Internal Security - 3 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Border Infrastructure |

|
| Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) 1958 |

|
| Spamouflage |

|
| Fugitive Economic Offender |

|
| Smishing |

|
Border Infrastructure
In a surprise briefing during a Parliament session, External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar divulged details about the government's projects concerning border infrastructure and connectivity, particularly focusing on the northern and eastern regions along India's extensive 3,488 km border with China.
Why border management is needed for India?
- The necessity for robust border management in India is inherently tied to the country's internal security challenges, which stem from the adversarial stance of certain neighboring nations and their inclination to exploit India's persistent national issues.
- The enduring disputes over boundaries and territories, exacerbated by challenging terrain, harsh climatic conditions, and porous borders, have left India's borders susceptible. As a result, efficient and effective border management has become a top priority for the Indian government.
What are the strategies for border management in India?
- The strategies employed for border management in India vary depending on the specific border and the country's relationship with its neighbors. The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) shoulders the responsibility for border management.
- The overarching approach to address border security challenges encompasses the management of international land and coastal borders, the reinforcement of border policing and guarding, the development of border infrastructure such as roads, fencing, and floodlighting, as well as the fortification of coastal security infrastructure.
- Additionally, initiatives such as the creation of Integrated Check Posts (ICPs) along land borders and the implementation of the Border Area Development Programme (BADP) contribute to the comprehensive efforts in ensuring effective border management.
What are the various schemes for border management?
Border Infrastructure and Management (BIM) Scheme:
- It is a Central Sector Scheme comprising of projects aimed at infrastructure development of India’s international borders.
- It is being implemented by Border Management-I Division under MHA.
- The scheme aims to enhance the security along the borders of the country and involve implementing a number of projects for the development of border infrastructure.
- E.g., Border Fence, Border Roads, Border Floodlights, Border Out Posts (BOPs), Helipads and foot tracks along the international borders of the country.
- It also involves deployment of technological solutions in such patches of the borders, which are not feasible for physical fence.
Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS):
- CIBMS has been conceptualized to integrate manpower, sensors, networks, intelligence and command control solutions.
- It aims to improve situational awareness at different levels of hierarchy to facilitate prompt and quick response to emerging situations along the India-Pakistan Border (IPB) and India-Bangladesh Border (IBB).
News Summary: Govt. is ramping up border infrastructure
What was the purpose of the briefing?
- There have been successive skirmishes with the Chinese People’s Liberation Army in Chumar in 2014, Doklam in 2017 and the ongoing standoff along the entire LAC since April 2020.
- Since April 2020, the Chinese army amassed troops along the border, which resulted in the Galwan clashes, the first such violent incident in 45 years.
- Against this backdrop, the purpose of the briefing was to provide update on the India-China situation during the parliamentary session.
What initiatives did the briefing outline?
A multi-pronged approach was highlighted during the briefing which include:
- improving connectivity to the LAC through roads, bridges and tunnels;
- improving cross-border connectivity to neighbouring countries via highways, bridges, inland waterways, railroads, electricity lines and fuel pipelines;
- modernising and constructing integrated check posts (ICPs) at all the border crossings to smooth trade; and
- funding and constructing infrastructure projects in neighbouring countries.
- The briefing claimed that 6,806 km of roads were constructed in the China border areas in the period from 2014 to 2022.
What about neighbourhood projects?
The report lists dozens of projects in the neighbourhood that have been planned, financed or constructed. These include:
- Railway links to Nepal and Bangladesh,
- The Mahakali motorable bridge and the Maitri Setu between Tripura and Bangladesh,
- The Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP) which includes a 158 km waterway, the Sittwe port project and road to Mizoram.
It also speaks of:
- South Asia’s first cross-border petroleum products pipeline - between Motihari in India and Amlekhgunj in Nepal;
- Another High-Speed Diesel pipeline with Bangladesh that will reduce petrol prices and road congestion; and
- A Bhutanese dry port in Pasakha bordering West Bengal being developed under an Indian government grant.
Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) 1958
The enactment of the Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) was prompted by escalating violence in the North-eastern States several decades ago, presenting a challenge for State governments to manage effectively. The Armed Forces (Special Powers) Bill successfully passed through both Houses of Parliament and received presidential approval on September 11, 1958, officially becoming the Armed Forces Special Powers Act of 1958.
- AFSPA comprises two legislative components – the first, enacted in 1958, addresses insurgency in the North-east, while the second, passed in 1990, pertains to insurgency and terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir. These laws have been consistently controversial since their inception. Due to their substantial similarities, they are collectively referred to as AFSPA.
Why Afspa Is Necessary?
Conventional CrPc and IPC provisions prove inadequate in addressing situations marked by violence, such as insurgency and terrorist activities. The Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) is designed to bridge this gap.
Afspa: Definition
Under this act, "Armed forces" refers to military and air forces, encompassing any other armed forces of the Union. A "disturbed area" is one declared as such due to differences or disputes between members of different religious, racial, linguistic, regional, or caste communities.
Power to Declare Areas as Disturbed
- The authority to designate areas as disturbed lies with the Governor of the state, Administrator in the case of a union territory, or the central government. Once declared, armed forces can be deployed to assist civil power.
Special Powers of the Armed Forces
Officers of various ranks, including commissioned, warrant, and non-commissioned officers, are empowered to:
- Issue warnings and use force, including lethal force, against individuals contravening laws or orders in disturbed areas.
- Make arrests without a warrant and use force for that purpose.
- Destroy arms dumps, fortified positions, and shelters.
- Conduct premises searches on suspicion, without a warrant.
Presently, AFSPA is in effect in five North East states (parts of Arunachal, Assam, Manipur, Mizoram & Nagaland) and Jammu & Kashmir.
Power to Declare Areas as Disturbed
- AFSPA grants additional powers to armed forces for restoring normalcy. Its premature withdrawal may worsen the security situation, delaying the restoration of peace. Conventional CrPC offers limited authority in dealing with violent situations.
- Disturbed areas often involve the influence of proxy groups, necessitating extraordinary powers to break such networks. The armed forces face asymmetric warfare, including raids, ambushes, and sabotage, requiring exceptional authority.
Effective Functioning
- A sense of security is crucial for the Armed Forces to operate effectively in areas affected by insurgency and militancy.
Security of the Nation
- AFSPA's provisions have played a pivotal role in upholding law and order in disturbed areas, safeguarding the sovereignty and security of the nation.
Protection of Armed Forces Members
- Empowering armed forces members facing constant threats ensures their morale remains high. The withdrawal of AFSPA could adversely impact morale and compromise their safety in the face of insurgents and militants.
Arguments opposing AFSPA
- Abuse of provisions, resulting in issues like fake encounters and extrajudicial killings.
- AFSPA is criticized as a draconian, repressive, colonial, and outdated law within the framework of Indian democracy.
- Viewed as a license for the Armed forces to engage in lethal actions.
- Seen as a violation of various constitutional rights, including safeguards against arbitrary arrest, detention, and privacy.
- Abolishing AFSPA could help alleviate feelings of alienation, particularly in states like those in the north-east.
- Criticized for gross violations of constitutional values, human rights, and natural justice in the country.
- Allegations of power abuse, with claims that the immunity provided by the act has led to misuse by armed forces, resulting in offenses such as enforced disappearances, fake encounters, and sexual assault.
- Poses a threat to justiciable fundamental rights by suspending the rights and liberties guaranteed to citizens by the constitution, thereby weakening democracy.
- Lack of inquiry and appropriate action regarding human rights violations in AFSPA-designated areas goes against the principle of natural justice.
- Diminishes the credibility of democracy, as disillusionment with the democratic system is exploited by secessionists and sympathizers of terrorism, leading to increased violence and counter-violence in a destructive cycle.
- Criticized for ineffectiveness, with opponents arguing that the act has failed to achieve its objective of restoring normalcy in disturbed areas despite being in force for approximately 50 years.
Role of the Judiciary
Questions about the constitutionality of AFSPA arose due to the fact that law and order fall under the jurisdiction of states. In a 1998 judgment (Naga People’s Movement of Human Rights v. Union of India), the Supreme Court affirmed the constitutionality of AFSPA. The key conclusions from this judgment include:
- A suo-motto declaration can be made by the Central government, with a preference for consulting the state government before such a declaration.
- AFSPA does not grant arbitrary powers to declare an area as a 'disturbed area.'
- Declarations must be for a limited duration, subject to periodic review every six months.
- Authorized officers, when exercising powers under AFSPA, should use minimal force necessary and adhere to the 'Dos and Don’ts' issued by the army.
- The recent ruling by the Supreme Court mandates a thorough inquiry into every death caused by armed forces in a disturbed area, regardless of whether the victim is a civilian or an insurgent. This ruling eliminates absolute immunity for armed forces personnel involved in alleged crimes in disturbed areas.
- The Supreme Court addressed a plea concerning 1528 deaths alleged to be fake or extra-judicial encounters by armed forces in Manipur.
AFSPA: Current Status
AFSPA is currently enforced fully or partially in the North-Eastern States, excluding Sikkim, Meghalaya, and Tripura (as of 2018), along with the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir. The Supreme Court has removed blanket immunity for armed forces members.
AFSPA: Conclusion
The idea that alternatives are needed to run the country is emphasized. Peace requires synchronized efforts from central and state governments along with security forces. Political solutions, demonstrated in the cases of Tripura and Mizoram, are essential. Building trust between the armed forces and the public is crucial, emphasizing resolution through dialogue rather than force.
AFSPA: Way Forward
- Adherence to Human Rights: It is crucial to emphasize that compliance with human rights norms and principles strengthens counterinsurgency capabilities without compromising operational effectiveness.
- Robust Safeguards: Protections for armed forces should be accompanied by provisions ensuring responsibility and accountability within legal parameters. The Supreme Court's judgment should be diligently followed.
- Removing Ambiguity in Law: Clear definitions of terms like "disturbed," "dangerous," and "armed forces" are necessary for greater clarity.
- Ensuring Transparency: Greater transparency in communicating the status of ongoing cases, including displaying information on army and government websites, is essential.
- Independent Inquiry: Thorough inquiries into every death caused by armed forces in disturbed areas, regardless of the individual's status as a civilian or a criminal, should be conducted.
Spamouflage
The Spamouflage campaign, originating from China, has been active across more than 50 platforms and forums, including popular social media sites such as Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, YouTube, and X (formerly Twitter).
- Within this influence campaign, the accounts display a tendency to intersperse political posts, promoting positive narratives about China while expressing negative sentiments about the United States, Western foreign policies, and critics of the Chinese government.
Smishing Scam
- A newly identified scam known as 'Smishing' has been cautioned against by the Indian government.
- Smishing is a form of phishing cybersecurity attack executed through mobile text messaging, commonly referred to as SMS phishing. In this variant of phishing, victims are misled into divulging sensitive information to a deceptive attacker. The execution of SMS phishing may involve the use of malware or fraudulent websites.
Fugitive Economic Offender
In an era of globalized financial systems, the Fugitive Economic Offenders Act (FEOA) of 2018 stands as a pivotal piece of legislation aimed at addressing the burgeoning concern of economic offenders eluding legal consequences. This article delves into the intricacies of the Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, exploring its objectives, powers, and the significant impact it has on the financial landscape.
Fugitive Economic Offenders Act Objectives
- The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act 2018 was enacted to tackle the pressing issue of individuals fleeing the country to escape criminal prosecution for economic offenses. The primary objectives of the act include:
- Confiscation of Illegally Acquired Assets: The act empowers authorities to confiscate properties and assets acquired through illegal means by economic offenders.
Declaration of Fugitive Economic Offender
Under the provisions of the FEOA, an individual against whom an arrest warrant has been issued for an offense valued at least Rs. 100 crore can be declared a Fugitive Economic Offender (FEO). The special court designated under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) holds the authority to declare an individual as an FEO and confiscate their properties, both within India and abroad.
- Bar on Civil Claims: The act bestows civil courts and tribunals with the power to prohibit a declared FEO from filing or defending any civil claim. Companies or partnerships where the FEO holds a majority stake may also face restrictions in civil claims.
- Burden of Proof: The burden of proof lies with the accused, requiring them to demonstrate that alleged proceeds of crime are lawful property.
Powers and Authorities Under Fugitive Economic Offenders Act
The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act grants powers to authorities under the PMLA, resembling those of a civil court. These powers include search and seizure of documents or proceeds of crime, along with provisional attachment of properties during pending applications before the Special Court.
FEOA and Prevention of Money Laundering Act
Operating in conjunction with the PMLA, the Fugitive Economic Offenders Act addresses economic offenses specifically, while the PMLA covers a broader range of money laundering crimes. The following table illustrates the linkage between the two:
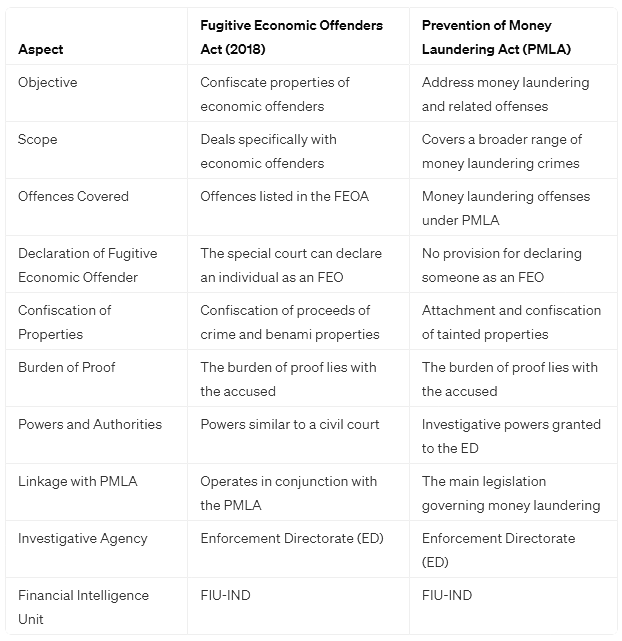
Fugitive Economic Offenders Act Significance and Impact
The FEOA, with its robust legal framework, leaves a profound impact on various aspects of the financial ecosystem:
- Strong Legal Framework: The act strengthens the legal framework to combat economic offenders evading prosecution.
- Property Confiscation: Authorities can confiscate proceeds of crime and benami properties, preventing offenders from enjoying illegal gains.
- Combatting Financial Frauds: The act aids in combating financial fraud and holds offenders accountable for their actions.
- Economic Recovery: Confiscated assets contribute to economic recovery, repayment of creditors, compensation for victims, and funding of welfare programs.
- Safeguarding National Interests: The act protects national interests by preventing offenders from fleeing and upholding financial system integrity.
- Deterrent Effect: Strict provisions and property confiscation act as deterrents against economic offenses.
- International Cooperation: The FEOA facilitates international cooperation in arresting, extraditing, and repatriating fugitive offenders.
- Transparency and Accountability: It promotes transparency and accountability, restoring public trust in the system.
Fugitive Economic Offenders Act 2018 Concerns
While the FEOA is a crucial step towards combating economic offenses, certain concerns need addressing:
- Access to Justice: Barring FEOs or associated companies from filing or defending civil claims may infringe upon the Right to Life under Article 21 of the Constitution, including the right to access justice.
- Treatment of Sale Proceeds: The act does not clarify if the central government will share the sale proceeds of confiscated properties with other claimants, potentially leaving unsecured creditors without a share.
- Absence of Safeguards: Conducting searches without a warrant and without the presence of a witness raises concerns about potential harassment and abuse of power.
- Confiscation Process: The immediate confiscation of property upon declaration, without a specific timeline for finalizing the process, differs from other laws.
- Addressing these concerns is imperative to ensure a balanced implementation of the Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, upholding fundamental rights and ensuring fair treatment for all parties involved.
Fugitive Economic Offenders Act 2018 UPSC
- For UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) aspirants, the Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018, holds significant relevance in areas such as governance, ethics, and the economy. A comprehensive understanding of this topic is crucial for candidates, and they can prepare through UPSC Online Coaching and UPSC Mock Tests. It reflects the government's commitment to combating economic offenses and preventing offenders from evading prosecution.
- Government Measures: Understanding the provisions, objectives, and implications of the Fugitive Economic Offenders Act is essential for aspirants to gain a comprehensive understanding of governance, ethics, and the measures taken to safeguard the financial system.
Conclusion
The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act of 2018 represents a bold stride towards ensuring accountability, transparency, and justice in the face of economic offenses, providing a beacon for legal frameworks worldwide.
Smishing
The Indian government has raised an alert regarding a newly identified scam known as 'Smishing,' a portmanteau of SMS and phishing. This deceptive technique utilizes carefully crafted language to trick users into divulging sensitive information. As reliance on mobile phones continues to grow, vigilance and awareness are essential for users.
Details
- The government advises individuals who have inadvertently fallen victim to Smishing to report online financial fraud by calling 1930 or reporting any cybercrime at cybercrime.gov.in. However, prevention remains crucial, and users are strongly advised to refrain from clicking on suspicious links or sharing personal information through unsolicited text messages.
About
Meaning:
- Smishing, a blend of "SMS" and "phishing," represents a cyber attack using text messages to deceive individuals into revealing sensitive details like passwords, credit card numbers, or personal identification information.
- Smishing perpetrators often pose as legitimate entities, employing urgent or threatening language to coerce recipients into responding, potentially leading to identity theft, financial losses, or malware infections.
How It Works:
Initial Contact:
- Attackers typically source phone numbers from various outlets, including data breaches or public directories. They then dispatch text messages to potential victims, masquerading as reputable institutions or well-known companies to enhance the credibility of their messages.
Urgent or Alarming Content:
- The content of smishing messages is meticulously crafted to induce a sense of urgency or alarm in recipients. This urgency prompts immediate action without thorough consideration. Messages may falsely claim suspicious account activity, pending transactions requiring verification, or security breaches demanding immediate attention.
Deceptive Links:
- Smishing messages commonly contain links redirecting recipients to fraudulent websites designed to closely resemble legitimate platforms. Attackers meticulously replicate the design, logos, and overall appearance of genuine websites to enhance their authenticity.
Data Collection:
- Upon clicking the provided links, victims are directed to counterfeit websites, where they are prompted to input sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, social security numbers, and other personal details.
- Subsequently, attackers harvest this entered information, opening avenues for various malicious purposes, including unauthorized access to accounts, financial fraud, or identity theft.
Impact:
Financial Loss:
- Access to victims' financial information allows attackers to conduct unauthorized transactions, resulting in direct financial losses. Stolen credit card numbers or banking credentials can be exploited for purchases or transfers without the victim's consent.
Identity Theft:
- Stolen personal information empowers attackers to commit identity theft, involving actions like opening new lines of credit, applying for loans, or engaging in other fraudulent activities under the victim's name. Recovering from identity theft is a complex and time-consuming process, potentially leading to long-term consequences for credit scores and financial stability.
Privacy Violation:
- Misuse of personal information acquired through smishing attacks can manifest in harmful ways. Attackers may resort to blackmail, leveraging the stolen data to extort money or coerce victims into specific actions. Additionally, attackers might engage in stalking or other forms of harassment using the victim's private information.
Reputation Damage:
- Public exposure of sensitive personal data obtained through a smishing attack can severely impact the victim's reputation, especially if the stolen information is embarrassing, incriminating, or damaging. This damage can extend to both personal and professional spheres.
Organizational Impact:
- Apart from individual consequences, it is crucial to acknowledge the potential fallout for organizations from smishing attacks. Successful impersonation of a company by attackers, leading to the gathering of sensitive customer information, can result in the loss of customer trust, legal liabilities, and damage to the company's brand and reputation.
Steps Taken by India
Awareness Campaigns
- Conducting awareness campaigns is crucial to educating the public about the risks posed by smishing and other cyber threats. By providing information on how smishing attacks work, common tactics used by attackers, and prevention measures, individuals can become better equipped to recognize and avoid falling victim to such attacks.
- Cybersecurity awareness campaigns often include informative materials, workshops, and public service announcements to reach a wide audience.
Reporting Mechanisms
- Introducing a dedicated phone number like 1930 for reporting online financial fraud and cybercrimes is a significant step toward encouraging victims to report incidents promptly. Having a centralized reporting mechanism makes it easier for individuals to report smishing incidents, as well as other cybercrimes, and helps law enforcement and cybersecurity agencies to take appropriate action against the perpetrators.
Cybercrime Portals
- Cybercrime portals like cybercrime.gov.in play a crucial role in providing individuals with resources and information to report and address cybercrimes, including smishing.
- These portals typically offer guidance on how to report incidents, steps to take after falling victim to a cybercrime, and information about the legal procedures and resources available for victims.
Challenges
Evolving Tactics
- Cyber attackers are known for their ability to evolve and adapt their tactics in response to security measures and awareness campaigns. This constant evolution means that individuals need to stay informed about the latest smishing techniques and remain vigilant in identifying suspicious messages. This challenge emphasizes the need for continuous education and proactive cybersecurity measures.
Human Vulnerability
- Smishing attacks often exploit human psychology, playing on emotions like fear, curiosity, and urgency. By manipulating these emotions, attackers increase the likelihood of victims responding impulsively without critically evaluating the situation. Overcoming this challenge requires not only cybersecurity education but also an understanding of social engineering tactics and how to recognize them.
Global Nature
- The digital nature of smishing allows attackers to launch their campaigns from anywhere in the world. This geographical anonymity makes it challenging to track down and prosecute perpetrators, as they can hide behind various layers of anonymity, including VPNs and Tor networks. International collaboration between law enforcement agencies becomes essential to address this challenge effectively.
Digital Illiteracy
- Digital literacy disparities can leave certain individuals more vulnerable to smishing attacks. People who are not well-versed in technology and online security may struggle to differentiate between legitimate messages and fraudulent ones. Bridging the digital divide through education and accessible resources is crucial to minimizing this vulnerability.
Way Forward
Continuous Education
- Regular and consistent awareness campaigns are crucial to ensure that individuals are up-to-date with the latest smishing tactics and prevention strategies. By raising awareness, people can be more cautious and better equipped to identify and avoid falling victim to these attacks.
Digital Literacy Programs
- Integrating cybersecurity education into educational institutions and community organizations is a proactive way to empower individuals, particularly the younger generation, with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate the digital landscape safely.
Technological Solutions
- Developing advanced detection mechanisms, such as AI-powered algorithms and machine learning, can help mobile carriers and cybersecurity companies identify and block smishing messages in real-time. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the success rate of these attacks.
Collaboration
- Collaboration is essential to effectively combat smishing on a broader scale. By sharing information, best practices, and threat intelligence, various stakeholders can collectively work towards minimizing the impact of smishing attacks.
Enhanced Legislation
- Strengthening cybercrime laws and regulations can provide law enforcement with the necessary tools to investigate and prosecute smishing perpetrators more effectively. Clear legal frameworks can deter attackers and ensure that justice is served.
User-Focused Security Features
- Mobile operating systems and app developers can contribute by integrating user-focused security features. These features might include warning messages when clicking on suspicious links, displaying alerts for potential smishing attempts, and providing tips for identifying fraudulent messages.
Conclusion
Addressing the smishing threat requires a comprehensive approach involving awareness, education, technological advancements, legislative support, and collaboration among various stakeholders. As technology evolves, individuals and organizations must remain vigilant and proactive to effectively counter this evolving cyber threat.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
FAQs on Internal Security - 3 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of border infrastructure? |  |
| 2. What is the purpose of the Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) 1958? |  |
| 3. What is "spamouflage"? |  |
| 4. What is a fugitive economic offender? |  |
| 5. What is "smishing"? |  |



















