Karl Marx: Historical Materialism | Sociology Optional for UPSC (Notes) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Karl Marx (1818 - 1883) |

|
| Historical Materialism |

|
| Relations of Production: Types According to Marx |

|
| Criticisms of Marx's Materialistic Conception of History |

|
Karl Marx (1818 - 1883)
A Biographical Sketch

- Karl Marx was one of the early pioneers of the discipline of Sociology. He laid the foundation of conflict perspective in Sociology, which was radically different from the then prevailing structural -functionalist view. Although conflict theories came under severe criticism during the 19th Century because of their radical nature, his contribution to Sociology in terms of theories, concepts, methods and perspectives is unmatched as he provided an alternative narrative which has endured the test of times even today.
- He wrote in a background when industrialization and capitalism were in full swing and Europe was witnessing post-French revolution changes. Changes in Europe were too profound and social environment was in a huge flux. It prompted Marx to give a thought about the misery and suffering of the people whom he saw as victims of the new economic order called capitalism. Inequality among the social classes prompted Marx to put forward a theory about the current state in capitalism and its origin in history.
Historical Materialism
- Historical Materialism or the Materialistic Conception of History is the pivot to all the works of Marx. Its clearest exposition is done in his Contribution to the Critique of Political Economy, 1859. It is a conception of society in terms of evolutions from one stage to another, which Marx refers to as modes of production, and material or economic factors have a pivotal role in historical change. It is an inquiry into nature of relations between man and man and man and things, as history proceeds.
- His theory is called historical because analysis of society is in terms of evolution from one state to another, as the time passes and history is made. According to Marx, History is a process of man’s self creation. Since mans involvement into relations of production creates history, it is necessary to understand history to understand society. It is called materialistic for two reasons, firstly, his conception of society is based upon materialistic and not metaphysical factors which are understood in terms of material production, Secondly, understanding of change is based upon changing material conditions and not ideas.
Further, his theory of historical materialism has two aspects :
- Materialistic conception of society is based on economic infrastructure and social superstructure.
- Marx uses these concepts to understand the modes of production in society.
- He views historical evolution as a dialectic process involving opposing forces.
- This interaction leads to the creation of new structures and the continuation of the dialectic process.
- Marx adopted Historical Materialism from Hegelian Dialectical Idealism.
- He criticized Hegel's idealism for its conservative political orientation.
- Marx found Feuerbach’s materialism more relevant to his theories.
- According to Marx, material sources and conditions are crucial in the modes of production.
- The material world exists independently of human thought.
- Political economists like Adam Smith and David Ricardo influenced Marx's views.
- They posited that labour is the source of all wealth.
- Marx recognized the horrors of capitalism and the exploitation of workers.
- He believed these evils were not inevitable and saw a solution in communism.
- Marx stated, "In order to survive, man must produce."
- Production is essential for human survival and is a fundamental aspect of history.
- Throughout history, production has been a constant human activity.
- In the process of production, man forms relationships with others.
- These relationships are fundamental to history.
- Humans produce to satisfy their ever-growing needs.
- Marx described man as a "perpetually dissatisfied animal."
- Once needs are satisfied, new ones arise, prompting continued production.
- To produce, man requires relations with others and various forces of production.
- These forces include tools, techniques, and skills.
Praxis
It literally means practical as against mere theory. David Harvey defines it as practical reflective activity. Critical theorists often argue for the use of praxis against theory in search of practical solutions to social problems. This concept in Sociology was initially put forward by Marx and it has two closely related meanings. First, it suggests action as opposed to philosophical speculation (it, thus, forms the basis of dialectic materialism). Secondly, it implies that the fundamental characteristic of human society is material production against idealism - to meet the basic needs. Man primarily acts on the natural world, i.e., he works and only secondarily thinks about it. In terms of Marx idea of social change, it also implies that it is not enough to understand the world. We must also try to improve it by real actions.
Relations of Production: Types According to Marx
According to Marx, the relations of production, also known as social relations of production, can be categorized into two main types within any mode of production:- Relations between man and man pertain to the associations formed for production.
- These associations lead to stratification and the formation of classes based on positions in the production process.
- There are broadly two classes: the haves who own production and earn profits, and the have nots who lack control over their labor.
- The have nots must sell their labor for wages in an industrial society.
- The nature of these relations is characterized by antagonistic cooperation, where opposing interests lead to collaboration in production.
- According to Marx, the have nots are in a disadvantaged position and are forced to accept this state.
- This situation accentuates the essential contradiction between the interests of the two classes.
- Relations between man and things involve ownership and non-ownership of resources needed for production.
- The haves control the production process, while the have nots are non-owners and only possess their labor.
- In an industrial society, man is free to sell his labor.
- Ownership and non-ownership relations exist across different modes of production.
- According to Marx, these relations are dynamic and characterized by increasing antagonism.
- This antagonism leads to conflict between the two classes.
- In a capitalist society, Marx predicts a level of exploitation where man loses control over his own labor.
- Marx asserts that social relationships determine man's existence, not his own will.
- He states, "It is not the consciousness of men that determines their being, but rather their social being determines their consciousness."
- Men do not choose their social relations; rather, these relations dictate who they will be—ruled or ruler.
- Material conditions shape the mental conditions of individuals.
- Forces of Production, according to Marx, include both men and things.
- Men are categorized into haves and have nots.
- Things encompass tools, techniques, equipment, and skills.
- Major societal changes occur when new forces of production arise, leading to new relations of production.
- A contradiction between older and newer forces is resolved through the replacement of the older mode of production.
- In every society, there is a centrality of one major element, such as land in feudal society or capital in capitalist society.
- The forces of production transform natural resources into marketable goods.
- This process represents man's control over nature.
- Historically, man's control over nature has been increasing.
- Consequently, there is a constant struggle between man and nature.
- Both the forces and relations of production change continuously, forming the economic base or infrastructure of society.
- This interplay results in a particular type of social formation or mode of production.
- Marx viewed society systemically, emphasizing that production is central to understanding societal dynamics.
- The forces and relations of production continuously interplay and influence one another.
According to his systemic view, society or mode of production consists of two parts:
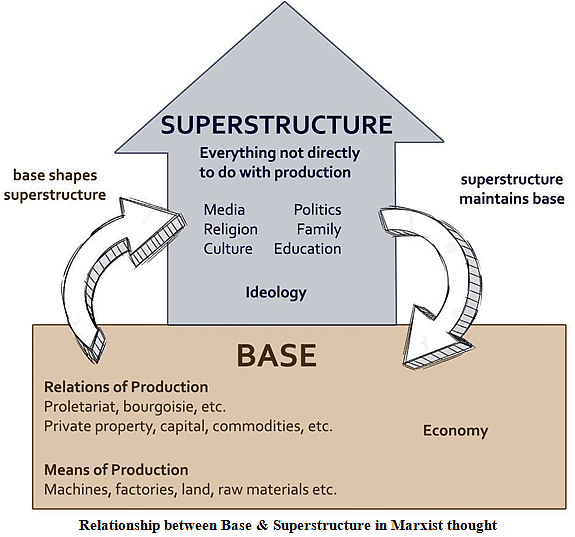
- Economic Base: It includes forces and relations, i.e., men and things being involved in production include classes, tools, techniques, etc. It represents the centrality of material or economic factors in shaping the whole mode of production.
- Social Superstructure: It includes all other aspects of society like-culture, law, state, family, religion and education and it is largely shaped by economic infrastructure. As economic infrastructure changes, social superstructure also changes.

- Economic infrastructure shapes social superstructure which in turns helps in the functioning of economic infrastructure. Thus, nature of forces and relations of production will result in similar superstructure and consequently, a typical organisation of society will emerge which is called as mode of production.
- A major contradiction in any production activity is that there is a conflict between forces and relations of production. There is a conflict of interest between the various social groups in the relations of production as forces of production are unequally controlled by such groups. For example, in capitalist production, forces of production include collective production by a large number of workers, yet they are privately controlled by the capitalists. Contradiction is that while production is collective or social in nature, control over forces is private as a handful of capitalists have the actual control over these forces. Further, the fruit of these forces is also appropriated unequally by the capitalists.
Criticisms of Marx's Materialistic Conception of History
Marx's materialistic conception of history has faced several criticisms:
- Reductionism and Economic Primacy: Critics argue that Marx's focus on material factors is overly reductionist. They contend that he downplays the significance of non-economic factors by reducing everything to economic considerations. Karl Popper even labeled this as "economic reductionism," accusing Marx of neglecting the role of ideas.
- Emphasis on Conflict: Marx is criticized for placing too much emphasis on conflict while overlooking the aspect of social order. Sociologist Georg Simmel pointed out that conflict itself can serve important functions within society.
- Sources of Conflict: While Marx attributes conflict primarily to relations within the economic infrastructure, sociologist Ralf Dahrendorf argues that differential authority structures are the fundamental cause of conflict.
- Macro vs. Micro Perspectives: Marx's approach is seen as predominantly macro-evolutionary, focusing on broad historical trends. Critics from the non-positivist tradition, however, emphasize the importance of micro-level realities in social life, which Marx tends to overlook.
|
122 videos|252 docs
|
FAQs on Karl Marx: Historical Materialism - Sociology Optional for UPSC (Notes)
| 1. What is historical materialism according to Karl Marx? |  |
| 2. How does historical materialism relate to class struggle? |  |
| 3. What are the key stages of historical development according to Marx's theory? |  |
| 4. How does historical materialism explain social change? |  |
| 5. What is the relevance of historical materialism in contemporary society? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|