Irodov Solutions: The First Law of Thermodynamics, Heat Capacity | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Q1: Demonstrate that the internal energy U of the air in a room is independent of temperature provided the outside pressure p is constant. Calculate U, if p is equal to the normal atmospheric pressure and the room's volume is equal to V = 40 m3.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Internal energy of air, treating as an ideal gas
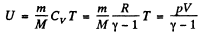 (1)
(1)
Using 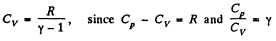
Thus at constant pressure U = constant, because the volume of the room is a constant.
Putting the value of p = Patm and V in Eq. (1), we get U = 10 MJ.
Q2: A thermally insulated vessel containing a gas whose molar mass is equal to M and the ratio of specific heats Cp/Cv = γ moves with a velocity v. Find the gas temperature increment resulting from the sudden stoppage of the vessel.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: From energy conservation
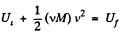
or, 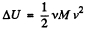 (1)
(1)
But from 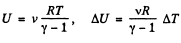 (from the previous problem) (2)
(from the previous problem) (2)
Hence from Eqs. (1) and (2).
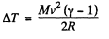
Q3: Two thermally insulated vessels 1 and 2 are filled with air and connected by a short tube equipped with a valve. The volumes of the vessels, the pressures and temperatures of air in them are known (V1, p1, T1 and V2, p2, T2). Find the air temperature and pressure established after the opening of the valve.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: On opening the valve, the air will flow from the vessel at higher pressure to the vessel at lower pressure till both vessels have the same air pressure. If this air pressure is p, the total volume of the air in the two vessels will be (V1 + V2). Also if v1 and v2 be the number of moles of air initially in the two vessels, we have
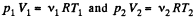 (1)
(1)
After the air is mixed up, the total number of moles are (v1 + v2) and the mixture is at temperature T.
Hence 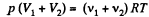 (2)
(2)
Let us look at the two portions of air as one single system. Since this system is contained in a thermally insulated vessel, no heat exchange is involved in the process. That is, total heat transfer for the combined system Q = 0
Moreover, this combined system does not perform mechanical work either. The walls of the containers are rigid and there are no pistons etc. to be pushed, looking at the total system, we know A = 0.
Hence, internal energy of the combined system docs not change in the process. Initially energy of the combined system is equal to the sum of internal energies of the two portions of air :
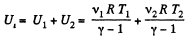 (3)
(3)
Final internal energy of (n1 + n2) moles of air at temperature T is given by
 (4)
(4)
Therefore, Ui = Uf implies :
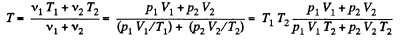
From (2), therefore, final pressure is given by :
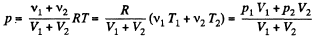
This process in an example of free adiabatic expansion of ideal gas.
Q4: Gaseous hydrogen contained initially under standard conditions in a sealed vessel of volume V = 5.0 l was cooled by ΔT = 55 K . Find how much the internal energy of the gas will change and what amount of heat will be lost by the gas.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: By the first law of thermodynamics,
Q = ΔU + A
Here A = 0, as the volume remains constant,
So, 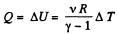
From gas law, 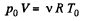
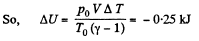
Hence amount of heat lost 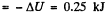
Q5: What amount of heat is to be transferred to nitrogen in the isobaric heating process for that gas to perform the work A = 2.0 J?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: By the first law of thermodynamics Q = ΔU + A
But 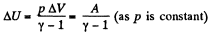
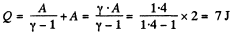
Q6: As a result of the isobaric heating by ΔT = 72 K one mole of a certain ideal gas obtains an amount of heat Q = 1.60 kJ. Find the work performed by the gas, the increment of its internal energy, and the value of γ = Cp/Cv.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Under isobaric process 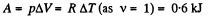
From the first law of thermodynamics
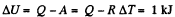
Again increment in internal energy 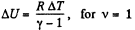
Thus 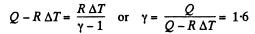
Q7: Two moles of a certain ideal gas at a temperature T0 = 300 K were cooled isochorically so that the gas pressure reduced n = 2.0 times. Then, as a result of the isobaric process, the gas expanded till its temperature got back to the initial value. Find the total amount of heat absorbed by the gas in this process.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let v = 2 moles of the gas. In the first phase, under isochoric process, A1 = 0, therefore from gas law if pressure is reduced n times so that temperature i.e. new temperature becomes T0/n.
Now from first law of thermodynamics
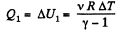
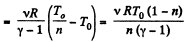
During the second phase (under isobaric process),
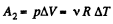
Thus from first law of thermodynamics :
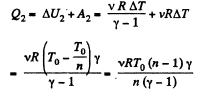
Hence the total amount of heat absorbed
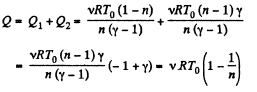
Q8: Calculate the value of γ = Cp/Cv for a gaseous mixture consisting of v1 = 2.0 moles of oxygen and v2 = 3.0 moles of carbon dioxide. The gases are assumed to be ideal.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Total no. of moles of the mixture v = v1 + v2
At a certain temperature, 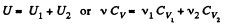
Thus 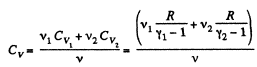
Similarly 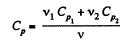
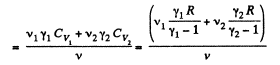
Thus 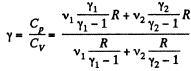
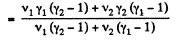
Q9: Find the specific heat capacities cv and cp for a gaseous mixture consisting of 7.0 g of nitrogen and 20 g of argon. The gases are assumed to be ideal.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
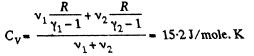
and 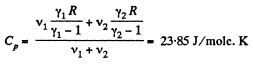
Now molar mass of the mixture 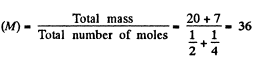
Hence 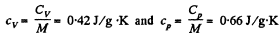
Q10: One mole of a certain ideal gas is contained under a weightless piston of a vertical cylinder at a temperature T. The space over the piston opens into the atmosphere. What work has to be performed in order to increase isothermally the gas volume under the piston it times by slowly raising the piston? The friction of the piston against the cylinder walls is negligibly small.
 View Answer
View Answer 
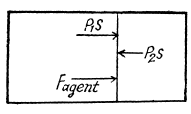
Ans: Let 5 be the area of the piston and F be the force exerted by the external agent Then, F + p S - p0S (Fig.) at an arbitrary instant of time. Here p is the pressure at the instant the volume is V. (Initially the pressure inside is p0)
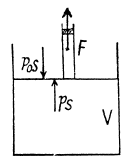

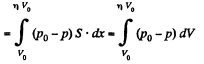
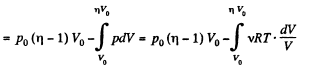
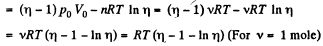
Q11: A piston can freely move inside a horizontal cylinder closed from both ends. Initially, the piston separates the inside space of the cylinder into two equal parts each of volume V0, in which an ideal gas is contained under the same pressure P0 and at the same temperature. What work has to be performed in order to increase isothermally the volume of one part of gas η times compared to that of the other by slowly moving the piston?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let the agent move the piston to the right by x. In equilibrium position,
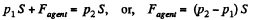
Work done by the agent in an infinitesmal change dx is
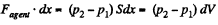
By applying PV = constant, for the two parts,
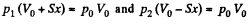
So, 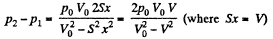
When the volume of the left end is η times the volume of the right end
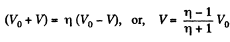
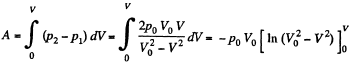
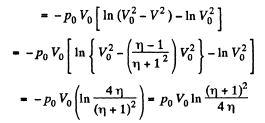
Q12: Three moles of an ideal gas being initially at a temperature T0 = 273 K were isothermally expanded n = 5.0 times its initial volume and then isochorically heated so that the pressure in the final state became equal to that in the initial state. The total amount of heat transferred to the gas during the process equals Q = 80 kJ. Find the ratio γ = Cp/Cv for this gas.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In the isothermal process, heat transfer to the gas is given by
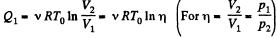
In the isochoric process, A = 0
Thus heat transfer to the gas is given by
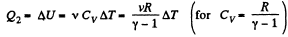
But 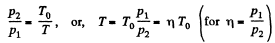
or, 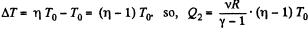
Thus, net heat transfer to the gas
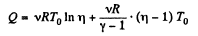
or, 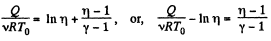
or, 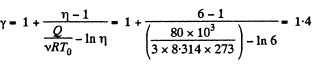
Q13: Draw the approximate plots of isochoric, isobaric, isothermal, and adiabatic processes for the case of an ideal gas, using the following variables:
(a) p, T; (b) V, T.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) From ideal gas law 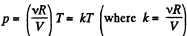
For isochoric process, obviously k = constant, thus p = kT, represents a straight line passing through the origin and its slope becomes k.
For isobaric process p = constant, thus on p - T curve, it is a horizontal straight line parallel to T - axis, if T is along horizontal (or x - axis)
For isothermal process, T = constant, thus on p - T curve, it represents a vertical straight line if T is taken along horizontal (or x - axis)
For adiabatic process 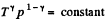
After diffrentiating, we get 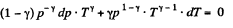
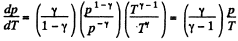
The approximate plots of isochoric, isobaric, isothermal, and adiabatic processes are drawn in the answer sheet.
(b) As p is not considered as variable, we have from ideal gas law
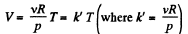
On V - T co-ordinate system let us, take T along x - axis.
For isochoric process V = constant, thus k' = constant and V = k'T obviously represents a straight line passing through the origin of the co-ordinate system and k' is its slope.
For isothermal process T = constant. Thus on the stated co- ordinate system it represents a straight line parallel to the V - axis.
For adiabatic process 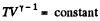
After differentiating, we get 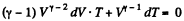
The approximate plots of isochoric, isobaric, isothermal and adiabatic processes are drawn in the answer sheet.
Q14: One mole of oxygen being initially at a temperature T0 = 290 K is adiabatically compressed to increase its pressure η = 10.0 times. Find:
(a) the gas temperature after the compression;
(b) the work that has been performed on the gas.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: According to T - p relation in adiabatic process, 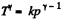 (where k = constant)
(where k = constant)
and 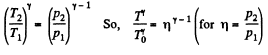
Hence 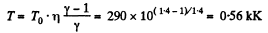
(b) Using the solution of part (a), sought work done
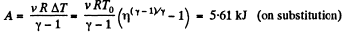
Q15: A certain mass of nitrogen was compressed η = 5.0 times (in terms of volume), first adiabatically, and then isothermally. In both cases the initial state of the gas was the same. Find the ratio of the respective works expended in each compression.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let (p0, V0,T0) be the initial state of the gas.
We know 
But from the equation 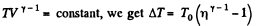
Thus 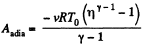
On the other hand, we know 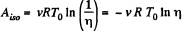 (work done by the gas)
(work done by the gas)
Thus 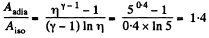
Q16: A heat-conducting piston can freely move inside a closed thermally insulated cylinder with an ideal gas. In equilibrium the piston divides the cylinder into two equal parts, the gas temperature being equal to T0 . The piston is slowly displaced. Find the gas temperature as a function of the ratio η of the volumes of the greater and smaller sections. The adiabatic exponent of the gas is equal to γ.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Since here the piston is conducting and it is moved slowly the temperature on the two sides increases and maintained at the same value.
Elementary work done by the agent = Work done in compression - Work done in expansion
i.e. dA - p2 dV - p1 dV = (p2 - P1) dV
where p1 and p2 are pressures at any instant of the gas on expansion and compression side respectively.
From the gas law 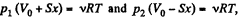 for each section
for each section
(x is the displacement of the piston towards section 2)
So, 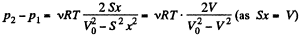
So 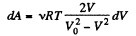
Also, from the first law of thermodynamics
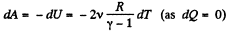
So, work done on the gas 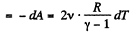
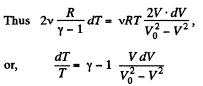
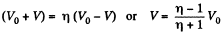
On integrating
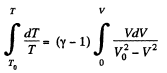
or 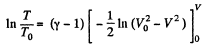
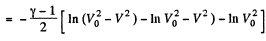
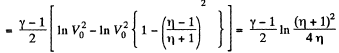
Hence 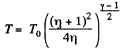
Q17: Find the rate v with which helium flows out of a thermally insulated vessel into vacuum through a small hole. The flow rate of the gas inside the vessel is assumed to be negligible under these conditions. The temperature of helium in the vessel is T = 1,000 K.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: From energy conservation as in the derivation of Bernoulli theorem it reads
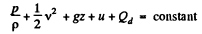 (1)
(1)
In the Eq. (1) u is the internal energy per unit mass and in this case is the thermal eneigy per unit mass of the gas. As the gas vessel is thermally insulated Qd = 0, also in our case.
Just inside the vessel 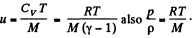 Inside the vessel v = 0 also. Just outside p = 0, and u = 0. Ingeneral gz is not very significant for gases.
Inside the vessel v = 0 also. Just outside p = 0, and u = 0. Ingeneral gz is not very significant for gases.
Thus applying Eq. (1) just inside and outside the hole, we get
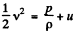
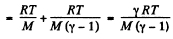
Hence 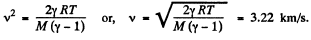
Note : The velocity here is the velocity of hydrodynamic flow of the gas into vacuum. This requires that the diameter of the hole is not too small (D > mean free path l). In the opposite case (D < < l) the flow is called effusion. Then the above result does not apply and kinetic theory methods are needed.
Q18: The volume of one mole of an ideal gas with the adiabatic exponent γ is varied according to the law V = a/T, where a is a constant. Find the amount of heat obtained by the gas in this process if the gas temperature increased by ΔT.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The differential work done by the gas
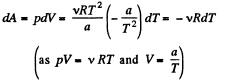
So, 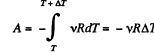
From the Grst law of thermodynamics
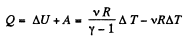
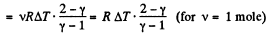
Q19: Demonstrate that the process in which the work performed by an ideal gas is proportional to the corresponding increment of its internal energy is described by the equation pVn = const, where n is a constant.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: According to the problem : A α U or dA = aU (where a is proportionality constant)
or, 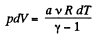 (1)
(1)
From ideal gas law, pV= v R T, on differentiating
p dV + V dp = v RdT (2)
Thus from (1) and (2)
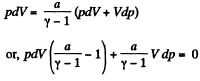
or, 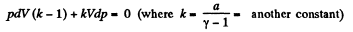
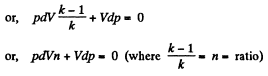
Dividing both the sides by pV
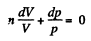
On integrating n In V + In p = In C (where C is constant)
or, 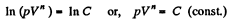
Q20: Find the molar heat capacity of an ideal gas in a polytropic process pVn = const if the adiabatic exponent of the gas is equal to γ. At what values of the polytropic constant n will the heat capacity of the gas be negative?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In the polytropic process work done by the gas
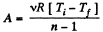
(where Ti and Tf are initial and final temperature of the gas like in adiabatic process)
and 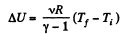
By the first law of thermodynamics Q = ΔU + A
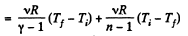
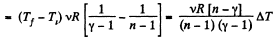
According to definition of molar heat capacity when number of moles v = 1 and ΔT = 1 then Q = Molar heat capacity.
Here, 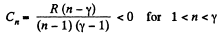
Q21: In a certain polytropic process the volume of argon was increased α = 4.0 times. Simultaneously, the pressure decreased β = 8.0 times. Find the molar heat capacity of argon in this process, assuming the gas to be ideal.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let the process be polytropic according to the law pVn = constant
Thus, 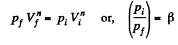
So, 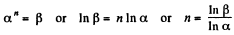
In the polytropic process molar heat capacity is given by
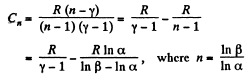
So, 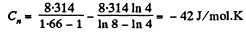
Q22: One mole of argon is expanded polytropically, the polytropic constant being n = 1.50. In the process, the gas temperature changes by ΔT = — 26 K. Find:
(a) the amount of heat obtained by the gas;
(b) the work performed by the gas
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Increment of internal energy for ΔT, becomes
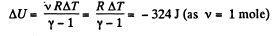
From first law of thermodynamics
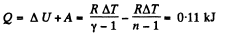
(b) Sought work done, 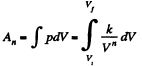
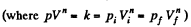
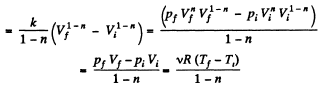
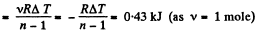
Q23: An ideal gas whose adiabatic exponent equals y is expanded according to the law p = αV , where a is a constant. The initial volume of the gas is equal to V0. As a result of expansion the volume increases η times. Find:
(a) the increment of the internal energy of the gas;
(b) the work performed by the gas;
(c) the molar heat capacity of the gas in the process.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Law of the process is p = α V or pV-1 = α
so the process is polytropic of index n = - 1
As p = αV so, Pi - αV0 and pf = α η V0
(a) Increment of the internal energy is given by
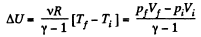
(b) Work done by the gas is given by
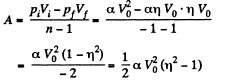
(c) Molar heat capacity is given by
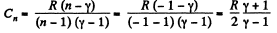
Q24: An ideal gas whose adiabatic exponent equals γ is expanded so that the amount of heat transferred to the gas is equal to the decrease of its internal energy. Find:
(a) the molar heat capacity of the gas in this process;
(b) the equation of the process in the variables T, V;
(c) the work performed by one mole of the gas when its volume increases η times if the initial temperature of the gas is T0.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 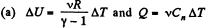
where Cn is the molar heat capacity in the process. It is given that 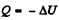
So, 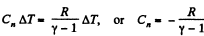
(b) By the first law of thermodynamics, dQ - dU + dA,
or, 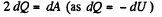
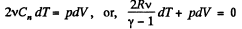
So, 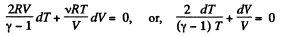
or, 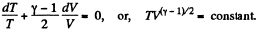
(c) 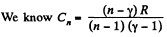
But from part (a), we have 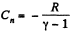
Thus 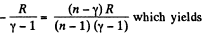
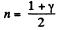
From part (b); we know 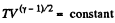
So, 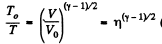 (where T is the final temperature)
(where T is the final temperature)
Work done by the gas for one mole is given by
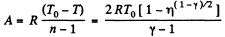
Q25: One mole of an ideal gas whose adiabatic exponent equals y undergoes a process in which the gas pressure relates to the temperature as p = aTα, where a and α are constants. Find:
(a) the work performed by the gas if its temperature gets an increment ΔT;
(b) the molar heat capacity of the gas in this process; at what value of α will the heat capacity be negative?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Given p = a Tα (for one mole of gas)
So, 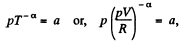
or, 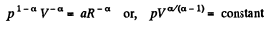
Here polytropic exponent 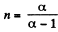
(a) In the poly tropic process for one mole of gas :
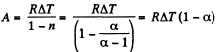
(b) Molar heat capacity is given by
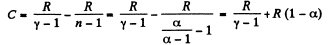
Q26: An ideal gas with the adiabatic exponent γ undergoes a process in which its internal energy relates to the volume as U = aVα, where a and α are constants. Find:
(a) the work performed by the gas and the amount of heat to be transferred to this gas to increase its internal energy by ΔU;
(b) the molar heat capacity of the gas in this process.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
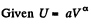
or, 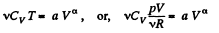
or, 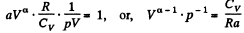
or 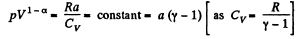
So polytropric index n = 1 - α
(a) Work done by the gas is given by
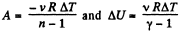
Hence 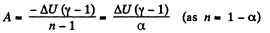
By the first law of thermodynamics, Q = ΔU+A
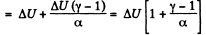
(b) Molar heat capacity is given by
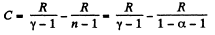
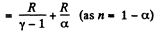
Q27: An ideal gas has a molar heat capacity Cv at constant volume. Find the molar heat capacity of this gas as a function of its volume V, if the gas undergoes the following process:
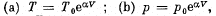
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: By the first law .of thermodynamics
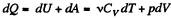
Molar specific heat according to definition
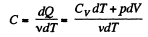
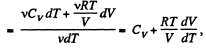
We have 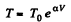
After differentiating, we get 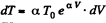
So, 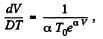
Hence 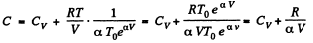
(b) 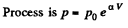
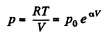
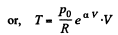
So, 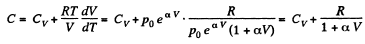
Q28: One mole of an ideal gas whose adiabatic exponent equals γ undergoes a process p = p0 + α /V, w here P0 and α are positive constants. Find:
(a) heat capacity of the gas as a function of its volume;
(b) the internal energy increment of the gas, the work performed by it, and the amount of heat transferred to the gas, if its volume increased from V1 to V2.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Using 2.52
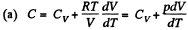 (for one mole of gas)
(for one mole of gas)
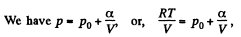
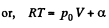
Therefore 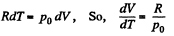
Hence 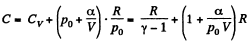
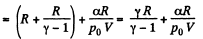
(b) Work done is given by
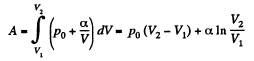
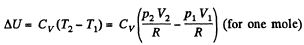
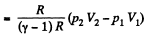
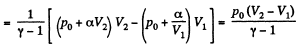
By the first law of thermodynamics Q = ΔU +A
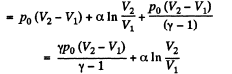
Q29: One mole of an ideal gas with heat capacity at constant pressure Cp undergoes the process T = T0 + αV, where T0 and α are constants. Find:
(a) heat capacity of the gas as a function of its volume;
(b) the amount of heat transferred to the gas, if its volume increased from V1 to V2.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Heat capacity is given by
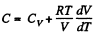 (see solution of 2.52)
(see solution of 2.52)
We have 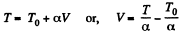
After differentiating, we get, 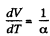
Hence 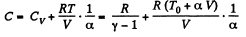
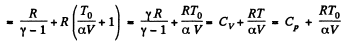
(b) 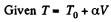
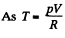 for one mole of gas
for one mole of gas
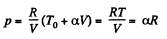
Now 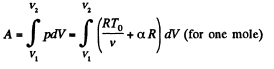
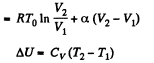
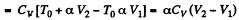
By the first law of thermodynamics Q = ΔU + A
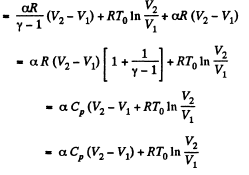
Q30: For the case of an ideal gas find the equation of the process (in the variables T, V) in which the molar heat capacity varies as:
(a) C = Cv + αT; (b) C = Cv + βV; (c) C = Cv + ap, where α, β, and a are constants.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Heat capacity is given by 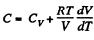
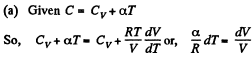
Integrating both sides, we get 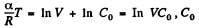 is a constant.
is a constant.
Or, 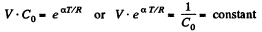
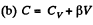
and 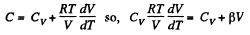
or, 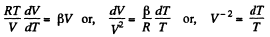
Integrating both sides, we get 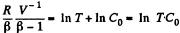
So, 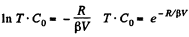
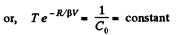
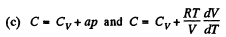
So, 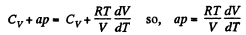
or 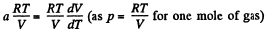
or, 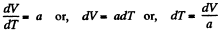
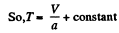 or V - a T = constant
or V - a T = constant
Q31: An ideal gas has an adiabatic exponent γ. In some process its molar heat capacity varies as C = α/T, where α is a constant. Find:
(a) the work performed by one mole of the gas during its heating from the temperature T0 to the temperature η times higher;
(b) the equation of the process in the variables p, V.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) By the first law of thermodynamics A = Q - ΔU
or, 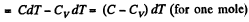
Given 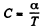
So, 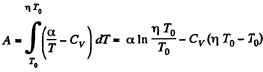
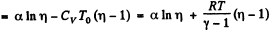
(b) 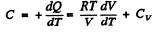
Given 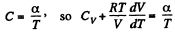
or, 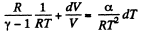
or, 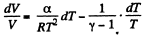
or, 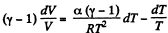
Integrating both sides, we get
or, 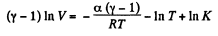
or, 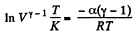
or, 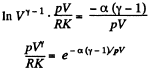
or, 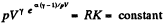
Q32: Find the work performed by one mole of a Van der Waals gas during its isothermal expansion from the volume V1 to V2 at a temperature T.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The work done is
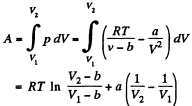
Q33: One mole of oxygen is expanded from a volume V1 = 1.00 1 to V2 = 5.0 l at a constant temperature T = 280 K. Calculate:
(a) the increment of the internal energy of the gas:
(b) the amount of the absorbed heat.
The gas is assumed to be a Van der Waals gas.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The increment in the internal energy is
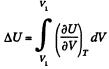
But from second law
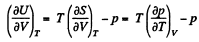
On the other hand 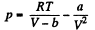
or, 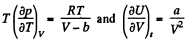
So, 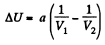
(b) From the first law
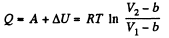
Q34: For a Van der Waals gas find:
(a) the equation of the adiabatic curve in the variables T, V;
(b) the difference of the molar heat capacities Cp, — Cv as a function of T and V.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) From the first law for an adiabatic
dQ = dU + pd V = 0
From the previous problem
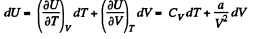
So, 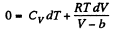
This equation can be integrated if we assume that Cv and b are constant then
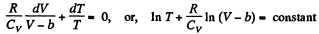
or, 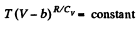
(b) We use
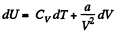
Now, 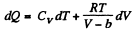
So along constant p, 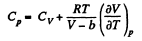
Thus 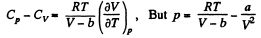
On differentiating, 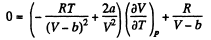
or, 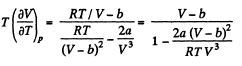
and 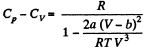
Q35: Two thermally insulated vessels are interconnected by a tube equipped with a valve. One vessel of volume V1 = 10 l contains v = 2.5 moles of carbon dioxide. The other vessel of volume V2 = 100 l is evacuated. The valve having been opened, the gas adiabatically expanded. Assuming the gas to obey the Van der Waals equation, find its temperature change accompanying the expansion.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: From the first law
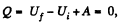 as the vessels are themally insulated.
as the vessels are themally insulated.
As this is free expansion, 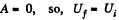
But 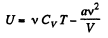
So, 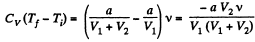
or, 
Substitution gives ΔT = - 3 K
Q36: What amount of heat has to be transferred to v = 3.0 moles of carbon dioxide to keep its temperature constant while it expands into vacuum from the volume V1 = 5.0 l to V2 = 10 l ? The gas is assumed to be a Van der Waals gas.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 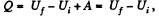 (as A = 0 in free expansion).
(as A = 0 in free expansion).
So at constant temperature.
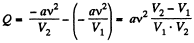
= 0.33 kJ from the given data.
|
122 videos|493 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: The First Law of Thermodynamics, Heat Capacity - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the First Law of Thermodynamics and how does it relate to heat capacity? |  |
| 2. How do we calculate heat capacity and what are its units? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between specific heat capacity and molar heat capacity? |  |
| 4. Why is heat capacity important in thermodynamics and real-world applications? |  |
| 5. How does heat capacity change with temperature and phase changes? |  |





















