Periodic Classification of Elements | Lucent for GK - UPSC PDF Download
Need for the Periodic Classification of Elements
Many tables were made to arrange the elements in an ordered manner based on their characteristics to study the properties of elements in a fixed pattern.
- All existing matter in our surroundings is made up of basic units known as elements. Initially, in 1800, only 31 chemical elements were discovered.
- When there were only 31 elements it was relatively easy to study the properties of these chemical elements individually. Now the number of elements has raised to 118, it would be very cumbersome to study the properties of every element individual.
- In order to ease the work, scientists started thinking about a method so that the study of elements can be simplified.
- They decided to organize the elements in a periodic table according to the information available about the elements and various characteristics shown by them.
Periodic Table
The periodic table is the arrangement of the elements in tabular form according to their properties so that similar elements fall within the same vertical column and dissimilar elements are separated.
Modern Periodic Law
The modern Periodic law can be stated as: The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.
- If elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic numbers, there is a repetition of properties after 2, 8, 18 and 32 elements.
- The numbers 2, 8, 18 and 32 are also referred to as magic numbers.
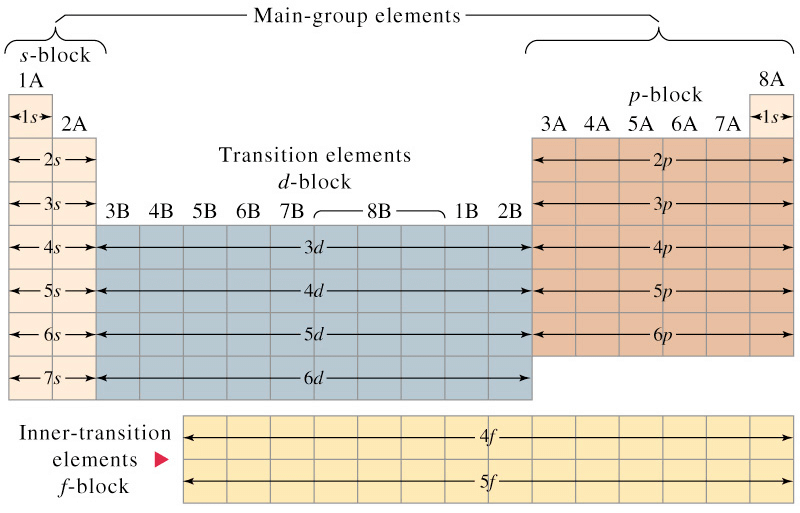
Long Form of Periodic Table
The arrangement of elements in the long form of periodic table is a perfect matching of electronic configuration of the elements on one hand and physical and chemical properties of the elements on the other.
- The elements have been arranged in the increasing order of atomic number.
- The horizontal rows constitute periods while the vertical rows constitute groups or families.
- The periodic table is divided into four main blocks. These are s, p, d and f-blocks. The division of elements into blocks is primarily based upon their electronic configuration.
 Electronic Configuration According to Different Blocks
Electronic Configuration According to Different Blocks - Representative Elements: All the s and p block elements are known as representative elements except zero group.
- Typical Elements: Elements of the second and the third period are known as typical elements.
Classification of Elements as Metals, Non-Metals & Metalloids
1. Metals
- About 80% of the elements are metals. Metals are the elements that are malleable and ductile, possess lustre, are good conductors of heat, electricity and have high densities.
- Metals usually have high melting and boiling points and are generally solids at room temperature.
- Mercury is the only metal that is liquid at room temperature. Gallium (303 K) also have very low melting points.
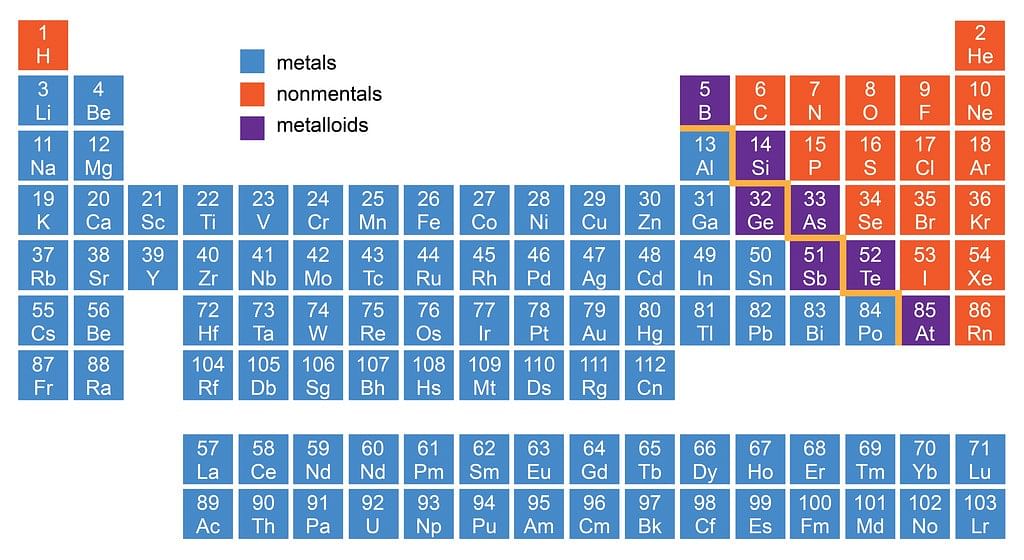
 Location of Metals, Non-metals and Metalloids in Periodic Table
Location of Metals, Non-metals and Metalloids in Periodic Table
2. Non-Metals
- Non-metals are much less in number than metals. Non-metals have low melting and boiling points.
- They are usually solids or gases at room temperature. Non-metals are neither malleable nor ductile. They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
- The non-metallic character increases going from left to right and the metallic character increases going down a group.
3. Metalloids
- There is no sharp dividing metals from non-metals. A zig-zag line separates metals from non-metals as shown in the figure.
- The borderline elements such as silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony and tellurium exhibit characteristic properties of metals as well as non-metals. These elements are called semi-metals or metalloids.
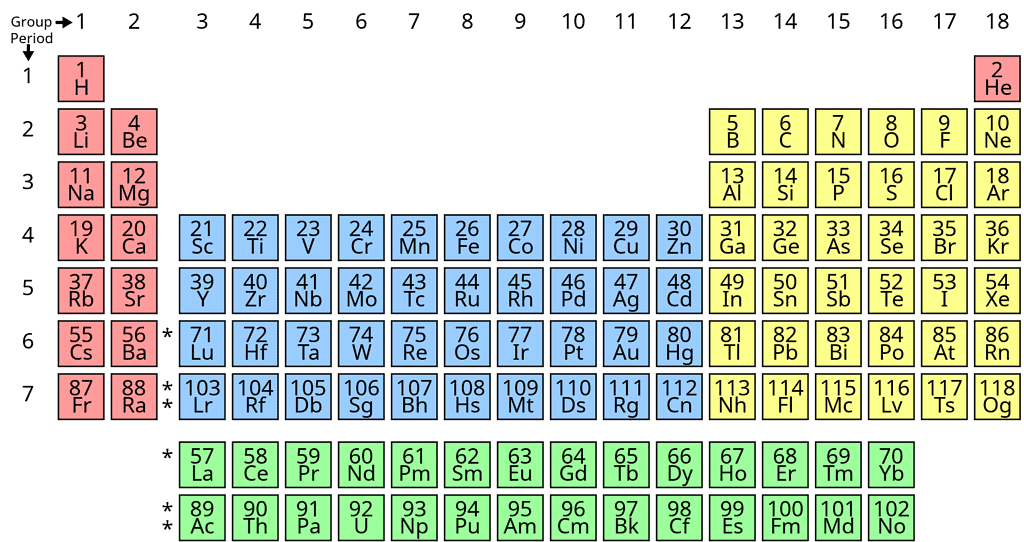
Classification of Elements on the Basis of Electronic Configuration
On the basis of electronic configuration, the elements may be divided into four groups:1. s-block Elements
- These are the elements in which the last electron enters s subshell.
- These are present in the left part of the periodic table.
- These include group 1 and 2 elements.
- All the s-block elements are metals.
- The general electronic configuration of valence shell for s block elements is ns1-2 ( n = 1 to 7).
2. p-block Elements
- These are the elements in which the last electron enters the p subshell.
- These are present in the right part of the periodic table.
- These are present in the 13 to 18 group of the periodic table.
- Most of the p block elements are metalloids and non-metals but some of them are metals also.
- The general electronic configuration of the valence shell is ns2np1-6 ( n = 2 to 7).
ns2 np6 is a stable noble gas configuration. The electronic configuration of He is 1s2.
3. d-block Elements
- These are the elements in which the last electron enters the d-subshell.
- These are present in the middle part of the periodic table (between s & p block elements)
- D block elements include group 3 to 12 groups of the periodic table.
- All d block elements are metals.
- The last electrons enter in (n – 1)d orbital.
- The outermost electronic configuration of d block elements is (n-1)d1-10 ns1-2 (n = 4 to 7).
- There are three series of d-block elements as under:
(i) 3d series – Sc(21) to Zn (30)
(ii) 4d series – Y (39) to Cd (48)
(iii) 5d series – La (57), Hf (72) to Hg (80)
4. f-block Elements
- These elements are also called inner transition elements.
- In these elements, the last electron enters the penultimate i.e. (n – 2)f orbital. The differentiating electron in transition elements may enter either 4f or 5f orbitals based upon which they are differentiated into lanthanides and actinides.
- All the f-block elements are metals.
- Lanthanides: In lanthanides, the differentiating electron enters 4f orbital. These are 14 elements from cerium to lutetium. The name is lanthanides because they come immediately after lanthanum.
- Actinides: In actinides, the differentiating electron enters 5f orbital. These are also 14 elements from thorium to lawrencium. These elements come immediately after actinium.
- General electronic configuration of f-block elements is: (n–2)f1–14 (n–1)d0–1 ns2
Lanthanides: [Xe] 4f1–14 5d0–1 6s2
Actinides: [Rn] 5f1–146 d0–1 7s2
IUPAC Nomenclature for Elements with (Z > 100)
- The elements beyond uranium (Z = 92) are all synthetic elements and are known as transuranium elements. The elements beyond fermium (Z = 100) are known as transfermium elements. These elements have an atomic number 101 onwards.
- The elements fermium (Z = 100), mendelevium (Z = 101), nobelium (Z = 102) and lawrencium (Z = 103) are named after the names of famous scientists.
- Nomenclature of the Elements: The names are derived by using roots for the three digits in the atomic number of the element and adding the ending –ium.
The roots for the number are:

- Thus element with atomic number 109 will be named as une (u for 1, n for 0 and e for 9).
Table: This summarises the names of the elements with an atomic number above 100. 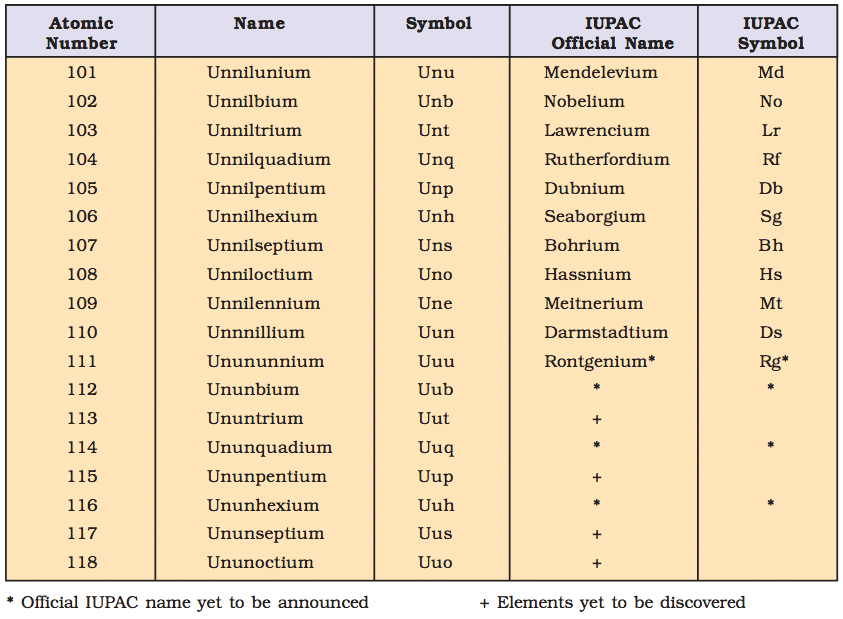
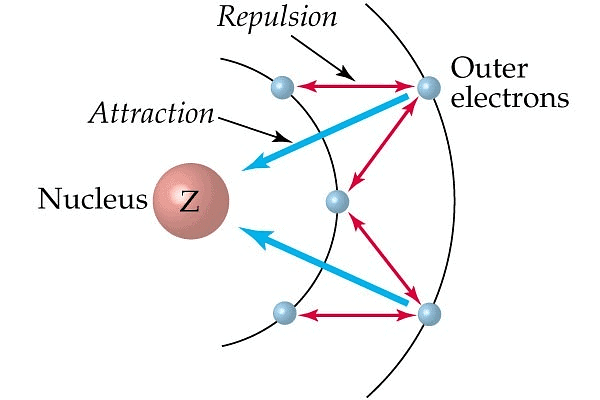
Effective Nuclear Charge (Z*)
It is the nuclear attractive force experienced by the e- when it is shielded by inner lying electrons. In simpler words , effective nuclear charge measures the force exerted on an electron by the nucleus. A higher effective nuclear charge results in a greater attractive force, pulling electrons closer to the nucleus.
- 2p e– is shielded more than or 2s e– as it penetrates the 1s orbital less than 2s orbital.
- As a result we have the energy sequence: [2s < 2p], [3s < 3p < 3d] and [4s < 4p < 4d < 4f].
- As we move to atoms of elements of higher atomic number, the energy difference between orbitals of the same value of n decreases.
Screening Effect
The e-s of the inner shell repels the e-s of outermost shells. This effect is known as the screening or shielding effect.
- The e-s of the outermost shell are thus shielded or screened from the nucleus by inner e-s.
- As a result of the screening effect the outermost e-s do not experience the complete nuclear charge.
- So an increase in no. of inner e-s increases the screening effect and an increase in screening effect decreases nuclear charge. This results in a decrease of I.E.

Penetrating Effect of Electrons
The penetrating power of e-s towards the nucleus in a given shell decreases in the order s > p > d > f.
- If penetration of e- is more, it will be more tightly held up by the nucleus, so it will be difficult to remove it.
- That means the I.E. increases with an increase in the penetrating power of e-s in the subshells.
Empirical Rules for Estimating Effective Nuclear Charge:
“Slater Rule”
- The actual nuclear charge experienced by the electrons in different orbitals is estimated by Slater Rules.
- The ENC (Z*) acting on a given e- is obtained by subtracting the screening (shielding) constant ‘S’. Z*(ENC) = Z(Nuclear charge) – S(Shielding constant)
- Write the electronic configuration in the following order and groupings (1s), (2s, 2p), (3s, 3p)(3d), (4s, 4p), (4d) (4f), (5s, 5p) etc.
- Electron in any group higher in this sequence than the electron under consideration contributes nothing to ‘S’.
- Then for an electron in an ‘ns’ or np orbital:
(a) All other electrons in the (ns, np) group contribute S = 0.35 each.
(b) All electrons in the (n – 1) shell contribute S = 0.85 each.
(c) All electrons in (n – 2) or lower shells contribute S = 1.00 each. - For an electron in nd or nf orbital, all electrons in the same group contribute s = 0.35 each.
- Those in groups lying lower in the sequence than (nd) or (nf) contribute s = 1.00 each.
Example: ‘K’ = (1s2)(2s2p6)(3s2p6)(4s1).
The ENC experienced by ‘4s’ e- is Z* = Z - S = 19 - (0.85 × 8) + (1.00 × 10) = 2.20
If we consider the E.C. of K as (1s2)(2s2p6)(3s2p6)(3d1) then Z* would be
Z* = 19 - (1 × 18) = 1
Thus the e- in the 4s orbital is under the influence of the greater effective nuclear charge and hence in the ground state, it is this orbital that is occupied.
|
624 videos|779 docs|415 tests
|
FAQs on Periodic Classification of Elements - Lucent for GK - UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of the periodic classification of elements in chemistry? |  |
| 2. How are elements classified as metals, non-metals, and metalloids in the periodic table? |  |
| 3. What is the IUPAC nomenclature for elements with atomic numbers greater than 100? |  |
| 4. What is effective nuclear charge (Z*) and how is it calculated? |  |
| 5. What are Slater's rules and how do they help in estimating effective nuclear charge? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|