UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC > Japanese Encephalitis-Etiology
Japanese Encephalitis-Etiology | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| JE-Clinical presentation |

|
| JE-Diagnosis |

|
| JE-Control |

|
| JE-Prognosis |

|
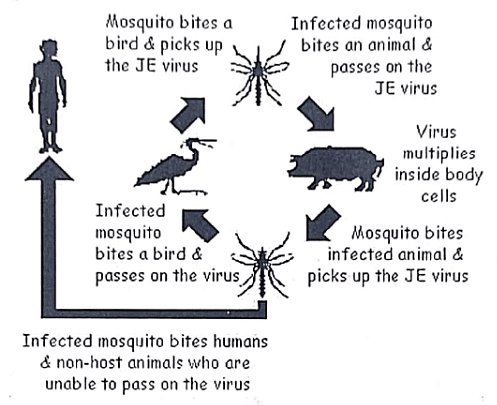
JE-Clinical presentation
- Japanese Encephalitis (JE) Clinical Presentation: The disease progresses through three phases:
- Prodromal Phase: Occurs before the involvement of the nervous system.
- Acute Encephalitic Phase: Involves acute inflammation of the brain.
- Recovery Phase: Marked by either complete or partial recovery from neurological deficits.
- Suspected JE Case: A person of any age, at any time of the year, displaying an abrupt onset of fever and a change in mental status (such as confusion, disorientation, coma, or inability to talk), and/or experiencing new-onset seizures (excluding simple febrile seizures).
- JE Vaccination:
- The Japanese Encephalitis vaccine (SA 14-14-2 Vaccine) is administered in selected endemic districts.
- The vaccine is given subcutaneously, with a dosage of 0.5 ml in the left upper arm.
- Vaccination is conducted after a campaign, typically at 16-24 months of age, in conjunction with DPT/OPV booster shots.
Question for Japanese Encephalitis-EtiologyTry yourself: In which phase of Japanese Encephalitis does acute inflammation of the brain occur?View Solution
JE-Diagnosis
- In individuals with Japanese Encephalitis (JE) virus IgM antibodies, it is advisable to conduct confirmatory neutralizing antibody testing. In the United States, this confirmatory testing is exclusively available at the CDC and a few specialized reference laboratories.
- In fatal cases, the utilization of nucleic acid amplification and virus culture on autopsy tissues can provide valuable information.
- The presence of viral antigen in tissues can be demonstrated through Indirect Fluorescent Antibody Testing.
- In cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis, there is an elevated opening pressure, high levels of CSF pressure, and normal CSF glucose.
- Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) typically reveals bilateral thalamic lesions with hemorrhage in fatal cases.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG) findings commonly show diffuse slowing of brain activity.
Question for Japanese Encephalitis-EtiologyTry yourself: What is a common finding in the electroencephalogram (EEG) of individuals with Japanese Encephalitis (JE)?View Solution
JE-Control
Treatment of Japanese Encephalitis (JE)
- No Specific Treatment: There is no targeted or specific treatment for Japanese encephalitis; supportive care is the main approach.
- Ineffectiveness of Antibiotics: Antibiotics do not exhibit effectiveness against the JE virus.
- Supportive Therapy for Symptomatic Cases:
- Symptomatic JEV infection is managed through supportive therapy.
- Patients often require assistance with feeding, airway management, and anticonvulsants for seizure control.
- Mannitol may be employed to reduce intracranial pressure when necessary.
Control Measures
- Focus on Mosquito Vector: Control measures primarily target the mosquito vector.
- Use of ULV Insecticides: Ultra low volume (ULV) insecticides, such as malathion and fenitrothion, are effectively utilized through aerial or ground fogging.
Vaccination for Japanese Encephalitis
- JE Vaccine Administration:
- The PHK cell-cultured, live-attenuated Japanese Encephalitis vaccine (SA 14-14-2 Vaccine) is given in selected endemic districts.
- Administered subcutaneously in the left upper arm, typically after a campaign, at 16-24 months of age, along with DPT/OPV booster shots.
- Limitations in Adult Vaccination: JE vaccine is not recommended for routine use in adults.
Question for Japanese Encephalitis-EtiologyTry yourself: What is the main approach for the treatment of Japanese encephalitis?View Solution
JE-Prognosis
- Favorable Prognostic Indicators: A positive prognostic factor is the presence of a high concentration of neutralizing antibodies in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- Unfavorable Prognostic Indicators:
- Negative prognostic factors include a low Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS).
- Additionally, hyponatremia and being under the age of 10 years are associated with a poorer prognosis.
The document Japanese Encephalitis-Etiology | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Japanese Encephalitis-Etiology - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the clinical presentations of Japanese Encephalitis? |  |
Ans. The clinical presentations of Japanese Encephalitis include fever, headache, neck stiffness, disorientation, seizures, paralysis, and coma.
| 2. How is Japanese Encephalitis diagnosed? |  |
Ans. Japanese Encephalitis is diagnosed through laboratory tests, such as testing cerebrospinal fluid or blood for the presence of antibodies against the virus.
| 3. What measures can be taken to control Japanese Encephalitis? |  |
Ans. Control measures for Japanese Encephalitis include vaccination programs, mosquito control through insecticide spraying and bed nets, and public awareness campaigns to promote personal protection against mosquito bites.
| 4. What is the prognosis of Japanese Encephalitis? |  |
Ans. The prognosis of Japanese Encephalitis varies depending on the severity of the disease and the age of the patient. While some cases can be mild with complete recovery, others can result in long-term neurological complications or death.
| 5. What is the etiology of Japanese Encephalitis? |  |
Ans. Japanese Encephalitis is caused by the Japanese Encephalitis virus (JEV), which is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes, primarily the Culex species.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















