Indian Military Aircrafts & Helicopters | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Any aircraft that is operated by a legal or insurrectionary armed force may be called military aircraft. Military uses aircraft for both combat and non-combat applications.
- Combat aircraft are designed to destroy enemy equipment using their own aircraft ordnance. Combat aircraft are typically developed and procured only by military forces.
- Non-combat aircraft are not designed for combat as their primary function but may carry weapons for self-defence. These mainly operate in support roles and may be developed by either military forces or civilian organizations.
Combat Aircraft
Combat aircraft, or “Warplanes”, are divided broadly into multi-role, fighters, bombers, attackers, and electronic warfare support.
Fighters Aircraft
The primary role of fighters is destroying enemy aircraft in air-to-air combat, as part of both offensive and defensive counter-air operations. Many fighters also possess a degree of ground attack capability, allowing them to perform surface attack and close air support missions. In addition to their counter-air duties, they are tasked to perform escort missions for bombers or other aircraft. Fighters are capable of carrying a variety of weapons, including machine guns, cannons, rockets, guided missiles, and bombs. Many modern fighters can attack enemy fighters from a great distance before the enemy even sees or detects them.
Bombers
Bombers are normally larger, heavier, and less maneuverable than fighter aircraft. They are capable of carrying large payloads of bombs, torpedoes or cruise missiles. Bombers are used almost exclusively for ground attacks and not fast or agile enough to take on enemy fighters head-to-head. Some have a single engine and require one pilot to operate, while others have two or more engines and require crews of two or more.
Attack Aircraft
Attack aircraft can be used to provide support for friendly ground troops. Some are able to carry conventional or nuclear weapons far behind enemy lines to strike priority ground targets. Attack helicopters attack enemy armor and provide close air support for ground troops.
Electronic Warfare Aircraft
An electronic warfare aircraft is a military aircraft equipped for electronic warfare (EW) – i.e. degrading the effectiveness of enemy radar and radio systems. They have generally modified versions of other pre-existing aircraft.
Maritime Patrol Aircraft
A maritime patrol aircraft fixed-wing military aircraft designed to operate for long durations over water in maritime patrol roles—in particular anti-submarine, anti-ship, and search and rescue, and In order to detect, identify enemy ships and submarines and destroy them using air-to-surface weapons, torpedoes, and underwater mines.
Multirole Combat Aircraft
Many combat aircraft today have a multirole ability. The MRCA roles may include air-to-air combat, bombing operation, aerial photo-reconnaissance, etc. Normally only applied to fixed-wing aircraft, this term signifies that the plane in question can be a fighter or a bomber, depending on what the mission calls for.
Non-Combat Aircraft
Non-combat roles of military aircraft include search and rescue, reconnaissance, observation/surveillance, Airborne Early Warning and Control, transport, training, and aerial refueling.
Military Transport Aircraft
Military transport (logistics) aircraft are primarily used to transport troops and war supplies. Cargo can be attached to pallets, which are easily loaded, secured for flight, and quickly unloaded for delivery. Cargo also may be discharged from flying aircraft on parachutes, eliminating the need for landing. Also included in this category are aerial tankers; these planes can refuel other aircraft while in flight.
Airborne Early Warning and Control
An airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) system is an airborne radar system designed to detect aircraft, ships and ground vehicles at long ranges and control and command the battle space in an air engagement by directing fighter and attack aircraft strikes.
AEW&C units are also used to carry out surveillance, including over ground targets, and frequently perform C2BM (command and control, battle management) functions similar to an Airport Traffic Controller given military command over other forces.
Used at a high altitude, the radars on the aircraft allow the operators to distinguish between friendly and hostile aircraft hundreds of miles away.
Reconnaissance and Surveillance
Reconnaissance aircraft are primarily used to gather intelligence. They are equipped with cameras and other sensors.
Experimental Aircraft
Experimental aircraft are designed in order to test advanced aerodynamic, structural, avionic, or propulsion concepts. These are usually well instrumented, with performance data telemetered on radio-frequency data links to ground stations located at the test ranges where they are flown.
Aircrafts and Helicopter
Rafale Combat Aircraft
Rafale is a twin-engine manufactured by Dassault Aviation of France, being produced for both the French Air Force and for carrier-based operations in the French Navy. It is primarily used by the French Air Force.
Rafale fighter Jets will be operated by Indian Air Force, a deal was signed for 36 Rafale Fighter Jets. The deal was signed in 2016, it includes a package of spares and weapons including the highly acclaimed Meteor Beyond Visual Range Air to Air Missile (BVRAAM). Apart from Indian Airforce, Rafale has been chosen by the Egyptian Air Force, Qatar Air Force.
Rafale fighter jets were used in combat operations in Afghanistan, Iraq, Syria, Libya, Mali.
Specification
- Air Supremacy: Equipped with a wide range of weapons, the Rafale is intended to perform air supremacy, interdiction (the act of disrupting), aerial reconnaissance (observation to locate an enemy), ground support, in-depth strike, anti-ship strike, and nuclear deterrence missions.
- Wide Range of Weapons: Meteor missile, Scalp cruise missile, and MICA weapons system will be the mainstay of the weapons package of the Rafale jets.
- Meteor: It is the next generation of Beyond Visual Range (BVR) air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) designed to revolutionize air-to-air combat.
(i) The Meteor missile can target enemy aircraft from 150 km away. It can destroy enemy aircraft before they actually even get close to the Indian aircraft. - SCALP Cruise Missiles: It can hit targets 300 km away.
- MICA Missile System: It is a very versatile air-to-air missile. It comes with a radar seeker and can be fired for the short-range to long-range as well right up to 100 km.
(i) It’s already in service with the IAF i.e. Mirages and is the primary weapon system of Rafales as well.
- Meteor: It is the next generation of Beyond Visual Range (BVR) air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) designed to revolutionize air-to-air combat.
- Air to Air Target: The ability to strike air-to-air targets from up to 150 km away and safely hit land targets 300 km within enemy territory makes them some of the deadliest fighter jets flying in the world.
- Flight Hours: The aircraft has 30,000 flight hours in operations.
Significance For India
- Joint Strategic Vision: The Rafale would be an aid to the Joint Strategic Vision of India-France Cooperation in the Indian Ocean Region to curb over-flights and the threat of weapons of mass destruction in the area.
- Upgradation of Air Combat Capabilities: It will significantly bolster India’s air combat capabilities especially when it is facing hostile neighbors like Pakistan and China.
- Unmatched Capabilities: The aircraft proved its unmatched capabilities in air combat missions in Afghanistan, Libya, Mali, Iraq, and Syria in the last few years.
- India is the fourth country to have a strategic platform with Rafale after France, Egypt, and Qatar.
- The Indian Air Force is also in the process of procuring a new generation medium-range modular air-to-ground weapon system Hammer to integrate with the Rafale jets. The Hammer (Highly Agile Modular Munition Extended Range) is a precision-guided missile developed by French defence major Safran.
- Game Changer: Rafales could be a game-changer for India after all the 36 jets join the Indian Air Force as no aircraft in possession of any country in the neighbourhood will be able to match their superior kinematic performance and powerful electronic warfare systems.
- The Rafale jet is often compared with the USA stealth F-35 aircraft and F-22.
- Border Clash with China: It is much more advanced and lethal than the current fighter aircraft available with China i.e.jet J-20. Therefore, it is definitely a boost to India’s defence preparedness especially at times of border clash with China.
Sukhoi Su-30MKI
- Sukhoi Aircraft was developed by Russia. The licence for building it was given to Indian Air Force in the past 2 decades.
- It is a twin-finned, twin-jet multi-role aircraft capable of attaining speeds of Mach 2 at high altitudes.
- It can carry guns, missiles, bombs, rockets, and other weaponry.
- The first indigenously overhauled Sukhoi Su-30MKI supersonic aircraft was recently handed over to the
- Indian Air Force.
- During the overhaul, the aircraft was stripped completely and rebuilt from scratch, replacing certain worn out parts/components.
- Range – 3000 Km
There are many variants of Sukhoi-30 aircraft, and the variant used by Indian Air Force is Sukhoi 30 MkI.
Apart from the Russian and Indian Air Force, the other users of Sukhoi-30 aircraft are Algeria, China, Vietnam, Venezuela, Malaysia.
Sukhoi 30 jets have been modified to carry BrahMos air-to-surface missiles with a range of nearly 300 km, giving them the capacity to conduct long-range precision strikes.
Tejas
- It is an indigenous fighter aircraft inducted into the Indian Airforce in the year 2016.
- It has recently commenced its operation.
- It is designed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- It is a single-seat, single-jet engine, the multirole light fighter.
- It is the smallest and lightest multi-role supersonic fighter aircraft in its class.
- It can fire Air to Air Missiles, carry bombs and Precision Guided ammunition.
- It has its root in the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) programme, which began in the 1980s to replace the ageing MiG-21 fighters.
- MiG-21 fighters are purchased from Russia in 1961.
- Recent Developments – The naval variant of the LCA Tejas has made a first successful “Arrested landing” test.
- Arrested landing means to rapidly decelerate an aircraft as it lands.
- An “arrested landing” on the deck of an aircraft carrier is a feat achieved by only a handful of fighter jets developed in the US, Russia, the UK, France, and China.
- The aircraft has to land on a 100-meter runaway on an aircraft carrier (a normal LCA lands on a one-kilometer
- runway).
- The Tejas will need to replicate this, out at sea when it attempts to land on the deck of India’s only operational aircraft carrier, INS Vikramaditya.
- The Indian Air Force has successfully carried out the first-ever mid-air refuelling of Tejas.
- A Russian-built IL-78 MKI tanker transferred fuel to a Tejas MK I aircraft.
- It is considered as a major milestone in its development cycle.
- The ability to carry out air-to-air refuelling is one of the critical requirements for Tejas to achieve final operational clearance.
- Earlier, Tejas has successfully fired an air-to-air beyond visual (BVR) range missile.
Planned Variants of Tejas
The following table provides details of the variants of the LCA Tejas planned by HAL.
Tejas LCA Mk.1A (Light Combat Aircraft)
- As per recent media reports, the Government of India may soon give go-ahead for the procurement of 83 Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas Mk.1A.
- The size of the deal is likely to be more than $ 5 billion.
- The manufacturer of Tejas LCA Mk.1A will be Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd (HAL).
- Tejas LCA Mk.1A will be superior over previous variants of LCA Tejas, in terms of avionics, performance, and weapons capabilities.
- Tejas LCA Mk.1A will be able to fire different types of Beyond Visual Range (BVR) missiles. This proves LCA Tejas Mk.1A will be flexible enough for smooth hardware and software integration, which would be required for carrying a variety of BVR missiles, which are available in the inventory of the Indian Air Force (IAF).
C-130J Super Hercules
The Lockheed Martin C-130J Super Hercules is a four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft.
India is one of the 17 countries to whom the US has sold its C-130J Super Hercules aircraft. The Indian Air Force currently operates a fleet of five C-130J-30s. India has placed an order for an additional six C-130J-30s Super Hercules aircraft.
In the summer of 2013, Indian Air Force performed the highest landing of a C-130J at the Daulat Beg Oldi airstrip in Ladakh at the height of 16,614 ft. The aircraft was used extensively by the US in Afghanistan and Iraq.
C-17 Globemaster
The Boeing C-17 Globemaster is a large military transport aircraft.
It was developed for the United States Air Force (USAF) from the 1980s to the early 1990s by McDonnell Douglas. The C-17 commonly performs tactical and strategic airlift missions, transporting troops and cargo throughout the world. It can also perform medical evacuation and airdrop duties.
The C-17 is capable of strategic delivery of up to 170,900 pounds of personnel and/or equipment to main operating bases or forward operating locations.
C-17 has a fully integrated electronic cockpit and advanced cargo delivery system. It allows a crew of three: pilot, co-pilot, and loadmaster, to operate the aircraft on any type of mission.
The aircraft is capable of short field landings with a full cargo load. It can also perform tactical airlift and airdrop missions as well as transport litters and ambulatory patients during aeromedical evacuation when required.
Sepecat Jaguar
The SEPECAT Jaguar is a fighter jet developed together by British Royal Air Force and French Air Force. Only the Indian Air Force is currently using the upgraded Jaguar in active duty. The SEPECAT Jaguar is known as Shamsher and serves IAF as primary ground attack aircraft.
Indian Jaguar is quite different from the RAF’s Jaguar and is built locally by HAL under a license agreement. IAF recently upgraded its entire fleet of Jaguar’s by adding Avionics support. The only problem with the Jaguar is its inability to fly at high altitude with a heavy load on board.
Mirage 2000 Fighter Jet
Indian Air Force Mirage 2000 fighters were used to destroy the Jaish-e-Mohammad camps at Balakot along the Line of Control.
It is a French multirole, single-engine fourth-generation fighter jet.
It is manufactured by Dassault Aviation.
It gained prominence after their remarkable success rate in the 1999 Kargil war.
It has a maximum climbing speed of 60,000 feet per minute and is designed for all-weather penetration at low altitude.
Apache Helicopters
- Apache is the most advanced multi-role heavy attack helicopter in the world.
- Its modern capabilities include fire-and-forget, anti-tank missiles, air-to-air missiles, rockets, and other ammunition.
- Apaches have their ability to operate at much higher altitudes, unlike the aging Russian Mi-24/Mi-35 attack helicopters.
- It also has modern electronic warfare capabilities to provide versatility in network-centric aerial warfare.
- It carries a 30 mm chain gun with 1,200 rounds as part of the area weapon subsystem.
- The helicopter carries the fire control Longbow radar, which has 360-degree coverage.
- It also has a nose-mounted sensor suite for target acquisition and night-vision systems.
- The Radar systems in the helicopter will enhance the capability of the IAF in providing integrated combat aviation cover.
- It is day/night, all-weather capable, and has high agility and survivability against battle damage.
- These are easily maintainable even in field conditions and are capable of prolonged operations in tropical and desert regions.
Eight US-made Apache AH-64E stealth attack helicopters have been inducted into IAF.
The IAF has signed a contract with Boeing‘ and the US government for 22 Apache attack helicopters.
It will replace the ageing Russian Mi-35 attack helicopters in service.
MiG-21 Fighter Jets
- MiG is a product of the Soviet Union which entered into the service in 1959.
- It is the first supersonic fighter aircraft of the Indian Air Force.
- India inducted the MiG-21 in 1963 and got full technology transfer and rights to licence-build the aircraft in the country.
- Russia stopped producing the aircraft in 1985, while India continued operating the upgraded variants.
- In the upcoming India-Russia Bilateral summit, India is likely to gift 3 MiG fighter jets to Russia.
- MiG-21 fighter jets will be phased out of service by 2021-22.
- Tejas, an indigenous fighter aircraft will replace the ageing MiG-21.
Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft
- It is India‘s next indigenous fighter and expected to make its first flight by 2032.
- It is built under India‘s only fifth-generation aircraft programme.
- The aircraft will feature geometric stealth which is different from the material stealth feature.
- In material stealth, radar-absorbing materials are used to absorb the radio waves thus reducing the radar footprint.
- Whereas, in geometric stealth, the aircraft is designed at such angles to deflect away maximum radar waves to minimize radar cross-section.
- Thus, the fighter will have a low radar cross-section, making it difficult for the enemy to spot it.
Biojet fuel for Aircraft
- IAF flew an An-32 aircraft in ‘vic’ formation, whose lead plane used a mix of Aviation Turbine Fuel blended with 10% biofuel.
- The biofuel has been extracted from Jatropha plant seeds using a technology patented by the CSIR and the Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun.
- Following the clearance given by the Centre for Military Airworthiness and Certification IAF is expected to use biofuel for its transport fleet and helicopters.
- The ‘vic’ formation comprises 3 or more aircraft flying in close formation with the leader at the apex and the rest to left and right, the whole resembling the letter ‘V’.
Kamov Ka-226T
- Russia plans to deliver 200 Kamov Ka-226T military helicopters to India in a first tranche as part of a $1 billion deal, signed in Indo-Russia Summit in Moscow, 2015.
- The Kamov 226T is a lightweight, twin-engine multi-role chopper that offers services for both military and civilian purposes.
- It will replace India’s ageing fleet of Cheetah and Chetak.
- The military version is capable of working in extreme and difficult weather conditions such as hot climate, marine areas, and high mountains.
- The helicopter has a maximum speed of 250 km/hour and the maximum takeoff weight is 3,600 kg.
- The Ka-226T uses coaxial rotors, that is, it has two sets of rotors mounted one on top of the other and typically no tail rotor.
- Coaxial rotors give helicopter improvements in lift and payload capacity over conventional choppers.
- This is especially advantageous in high-altitude environments where an aircraft’s performance at take-off tends to diminish due to the lower air density.
- The Ka-226T also has a unique, detachable ‘mission’ compartment instead of a conventional cabin.
- This allows the helicopter to be adapted for different roles such as surveillance and cargo delivery.
- Issues with the Old Fleet of Helicopters:
- About 75% of the Army’s fleet of Cheetah and Chetak helicopters is over 30 years old. Some of them are about 50 years old and they need urgent replacements.
(i) Operational capability has been impacted due to deficiencies and non-availability of replacement.
- About 75% of the Army’s fleet of Cheetah and Chetak helicopters is over 30 years old. Some of them are about 50 years old and they need urgent replacements.
- The requirement of Helicopters in the Indian Army: There is a requirement of around 400 such helicopters in the army.
HAL Dhruv
HAL Dhruv is a utility helicopter designed and developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
The indigenously designed and developed Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH-DHRUV) is a twin-engine, multi-role, multi-mission new generation helicopter in the 5.5-ton weight class.
The basic Helicopter is produced in the skid version and wheeled version. Dhruv is “type –Certified” for Military operations by the Centre for Military Airworthiness Certification (CEMILAC) and civil operations by the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA).
A total of 228 Dhruv Helicopters have been produced by March 2017 including 216 for the Indian Armed Forces. It has been supplied to Nepal Army & Mauritius Police, Maldives.
The major variants of Dhruv are classified as Dhruv Mk-I, Mk-II, Mk-III & Mk-IV.
HAL Rudra
The HAL Rudra, also known as ALH-WSI, is an armed version of HAL Dhruv which is designed and manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
It is equipped with Forward Looking Infrared (FLIR) and Thermal Imaging Sights Interface.
HAL Chetak
The Chetak Helicopter is a two-ton class helicopter. The seven-seater Chetak helicopter is a versatile, multi-role, multi-purpose, and spacious.
The helicopter is suitable for commuting, cargo/material transport, casualty evacuation, Search & Rescue (SAR), Aerial Survey & Patrolling, Emergency Medical Services, Off-shore operations, and Underslung operations.
- The Chetak is being replaced by HAL Dhruv in the armed forces.
- HAL Chetak – Single engine
- Maximum speed – Over 210 km/hrs.
HAL Cheetah
HAL Cheetah built by Aérospatiale of France and have been built under licence by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) in India.
The Cheetah Helicopter is a high-performance helicopter designed for operation over a very wide range of weight, the center of gravity, and altitude conditions.
The five-seater Cheetah helicopter is versatile, multi-role, multi-purpose, highly manoeuvrable, and rugged in construction. It holds the world record in high altitude flying among all categories of Helicopters.
Military Awards
1. Wartime Gallantry Awards
- Param Vir Chakra — Highest military award for, equivalent to the Victoria Cross (which was replaced once India gained its independence).
- Maha Vir Chakra – Maha Vir Chakra is the second-highest military decoration in India and is awarded for acts of conspicuous gallantry in the presence of the enemy, whether on land, at sea, or in the air.
- Vir Chakra – Third in precedence in the awards for wartime gallantry.
2. Peacetime Gallantry Awards
- Ashok Chakra – An Indian military decoration awarded for valour, courageous action, or self-sacrifice away from the battlefield. It is the peacetime equivalent of the Param Vir Chakra.
- Kirti Chakra – Second in order of precedence of peacetime gallantry awards.
- Shaurya Chakra – Third in order of precedence of peacetime gallantry awards.
Military Exercises of India with Other Countries
Bilateral Exercises:
Bilateral Exercise is the exercise that is conducted between two countries. Below is a table that shows the list of bilateral exercise:
1. Indian Army
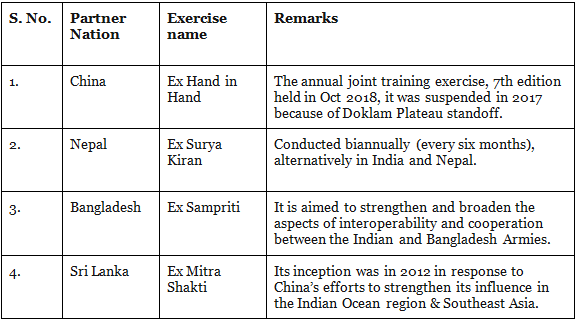
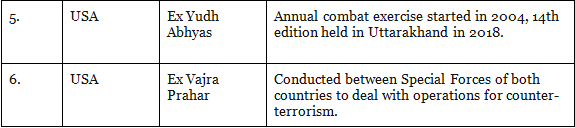
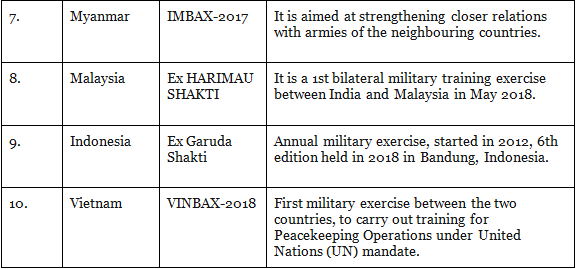
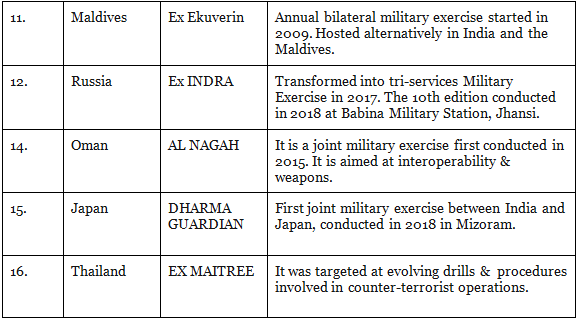
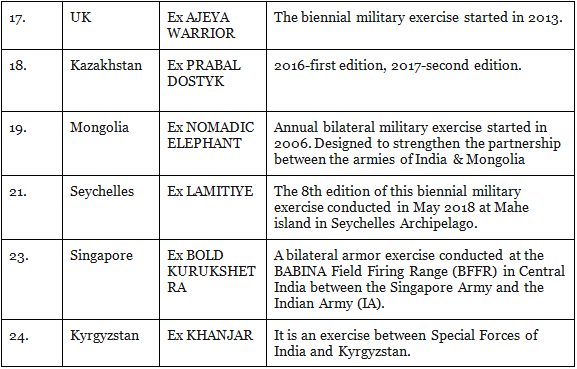
2. Indian Navy
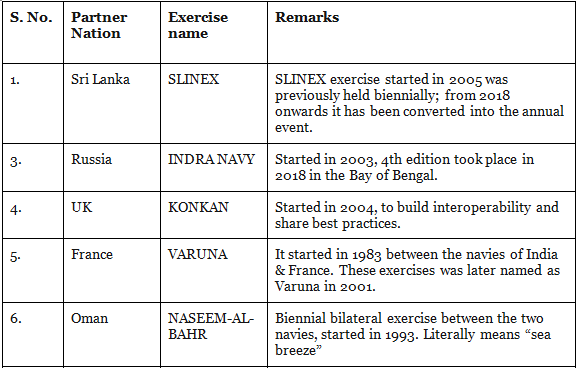
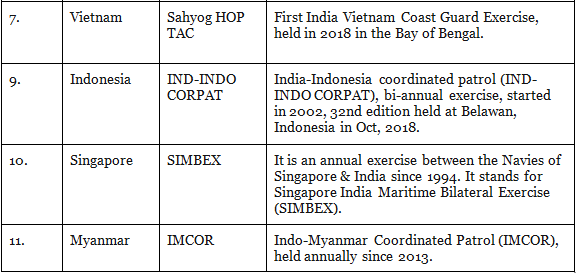
3. Indian Air Force
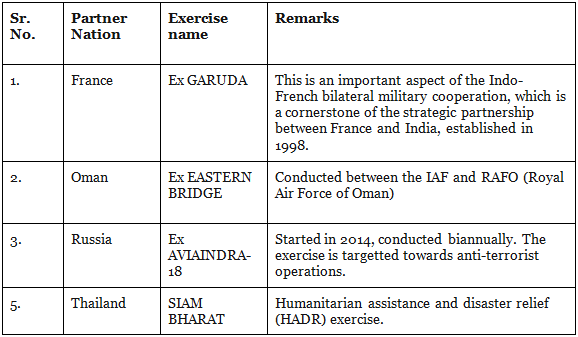
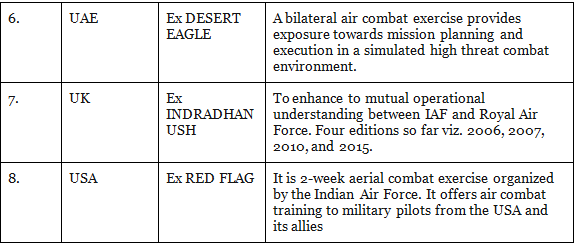
Multilateral Exercises:
They are those exercise which consists of more than one military partners.
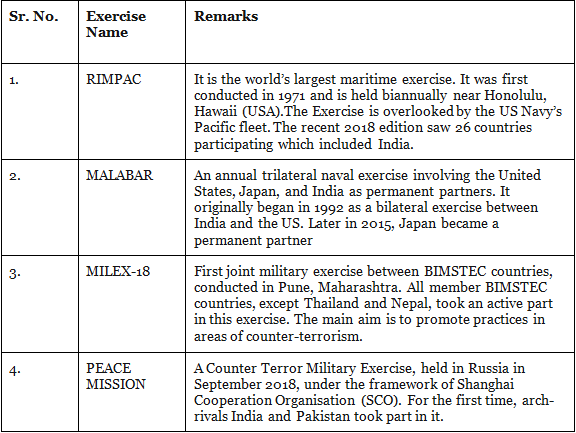
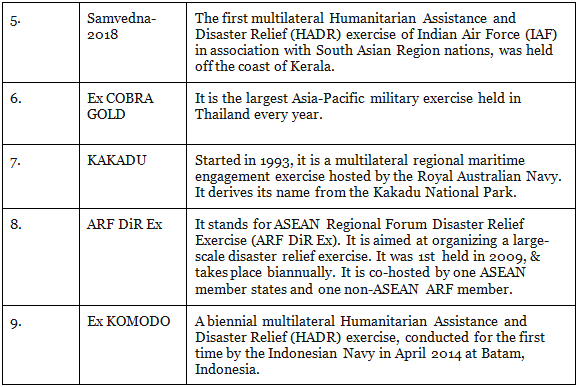
|
146 videos|358 docs|249 tests
|
FAQs on Indian Military Aircrafts & Helicopters - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the different types of military aircraft and helicopters used by the Indian military? |  |
| 2. How does the Indian military maintain and service its aircraft and helicopters? |  |
| 3. Can you provide information on the combat capabilities of Indian military aircraft and helicopters? |  |
| 4. How does the Indian military train its pilots for aircraft and helicopter operations? |  |
| 5. Are there any ongoing or planned acquisitions of new aircraft and helicopters by the Indian military? |  |
|
146 videos|358 docs|249 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















