Inheritance of Two Genes: Chromosomal Theory | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
CHROMOSOMAL THEORY OF INHERITANCE
This theory was proposed by Walter Sutton and Theodor Boveri (1902). Following are the main points of this theory
1. Gametes serve as the bridge between two successive generations.
2. Male and Female gametes play an equal role in contributing hereditary components of future generation.
3. Only the nucleus of sperm combines with ovum. Thus, the hereditary information is contained in the nucleus.
4. Chromatin in the nucleus is associated with the cell division in the form of chromosomes.
5. Any type of deletion or addition in the chromosomes can cause structural and functional changes in living beings.
6. A sort of parallelism is observed between Mendelian factors and chromosomes.
7. A number of genes or Mendelian factors are found in each chromosome.
8. Determination of sex in most of the animals and plants is affected by specific chromosomes. These chromosomes are called sex chromosomes.
Parallelism Between Gene and Chromosomes
1. Chromosomes are also transferred from one generation to the next as in the case of genes (Mendelian factors).
2. The number of chromosomes is fixed in each living species.These are found as homologous pairs in diploid cells. One chromosome from father and the other contributed by the mother constitute a homologous pair.
3. Before cell division, each chromosome as a whole and the alleles of genes get replicated and are separated during mitotic division.
4. Meiosis takes place during gamete formation. Homologous chromosomes form synapses during prophase-I stage which in later course get separated and transferred to daughter cells. Each gamete or a haploid cell has only one allele of each gene present in the chromosome.
5. A characteristic diploid number is again established by the union of the two haploid gametes.
6. Both chromosomes and the alleles (Mendelian factors) behave in accordance to Mendel's law of segregation.
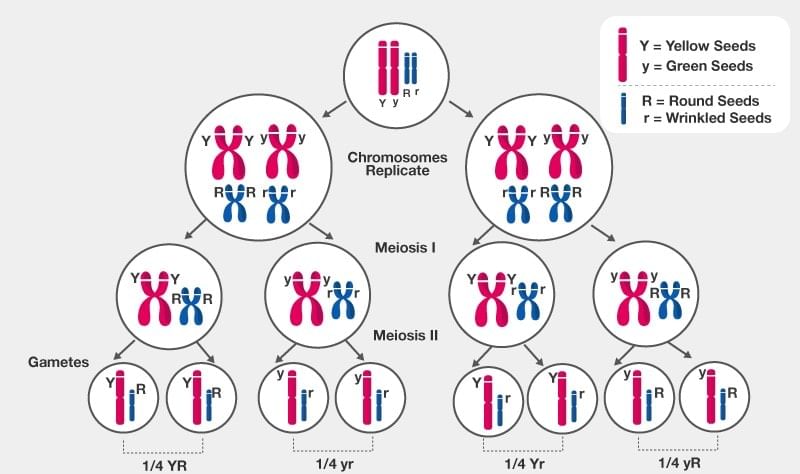 In the homologus chromosomes of a pure tall plant, allele (T) is found for tallness in each chromosome. Likewise, in a pure dwarf plant (tt), allele (t) is present in each chromosome.
In the homologus chromosomes of a pure tall plant, allele (T) is found for tallness in each chromosome. Likewise, in a pure dwarf plant (tt), allele (t) is present in each chromosome.
These homologous chromosomes get separated during meiotic division. Hence, each gamete possesses only one chromosome of an each pair. Accordingly, all the gametes of tall plants possess a chromosome with an allele of tallness (T), while the gametes of dwarf plants possess a chromosome with an allele for dwarfness (t). Their cross to produce F1 generation will yield tall hybrid plants with homologous chromosomal pair containing Tt allelic pair. In this generation two kinds of gamete will be formed during gameto -genesis, 50% with the allele (T) for tallness and 50% with the allele for dwarfness (t).Random combination of these gametes will produce offsprings in F2 generation in the ratio of 25% pure tall (TT), 50% hybrid tall (Tt) and 25% dwarf (tt)

|
26 videos|287 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Inheritance of Two Genes: Chromosomal Theory - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What is the chromosomal theory of inheritance? |  |
| 2. How does the chromosomal theory explain the inheritance of two genes? |  |
| 3. Can genes located on different chromosomes be inherited together? |  |
| 4. How can the chromosomal theory be applied in genetic counseling? |  |
| 5. Can the chromosomal theory explain all patterns of inheritance? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















