the force multiplied by the duration of its application, represented as
impulse = force × change in time or impulse = FΔt. - This impulse, denoted as Δp, is synonymous with the change in momentum experienced by the mass.
- The change in momentum can also be described as the difference between the final momentum (mv) and the initial momentum (mu), expressed as Δp = Δ(mv) or Δp = mv − mu.
- Here,
'm' stands for mass in kilograms,
'v' represents the final velocity in meters per second, and
'u' indicates the initial velocity in meters per second. - Thus, the overall equation can be succinctly stated as impulse = FΔt = Δp = mv − mu.
- In everyday scenarios, an instance of impulse can be observed when sheltering under an umbrella during rain compared to hail (frozen water droplets).
- When rain strikes an umbrella, the water droplets typically scatter and drip off, resulting in minimal alteration in momentum.
- Conversely, hailstones possess a greater mass and tend to rebound off the umbrella, causing a more significant change in momentum.
- Consequently, the impulse experienced by an umbrella is higher in hail than in rain.
- This implies that a greater force is necessary to maintain an umbrella's stability in hail compared to rain.
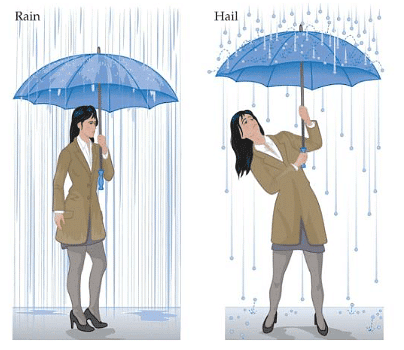 Since hailstones bounce back off an umbrella, compared to water droplets from rain, there is a greater impulse on an umbrella in hail than in rain
Since hailstones bounce back off an umbrella, compared to water droplets from rain, there is a greater impulse on an umbrella in hail than in rain
Force & Momentum
- Force can be described as the rate at which momentum changes in an object.
- The alteration in momentum is calculated as the final momentum subtracted by the initial momentum of the object.
- These concepts can be expressed as:
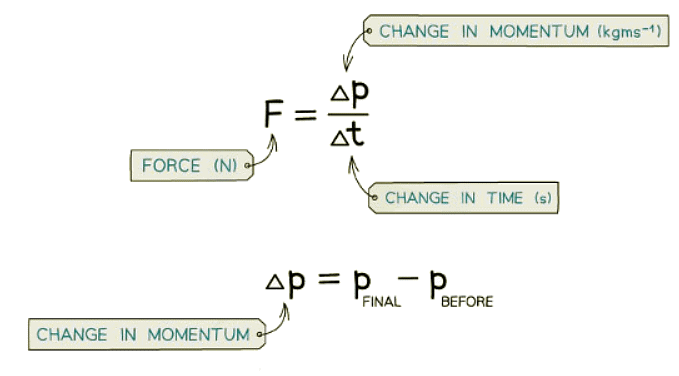
The document Impulse | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|194 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Impulse - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is impulse in the context of physics? |  |
Ans. Impulse is the product of force and the time for which the force acts on an object. It is a vector quantity and is calculated by the formula Impulse = Force x Time.
| 2. How is impulse related to linear momentum? |  |
Ans. Impulse is directly related to the change in linear momentum of an object. The impulse acting on an object is equal to the change in momentum of the object.
| 3. How does force affect momentum in the context of impulse? |  |
Ans. When a force acts on an object for a certain amount of time, it causes a change in the object's momentum. The greater the force or the longer the time it acts, the greater the change in momentum.
| 4. How is impulse calculated in practical scenarios? |  |
Ans. In practical scenarios, impulse can be calculated by determining the force applied on an object and the time duration for which the force is applied. The product of these two values gives the impulse.
| 5. Why is understanding impulse important in the study of physics? |  |
Ans. Understanding impulse is crucial in physics as it helps in analyzing the effects of forces on objects and how they affect the momentum of those objects. It is also essential in studying collisions and understanding the transfer of momentum during such events.
Related Searches




















