JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Compounds Containing Nitrogen- 2 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.13. Acetophenone on reaction with hydroxylamine hydrochloride can produce two isomeric oximes. Write structures of the oximes. (1997 - 2 Marks)
Solution.
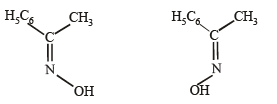
Q.14. Compound A (C8H8O) on treatment with NH2OH. HCl gives B and C. B and C rearrange to give D and E, respectively, on treatment with acid. B, C, D and E are all isomers of molecular formula (C8H9NO). When D is boiled with alcoholic KOH an oil F (C6H7N) separates out. F reacts rapidly with CH3COCI to give back D. On the other hand, E on boiling with alkali followed by acidification gives a white solid G (C7H6O2). Identify A-G. (1999 - 7 Marks)
Ans.
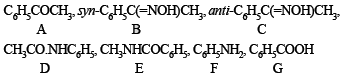
Solution. Summarise the given facts.
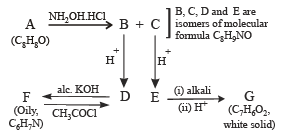
From the above set, following conclusions can be drawn.
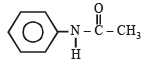
(i) Since the oily compound F (C6H7N) reacts with acetyl chloride, it must have - NH2 or > NH group. Thus (F) can be written as C6H5NH2 or C6H5-NH-H, i.e., it is C6H5NH2 and hence D is C6H5NHCOCH3.
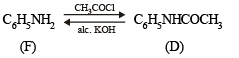
(ii) Compound E on treatment with alkali followed by acidification gives a white solid compound (G), C7H6O2.
Thus (G) seems to be an acid, hence it is C6H5COOH.
(iii) Since (D) and (E) are isomers of the formula C8H9NO, and give C6H5NH2 and C6H5COOH respectively, both should be amides having different alkyl or aryl group.
Thus (D) should be C6H5NHCOCH3, and (E) must be CH3NHCOC6H5.
(iv) Since compounds (D) and (E) are formed by the rearrangement of compounds (B) and (C) respectively.
Compounds (B) and (C) should be oximes > C = NOH (recall that oximes rearrange to amides - Beckmann rearrangement). Further oximes having different alkyl (aryl) groups show geometrical isomerism (syn and anti), compounds (B) and (C) must have following structures.
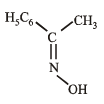
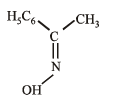
Recall that Beckmann rearrangement involves migration of anti -alkyl or aryl group, i.e.,
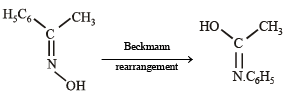
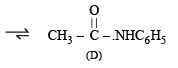
Since (D) is formed from (B), and (E) from (C), (B) and (C) should have following structures.
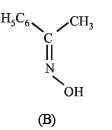
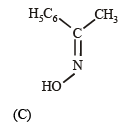
(v) Lastly, oximes (B) and (C) are formed from (A), the latter should be a ketone of the formula C6H5COCH3,
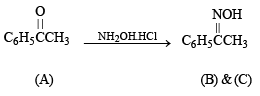
Q.15. Complete the following reaction with appropriate reagents : (1999 - 4 Marks)
Solution.
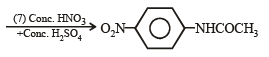
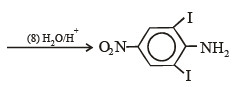
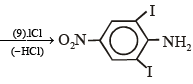 |
|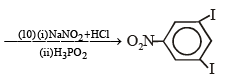
Q.16. Explain briefly the formation of the products giving the structures of the intermediates. (1999 - 2 Marks)
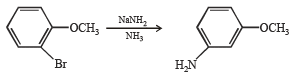
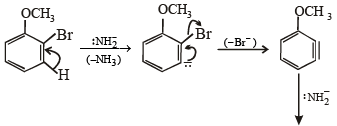
Solution. The reaction proceeds via benzyne formation

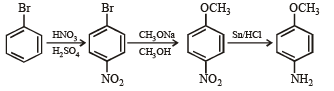
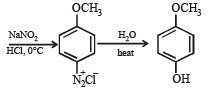
Q.17. How would you synthesise 4–methoxyphenol from bromobenzene in NOT more than five steps? State clearly the reagents used in each step and show the structures of the intermediate compounds in your synthetic scheme. (2001 - 5 Marks)
Solution.
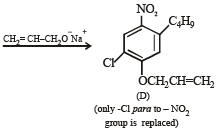
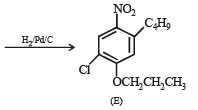
Q.18. Write structures of the products A, B, C, D and E in the following scheme. (2002 - 5 Marks)
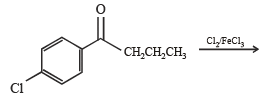
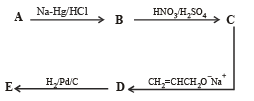
Solution.
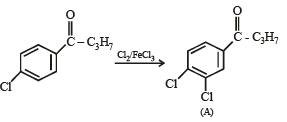
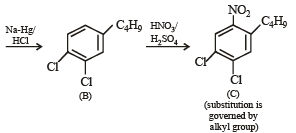
Q.19. There is a solution of p–hydroxybenzoic acid and p-aminobenzoic acid. Discuss one method by which we can separate them and also write down the confirmatory tests of the functional groups present. (2003 - 4 Marks).
Solution.
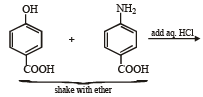
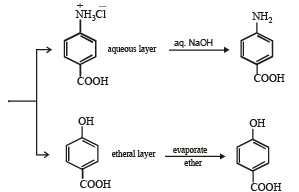
Test of phenolic group :
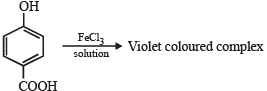
Test of 1° amino group :
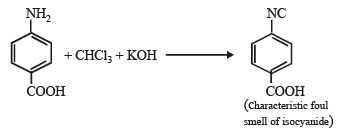
Test of – COOH group :
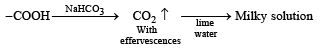
Q.20. Identify (A) to (D) in the following series of reactions. (2004 - 4 Marks)
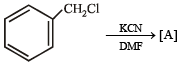
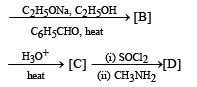
Solution.
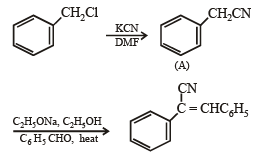
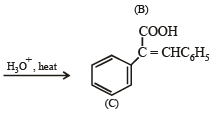

Q.21. 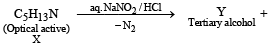 Some other products (2005 - 4 Marks)
Some other products (2005 - 4 Marks)
(i) Identify (X) and (Y)
(ii) Is (Y) optically active?
(iii) Give structure(s) of intermediate(s), if any, in the formation of (Y) from (X).
Ans. 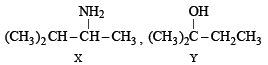
Solution.
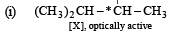
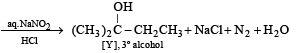
(ii) [Y], a 3° alcohol is optically inactive.
(iii) Formation of [Y] from [X].
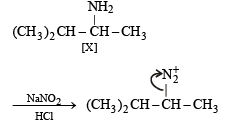
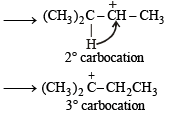
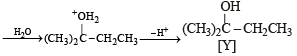
|
481 docs|964 tests
|
















