Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Geography for GCSE/IGCSE > Industrial Systems
Industrial Systems | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Industrial Systems
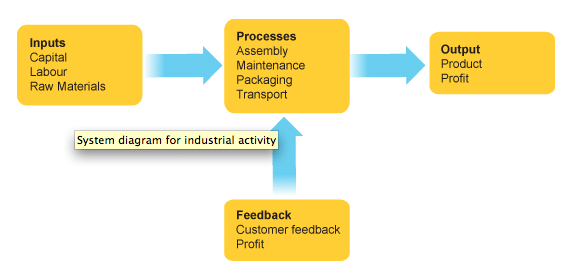
- Industrial systems involve inputs, processes, and outputs:
- Inputs include raw materials, labor, energy, capital, land, and buildings.
- Processes encompass activities like cutting, sewing, welding, brewing, painting, and steel molding.
- Outputs consist of finished products, by-products, products for further manufacturing, and waste.
- Finished products can be cars, clothing, beer, shoes, etc.
- By-products like Marmite can be obtained from beer brewing.
- Continued manufacturing involves processes like cleaning wool or cotton, weaving material, and producing clothes.
- Waste is an inevitable byproduct of manufacturing, incurring disposal costs.
- Manufacturing can be categorized as:
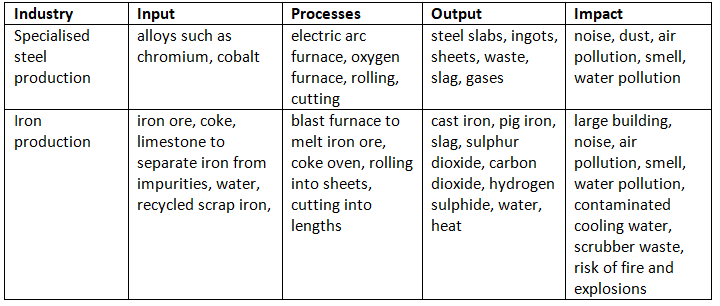
- Heavy industries, exemplified by iron and steel manufacturing, utilize large raw materials to produce substantial items.
- Light industries, such as computer manufacturing, smartphone assembly, clothing production, and micro-brewing, deal with smaller, more intricate products.
- Certain sectors require extensive processing, which can result in significant pollution levels.
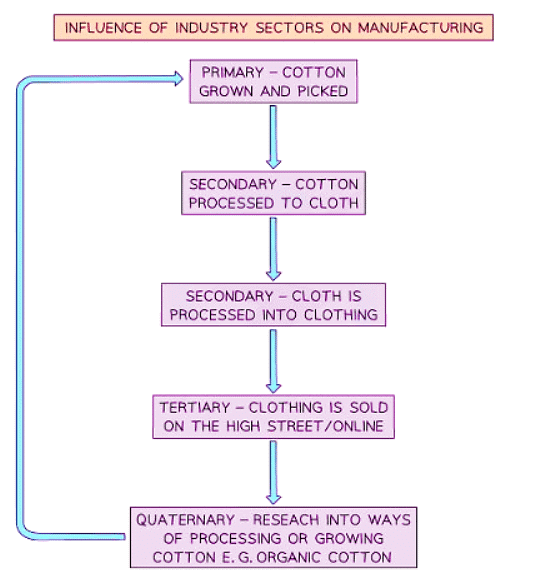
- Industries are interconnected, often relying on multiple sectors to create their products. For example, a car manufacturing industry might require inputs from sectors like metal fabrication, electronics, and plastics to produce vehicles.
Question for Industrial SystemsTry yourself: What are the inputs involved in industrial systems?View Solution
High-Tech Industry
- Fastest growing industry globally, with a significant presence in most More Economically Developed Countries (MEDCs) and Newly Industrialized Countries (NICs).
- Emphasizes research and development to stay competitive in the market.
- Utilizes advanced technologies such as computer automation in manufacturing processes.
- Produces sophisticated items like precision instruments, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology products, mobile phones, and vaccines.
The document Industrial Systems | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Geography for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
55 videos|68 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Industrial Systems - Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the key components of an industrial system? |  |
Ans. Inputs, processes, and outputs are the key components of an industrial system. Inputs refer to the resources such as raw materials, energy, and labor required for production. Processes involve the transformation of inputs into goods or services. Outputs are the final products or services generated by the industrial system.
| 2. Can you provide examples of different types of industries within an industrial system? |  |
Ans. Some examples of types of industries include manufacturing, agriculture, mining, construction, and service industries. Each type of industry plays a specific role in the economy and has its own set of processes and outputs.
| 3. What are the roles and objectives of industrial systems? |  |
Ans. The roles of industrial systems include producing goods and services, creating employment opportunities, generating income, and contributing to economic growth. The objectives of industrial systems are to efficiently utilize resources, minimize waste, increase productivity, and meet consumer demand.
| 4. How do industrial systems impact the environment? |  |
Ans. Industrial systems can have both positive and negative impacts on the environment. While they contribute to economic development and technological advancement, they also produce pollution, waste, and resource depletion. It is important for industrial systems to adopt sustainable practices to minimize their environmental footprint.
| 5. What factors influence the location of industries within an industrial system? |  |
Ans. Factors such as access to raw materials, labor availability, transportation networks, market demand, government policies, and infrastructure influence the location of industries within an industrial system. Companies often consider these factors when deciding where to establish their operations.
Related Searches















