Irodov Solutions: Relativistic Mechanics | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Q.340. A rod moves lengthwise with a constant velocity v relative to the inertial reference frame K. At what value of v will the length of the rod in this frame be η = 0.5% less than its proper length?
Solution. 340. From the formula for length contraction
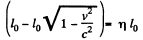
So, 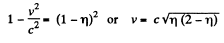
Q.341. In a triangle the proper length of each side equals α. Find the perimeter of this triangle in the reference frame moving relative to it with a constant velocity V along one of its
(a) bisectors;
(b) sides.
Solution. 341. (a) In the frame in which the triangle is at rest the space coordinates of the vertices are 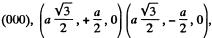 all measured at the same time t. In the moving frame the corresponding coordinates at time t' are
all measured at the same time t. In the moving frame the corresponding coordinates at time t' are
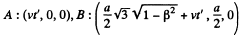
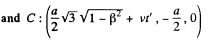
The perimeter P is then
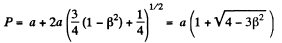
(b) The coordinates in the first frame are shown at time t. The coordinates in the moving frame are,
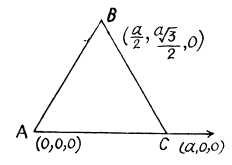
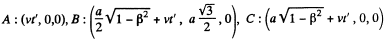
The perimeter P is then
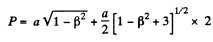
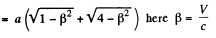
Q.342. Find the proper length of a rod if in the laboratory frame of reference its velocity is v = c/2, the length l = 1.00 m, and the angle between the rod and its direction of motion is θ = 45°.
Solution. 342. In the rest frame, the coordinates of the ends of the rod in terms of proper length l0
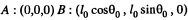
at time t. In the laboratory frame the coordinates at time t' are
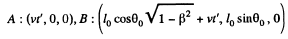
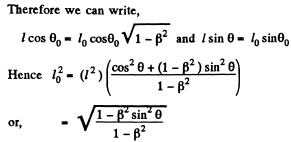
Q.343. A stationary upright cone has a taper angle θ =. 45°, and the area of the lateral surface So = 4.0 m2. Find: (a) its taper angle; (b) its lateral surface area, in the reference frame moving with a velocity v = (4/5)c along the axis of the cone.
Solution. 343. In the frame K in which the cone is at rest the coordinates of A are (0,0,0) and of B are (h, h tan θ, 0) . In the frame K , which is moving with velocity v along the axis o f the cone, the coordinates of A and B at time t' are
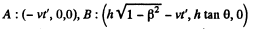
Thus the taper angle in the frame K is
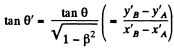
and the lateral surface area is,
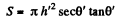
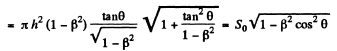
Here S0 - πh2 secθ tanθ is the lateral surface area in the rest frame and
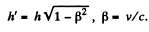
Q.344. With what velocity (relative to the reference frame K) did the clock move, if during the time interval t = 5.0 s, measured by the clock of the frame K, it became slow by Δt = 0.10 s?
Solution. 344. Because of time dilation, a moving clock reads less time. We write,
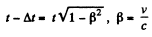
Thus, 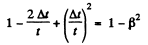
or, 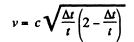
Q.345. A rod flies with constant velocity past a mark which is stationary in the reference frame K. In the frame K it takes Δt = 20 ns for the rod to fly past the mark. In the reference frame fixed to the rod the mark moves past the rod for Δt' = 25 ns. Find the proper length of the rod.
Solution. 345. In the frame K the length l of the rod is related to the time of flight Δt by
l = v Δt
In the reference frame fixed to the rod (frame K')the proper length l0 of the rod is given by
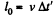
But 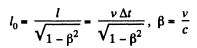
Thus, 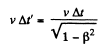
So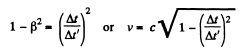
and 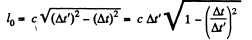
Q.346. The proper lifetime of an unstable particle is equal to Δt0 = 10 ns. Find the distance this particle will traverse till its decay in the laboratory fraine of reference, where its lifetime is equal to Δt = 20 ns.
Solution. 346. The distance travelled in the laboratory frame of reference is vΔ t where v is the velocity of the particle. But by time dilation
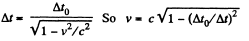
Thus the distance traversed is
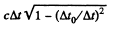
Q.347. In the reference frame K a muon moving with a velocity v = 0.990c travelled a distance l = 3.0 km from its birthplace to the point where it decayed. Find:
(a) the proper lifetime of this muon;
(b) the distance travelled by the muon in the frame K "from the muon's standpoint".
Solution. 347. (a) If τ0 is the proper life time of the muon the life time in the moving frame is
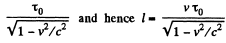
Thus 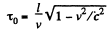
(The words "from the muon’s stand point" are not part of any standard terminology)
Q.348. Two particles moving in a laboratory frame of reference along the same straight line with the same velocity v = (3/4)c strike against a stationary target with the time interval Δt = 50 ns. Find the proper distance between the particles prior to their hitting the target.
Solution. 348. In the frame K in which the particles are at rest, their positions are A and B whose coordinates may be taken as,
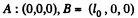
In the frame K' with respect to which K is moving with a velocity v the coordinates of A and B at time t' in the moving frame are
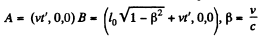
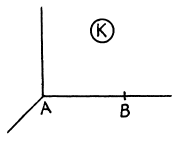
Suppose B hits a stationary target in K' after time t'B while A hits it after time tB + Δt. Then,
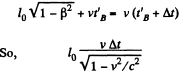
Q.349. A rod moves along a ruler with a constant velocity. When the positions of both ends of the rod are marked simultaneously in the reference frame fixed to the ruler, the difference of readings on the ruler is equal to Δx1 = 4.0 m. But when the positions of the rod's ends are marked simultaneously in the reference frame fixed to the rod, the difference of readings on the same ruler is equal to Δx2 = 9.0 m. Find the proper length of the rod and its velocity relative to the ruler.
Solution. 349. In the reference frame fixed to the ruler the rod is moving with a velocity v and suffers Lorentz contraction. If l0 is the proper length of the rod, its measured length will be
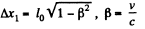
In the reference frame fixed to the rod the ruler suffers Lorentz contraction and we must have
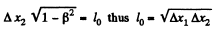
and 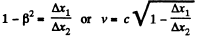
Q.350. Two rods of the same proper length l0 move toward each other parallel to a common horizontal axis. In the reference frame fixed to one of the rods the time interval between the moments, when the right and left ends of the rods coincide, is equal to Δt. What is the velocity of one rod relative to the other?
Solution. 350. The coordinates of the ends of the rods in the frame fixed to the left rod are shown. The points B and D coincides when
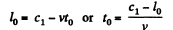
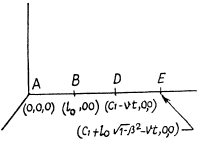
The points A and E coincide when
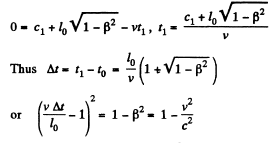
From this 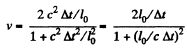
Q.351. Two unstable particles move in the reference frame K along a straight line in the same direction with a velocity v = 0.990c. The distance between them in this reference frame is equal to l = 120 m. At a certain moment both particles decay simultaneously in the reference frame fixed to them. What time interval between the moments of decay of the two particles will be observed in the frame K? Which particle decays later in the frame K?
Solution. 351. In K0, the rest frame of the particles, the events corresponding to the decay of the particles are,
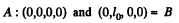
In the reference frame Kf the corresponding coordintes are by Lorentz transformation
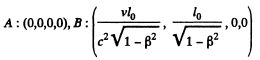
Now 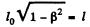
by Lorentz Fitzgerald contraction formula. Thus the time lag of the decay time of B is
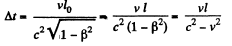
B decays later (B is the forward particle in the direction of motion)
Q.352. A rod AB oriented along the x axis of the reference frame K moves in the positive direction of the x axis with a constant velocity v. The point A is the forward end of the rod, and the point B its rear end. Find:
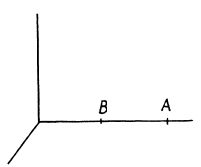
(a) the proper length of the rod, if at the moment tA the coordinate of the point A is equal to xA, and at the moment tB the coordinate of the point B is equal to xB;
(b) what time interval should separate the markings of coordinates of the rod's ends in the frame K for the difference of coordinates to become equal to the proper length of the rod.
Solution. 352. (a) In the reference frame K with respect to which the rod is moving with velocity v, the coordinates of A and B are
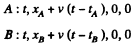
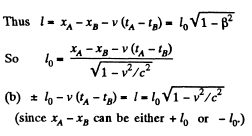
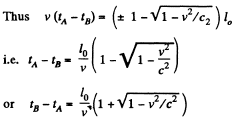
Q.353. The rod A'B' moves with a constant velocity v relative to the rod AB (Fig. 1.91). Both rods have the same proper length l0 and at the ends of each of them clocks are mounted, which are synchronized pairwise: A with B and A' with B'. Suppose the moment when the clock B' gets opposite the clock A is taken for the beginning of the time count in the reference frames fixed to each of the rods. Determine:
(a) the readings of the clocks B and B' at the moment when they are opposite each other;
(b) the same for the clocks A and A'.
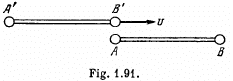
Solution. 353. At the instant the picture is taken the coordintes of A, B, A', B' in the rest frame of AB are
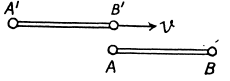
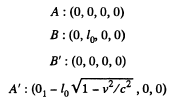
In this frame the coordinates o f B ' at other times are B': (t, vt, 0, 0). So B ' is opposite to B at time 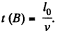 In the frame in which B', A' is at rest the time corresponding this is by Lorentz tranformation.
In the frame in which B', A' is at rest the time corresponding this is by Lorentz tranformation.
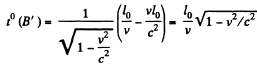
Similarly in the rest frame of A, B, te coordinates of A at other times are
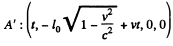
A' is opposite to A at time 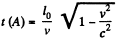
The corresponding time in the frame in which A', B' are at rest is
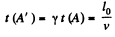
Q.354. There are two groups of mutually synchronized clocks K and K' moving relative to each other with a velocity v as shown in Fig. 1.92. The moment when the clock A' gets opposite the clock A is taken for the beginning of the time count. Draw the approximate position of hands of all the clocks at this moment "in terms of the K clocks"; "in terms of the K' clocks".
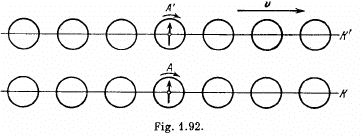
Solution. 354. By Lorentz transformation 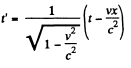
So at time 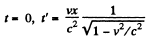
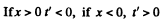 and we get the diagram given below "in terms o f th eif-clock ".
and we get the diagram given below "in terms o f th eif-clock ".
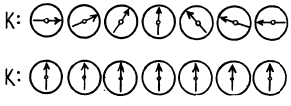
The situation in terms of the K' clock is reversed.
Q.355. The reference frame K' moves in the positive direction of the x axis of the frame K with a relative velocity V. Suppose that at the moment when the origins of coordinates O and O' coincide, the clock readings at these points are equal to zero in both frames. Find the displacement velocity 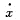 of the point (in the frame K) at which the readings of the clocks of both reference frames will be permanent- ly identical. Demonstrate that
of the point (in the frame K) at which the readings of the clocks of both reference frames will be permanent- ly identical. Demonstrate that 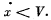
Solution. 355. Suppose x (t) is the locus of points in the frame K at which the readings of the clocks of both reference system are permanently identical then by Lorentz transformation
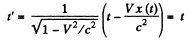
So differentiatin 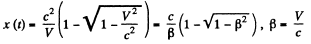
Let 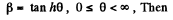
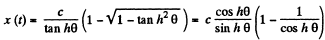
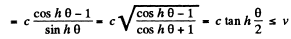
(tan h θ is a monotonically increasing function of θ)
Q.356. At two points of the reference frame K two events occurred separated by a time interval Δt. Demonstrate that if these events obey the cause-and-effect relationship in the frame K (e.g. a shot fired and a bullet hitting a target), they obey that relationship in any other inertial reference frame K'.
Solution. 356. We can take the coordinates of the two events to be
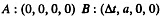
For B to be the effect and A to be cause we must have 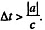
In the moving frame the coordinates of A and B become
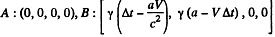
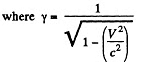
Since
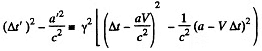
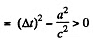
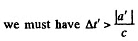
Q. 357. The space-time diagram of Fig. 1.93 shows three events A, B, and C which occurred on the x axis of some inertial reference frame. Find:
(a) the time interval between the events A and B in the reference frame where the two events occurred at the same point;
(b) the distance between the points at which the events A and C occurred in the reference frame where these two events are simultaneous.
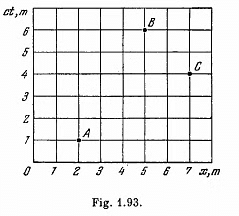
Solution. 357. (a) The four-dimensional interval between A and B (assuming Δy = Δz = 0) is :
52 - 32 bs 16 units
Therefore the time interval between these two events in the reference frame in which the events occurred at the same place is
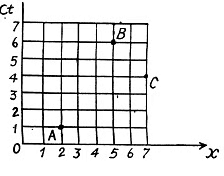
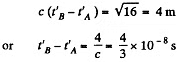
(b) The four dimensional interval between A and C is (assuming Δy = Δz = 0)
32 - 52 = - 16
So the distance between the two events in the fram in which they are simultaneous is 4 units = 4m.
Q. 358. The velocity components of a particle moving in the xy plane of the reference frame K are equal to vx and vy. Find the velocity v' of this particle in the frame K' which moves with the velocity V relative to the frame K in the positive direction of its x axis.
Solution. 358. By the velocity addition formula
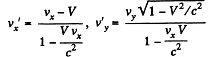
and 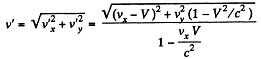
Q. 359. Two particles move toward each other with velocities v1 = 0.50c and v2 = 0.75c relative to a laboratory frame of reference.
Find:
(a) the approach velocity of the particles in the laboratory frame of reference;
(b) their relative velocity.
Solution. 359. (a) By definition the velocity of apporach is
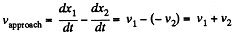
in the reference frame K .
(b) The relative velocity is obtained by the transformation law
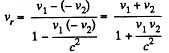
Q. 360. Two rods having the same proper length l0 move lengthwise toward each other parallel to a common axis with the same velocity v relative to the laboratory frame of reference. What is the length of each rod in the reference frame fixed to the other rod?
Solution. 360. The velocity of one of the rods in the reference frame fixed to the other rod is
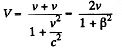
The length of the moving rod in this frame is
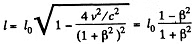
Q. 361. Two relativistic particles move at right angles to each other in a laboratory frame of reference, one 'with the velocity v1 and the other with the velocity v2. Find their relative velocity.
Solution. 361. The approach velocity is defined by
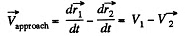
in the laboratory frame. 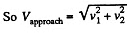
On the other hand, the relative velocity can be obtained by using the velocity addition formula and has the components
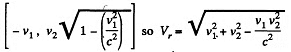
Q. 362. An unstable particle moves in the reference frame K' along its y' axis with a velocity v'. In its turn, the frame K' moves relative to the frame K in the positive direction of its x axis with a velocity V. The x' and x axes of the two reference frames coincide, the y' and y axes are parallel. Find the distance which the particle traverses in the frame K, if its proper lifetime is equal to Δt0.
Solution. 362. The components of the velocity of the unstable particle in the frame K are
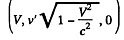
so the velocity relative to K is
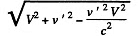
The life time in this frame dilates to
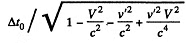
and the distance traversed is
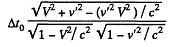
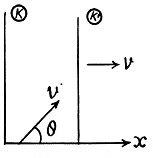
Q. 363. A particle moves in the frame K with a velocity v at an angle θ to the x axis. Find the corresponding angle in the frame K' moving with a velocity V relative to the frame K in the positive direction of its x axis, if the x and x' axes of the two frames coincide.
Solution. 363. In the frame K' the components of the velocity of the particle are
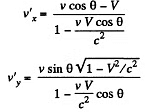
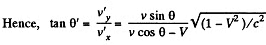
Q. 364. The rod AB oriented parallel to the x' axis of the reference frame K' moves in this frame with a velocity v' along its y' axis. In its turn, the frame K' moves with a velocity V relative to the frame K as shown in Fig. 1.94. Find the angle θ between the rod and the x axis in the frame K.
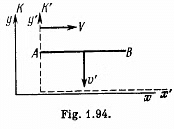
Solution. 364. In K' the coordinates of A and B are
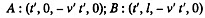
After performing Lorentz transformation to the frame K we get
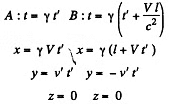
By translating 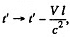 we can write
we can write
the coordinates of B as B : t = γ t'
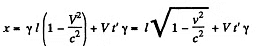
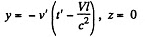
Thus 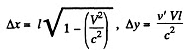
Hence 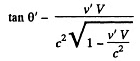
Q. 365. The frame K' moves with a constant velocity V relative to the frame K. Find the acceleration w' of a particle in the frame K', if in the frame K this particle moves with a velocity v and acceleration w along a straight line
(a) in the direction of the vector V;
(b) perpendicular to the vector V.
Solution. 365.
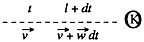
In K the velocities at time t and t + dt are respectively v and v + wdt along x - axis which is parallel to the vector 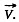 In the frame K' moving with velocity
In the frame K' moving with velocity 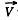 with respect to K, the velocities are respectively,
with respect to K, the velocities are respectively,
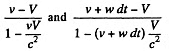
The latter velocity is written as
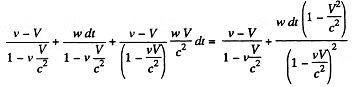
Also by Lorentz transformation
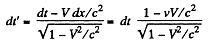
Thus the acceleration in the K' frame is
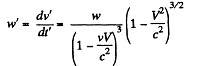
(b) In the K frame the velocities of the particle at the time t and t + di are repectively
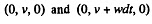
where 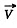 is along jt-axis. In the K frame the velocities are
is along jt-axis. In the K frame the velocities are

and 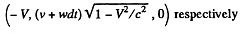
Thus the acceleration
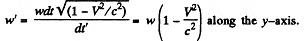
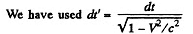
Q. 366. An imaginary space rocket launched from the Earth moves with an acceleration w' = 10g which is the same in every instantaneous co-moving inertial reference frame. The boost stage lasted τ =1.0 year of terrestrial time. Find how much (in per cent) does the rocket velocity differ from the velocity of light at the end of the boost stage. What distance does the rocket cover by that moment?
Solution. 366. In the instantaneous rest frame v = V and
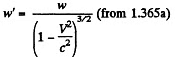
So, 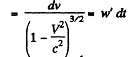
w' is constant by assumption. Thus integration gives
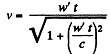
Integrating once again 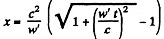
Q. 367. From the conditions of the foregoing problem determine the boost time τ0 in the reference frame fixed to the rocket. Remember that this time is defined by the formula where dt is the time in the geocentric reference frame.
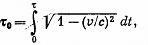
Solution. 367. The boost time τ0 in the reference frame fixed to the rocket is related to the time τ elapsed on the earth by
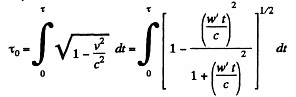
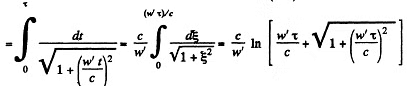
Q. 368. How many times does the relativistic mass of a particle whose velocity differs from the velocity of light by 0.010% exceed its rest mass?
Solution. 368. 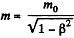
For 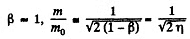
Q. 369. The density of a stationary body is equal to p0. Find the velocity (relative to the body) of the reference frame in which the density of the body is η = 25% greater than p0.
Solution. 369. We define the density p in the frame K in such a way that p dx dy dz is the rest mass dm0 of the element That is p dx dy dz = p0 dx0 dy0 dz0, where p0 is the proper density dx0, dy0 , dz0 are the dimensions of the element in the rest frame K0. Now
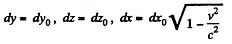
if the frame K is moving with velocity, v relative to the frame K0. Thus
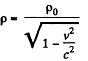
Defining 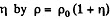
We get 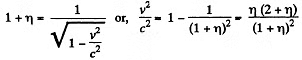
or 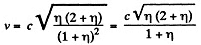
Q. 370. A proton moves with a momentum p = 10.0 GeV/c, where c is the velocity of light. How much (in per cent) does the proton velocity differ from the velocity of light?
Solution. 370. We have
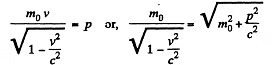
or 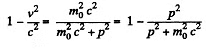
or 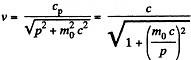
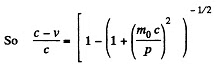
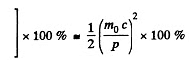
Q.371. Find the velocity at which the relativistic momentum of a particle exceeds its Newtonian momentum η = 2 times.
Solution. 371. By definition of η,
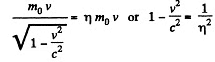
or 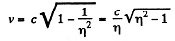
Q.372. What work has to be performed in order to increase the velocity of a particle of rest mass mo from 0.60 c to 0.80 c? Compare the result obtained with the value calculated from the classical formula.
Solution. 372. The work done is equal to change in kinetic energy which is different in the two cases Classically i.e. in nonrelativistic mechanics, the change in kinetic energy is
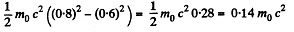
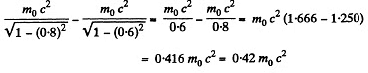
Q.373. Find the velocity at which the kinetic energy of a particle equals its rest energy.
Solution. 373.
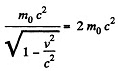
or 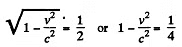
or 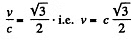
Q.374. At what values of the ratio of the kinetic energy to rest energy can the velocity of a particle be calculated from the classical formula with the relative error less than ε = 0.010?
Solution. 374. Relativistically
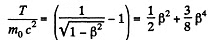
So 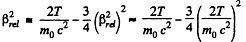
Thus 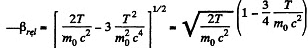
But Classically, 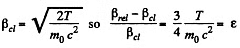
Hence if 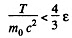
the velocity β is given by the classical formula with an error less than ε.
Q.375. Find how the momentum of a particle of rest mass m0 depends on its kinetic energy. Calculate the momentum of a proton whose kinetic energy equals 500 MeV.
Solution. 375. From the formula
we find 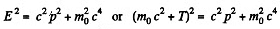
or 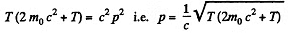
Q.376. A beam of relativistic particles with kinetic energy T strikes against an absorbing target. The beam current equals I, the charge and rest mass of each particle are equal to e and m0 respectively. Find the pressure developed by the beam on the target surface, and the power liberated there.
Solution. 376. Let the total force exerted by the beam on the target surface be .F and the power liberated there be P. Then, using the result of the previous problem we see
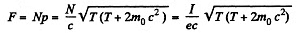
since I = Ne, N being the number of particles striking the target per second. Also,
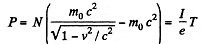
These will be, respectively, equal to the pressure and power developed per unit area of the target if I is current density.
Q.377. A sphere moves with a relativistic velocity v through a gas whose unit volume contains n slowly moving particles, each of mass m. Find the pressure p exerted by the gas on a spherical surface element perpendicular to the velocity of the sphere, provided that the particles scatter elastically. Show that the pressure is the same both in the reference frame fixed to the sphere and in the reference frame fixed to the gas.
Solution. 377. In the tome fixed to the sphere The momentum transferred to the eastically scattered particle is
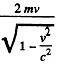
The density of the moving element is, from 1.369, 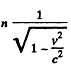
and the momentum transferred per unit time per unit area is
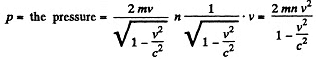
In the frame fixed to the gas When the sphere hits a stationary particle, the latter recoils with a velocity
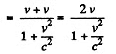
The momentum transferred is 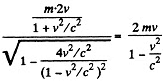
and the pressure 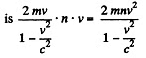
Q.378. A particle of rest mass mo starts moving at a moment t = 0 due to a constant force F. Find the time dependence of the particle's velocity and of the distance covered.
Solution. 378. The equation of motion is
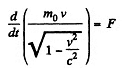
Integrating 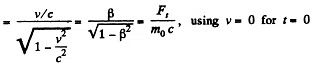
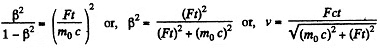
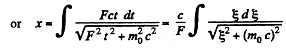
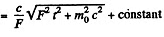
or using r = 0 at r - 0, we get, 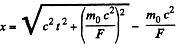
Q.379. A particle of rest mass m0 moves along the x axis of the frame K in accordance with the law 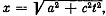 where a is a constant, c is the velocity of light, and t is time. Find the force acting on the particle in this reference frame.
where a is a constant, c is the velocity of light, and t is time. Find the force acting on the particle in this reference frame.
Solution. 379. 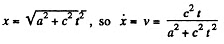
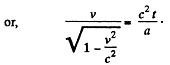
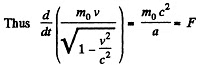
Q.380. Proceeding from the fundamental equation of relativistic dynamics, find:
(a) under what circumstances the acceleration of a particle coincides in direction with the force F acting on it;
(b) the proportionality factors relating the force F and the acceleration w in the cases when F ⊥ and F II v, where v is the velocity of the particle.
Solution. 380.
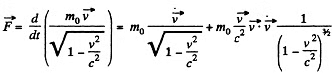
Thus 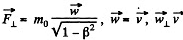
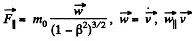
Q.381. A relativistic particle with momentum p and total energy E moves along the x axis of the frame K. Demonstrate that in the frame K' moving with a constant velocity V relative to the frame K in the positive direction of its axis x the momentum and the total energy of the given particle are defined by the formulas:
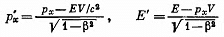
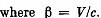
Solution. 381. By definition,
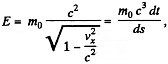
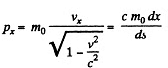
where 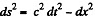 i.s the invariant interval (dy = dz - 0)
i.s the invariant interval (dy = dz - 0)
Thus, 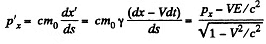
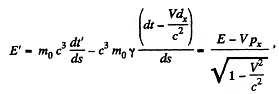
Q.382. The photon energy in the frame K is equal to ε. Making use of the transformation formulas cited in the foregoing problem, find the energy ε' of this photon in the frame K' moving with a velocity V relative to the frame K in the photon's motion direction. At what value of V is the energy of the photon equal to ε' = ε/2?
Solution. 382. For a photon moving in the x direction
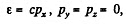
In the moving frame, 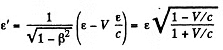
Note that 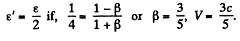
Q.383. Demonstrate that the quantity E2 — p2c2 for a particle is an invariant, i.e. it has the same magnitude in all inertial reference frames. What is the magnitude of this invariant?
Solution. 383. As before
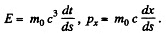
Similarly 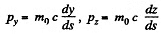
Then 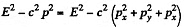
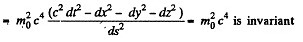
Q.384. A neutron with kinetic energy T = 2m0c2, where m0 is its rest mass, strikes another, stationary, neutron. Determine:
(a) the combined kinetic energy  of both neutrons in the frame of their centre of inertia and the momentu
of both neutrons in the frame of their centre of inertia and the momentu 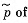 each neutron in that frame; (b) the velocity of the centre of inertia of this system of particles. Instruction. Make use of the invariant E2 — p2c2 remaining constant on transition from one inertial reference frame to another (E is the total energy of the system, p is its composite momentum).
each neutron in that frame; (b) the velocity of the centre of inertia of this system of particles. Instruction. Make use of the invariant E2 — p2c2 remaining constant on transition from one inertial reference frame to another (E is the total energy of the system, p is its composite momentum).
Solution. 384. (b) & (a) In the CM frame, the total momentum is zero, Thus
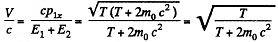
where wc have used the result of problem (Q.375) Then
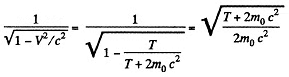
Total energy in the CM frame is
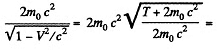
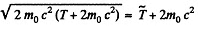
So 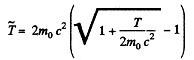
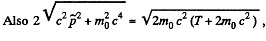
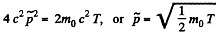
Q.385. A particle of rest mass m0 with kinetic energy T strikes a stationary particle of the same rest mass. Find the rest mass and the velocity of the compound particle formed as a result of the collision.
Solution. 385. 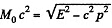
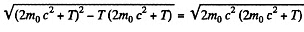
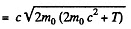
Also 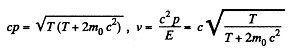
Q.386. How high must be the kinetic energy of a proton striking another, stationary, proton for their combined kinetic energy in the frame of the centre of inertia to be equal to the total kinetic energy of two protons moving toward each other with individual kinetic energies T = 25.0 GeV?
Solution. 386. Let T = kinetic energy of a proton striking another stationary particle of the same rest mass. Then, combined kinetic energy in the CM frame
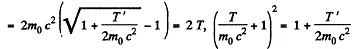
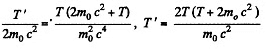
Q.387. A stationary particle of rest mass m0 disintegrates into three particles with rest masses m1, m2, and m3. Find the maximum total energy that, for example, the particle m1 may possess.
Solution. 387. We have
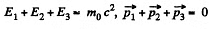
Hence 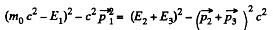
The L.H.S. 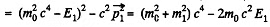
The R.H.S. is an invariant We can evaluate it in any frame. Choose the CM frame of the particles 2 and 3.
In this frame 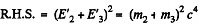
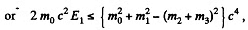
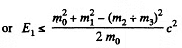
Q.388. A relativistic rocket emits a gas jet with non-relativistic velocity u constant relative to the rocket. Find how the velocity v of the rocket depends on its rest mass m if the initial rest mass of the rocket equals m0.
Solution. 388. The velocity of ejected gases is u realtive to the rocket. In an earth centred frame it is
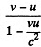
in the direction of the rocket The momentum conservation equation then reads
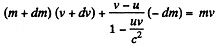
or 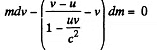
Here - dm is the mass of the ejected gases, so
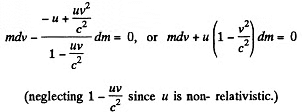
Integrating 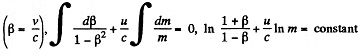
The constant 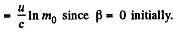
Thus 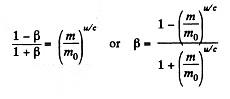
|
95 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Relativistic Mechanics - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the basic principles of relativistic mechanics? |  |
| 2. How does relativistic mechanics differ from classical mechanics? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of Einstein's mass-energy equivalence? |  |
| 4. How does relativistic mechanics explain the behavior of particles at high speeds? |  |
| 5. What are some practical applications of relativistic mechanics? |  |





















