Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9 Worksheet Science
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| 1. Common salt is _________. |

|
| Very Short Answer Question |

|
| Short Answer Types Questions |

|
| Crossword Puzzle |

|

Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Kerosene and Petrol are miscible liquids. The difference between their boiling points is more than 25°C. The two liquids can be separated from each other by _____.
(a) Simple distillation
(b) Steam distillation
(c) Fractional distillation
(d) Any of these
Q.2. How can a saturated solution be made unsaturated?
(a) By heating the solution
(b) By cooling the solution
(c) By increasing the amount of solute
(d) By centrifugation of the solution
Q.3. The cause of Brownian movement is:
(a) Heat changes in liquid state
(b) Convection currents
(c) Impact of molecules of dispersion medium on on dispersed phase
(d) Attractive forces between the particles of dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
Q.4. In which of the following, dispersed phase is a liquid and dispersion medium is a gas?
(a) Cloud
(b) Smoke
(c) Gel
(d) Soap bubble
Q.5. At room temperature, a non-metal which is a liquid is:
(a) Sulphur
(a) Bromine
(a) Chlorine
(a) Nitrogen
Fill in the Blanks
1. Common salt is _________.
2. A mixture contains more than ______ substance mixed in ______ proportion.
3. Properties of a __________ are different from its constituent elements, whereas a _______ shows the properties of its constituting elements.
4. A solution is defined as a mixture that is_________
5. We can remove salts from a solution by using the process of _________
6. A pure substance has a fixed__________ or ______ at constant temperature.
7. An element is made up of only one kind of _________.
8. Miscible liquids are separated by ________ .
9. Immiscible liquids are separated by using a _______.
10. Filtered tea is a _________ mixture.
11. Alloy is a _______.
12. Sublimation of camphor is a _________ change.
13. Most common chemical change we observe in our routine life is rusting of______.
Very Short Answer Question
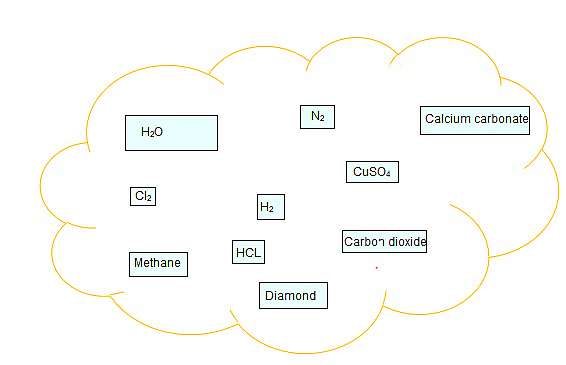
Q.1. Classify the substances given in below figure into elements and compounds
Q.2. Give one example each of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture.
Q.3. Name the apparatus by which mixture of oil and water can be separated.
Q.4. Is brass a mixture or a compound?
Q.5. What type of solution is an alloy? Liquid solution or solid solution
Q.6. A mixture consisting of two miscible liquids 'A' and 'B' whose boiling points differ by 50 C can be separated by which process?
Q.7. Give one example of solid- liquid homogeneous mixture.
Q.8. What is a Aqua regia?
Q.9. Which method is used to separate two immiscible liquids?
Q.10. Name two elements which are in liquid state at room temperature?
Short Answer Types Questions
Q.1. Try segregating the things around you as pure substances or mixtures.
Q.2. What is meant by a substance?
Q.3. What type of mixtures are separated by the technique of crystallisation?
Q.4. What is tyndall effect? Which kinds of solution show it?
Q.5. What is centrifugation? Where it is used?
Q.6. What is crystallization? Where is it used? Why is this better than simple evaporation technique?
Q.7. What is a colloid? What are its various properties?
Q.8. Write a method to separate different gases from air.
Q.9. Explain the following giving examples.
(a) saturated solution
(b) pure substance
(c) colloid
(d) suspension
Q.10. Write the steps you would use for making tea. Use the words solution, solvent, solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate and residue.
 |
Download the notes
Worksheet: Is Matter Around Us Pure
|
Download as PDF |
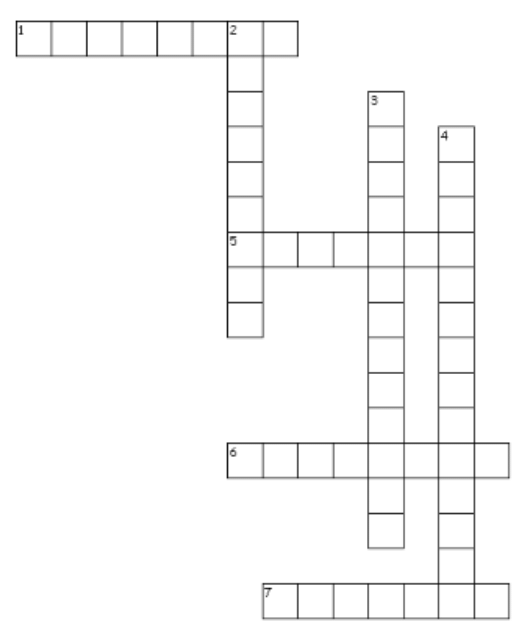
Crossword Puzzle
Across
1. hydrogen ______ is a color gas with a smell of rotten eggs
5. The major components in solution
6. Melting point and boiling point are _______ properties
7. Two elements are liquid at room temperature are mercury and _______
Down
2. In colloids ,The particles are called the ______ phase and the medium in which they are distributed is called the dispersion medium.
3. amount of solute present per unit volume or mass of the solution or solvent
4. denser particles are forced to the bottom and the lighter particles stay at the top when spun rapidly
You can find Worksheets Solutions here: Worksheet Solutions: Is Matter Around Us Pure
|
84 videos|384 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9 Worksheet Science
| 1. What is matter? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between a pure substance and a mixture? |  |
| 3. How can we determine if a substance is pure or impure? |  |
| 4. What is chromatography? |  |
| 5. What are the different methods to separate mixtures? |  |