Class 10 Geography Key Concepts - Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy
| Table of contents |

|
| Minerals |

|
| Types of Minerals |

|
| Distribution of Minerals |

|
| Conservation of Minerals |

|
| Energy Resources |

|
Minerals
These are homogeneous naturally occurring substances normally found in solid, liquid and gaseous state.
Minerals are typically solid, inorganic, have a crystal structure and are formed by geological processes naturally. A mineral may consist of a single chemical element or a compound more usually.
Types of Minerals
Metallic and non-metallic.
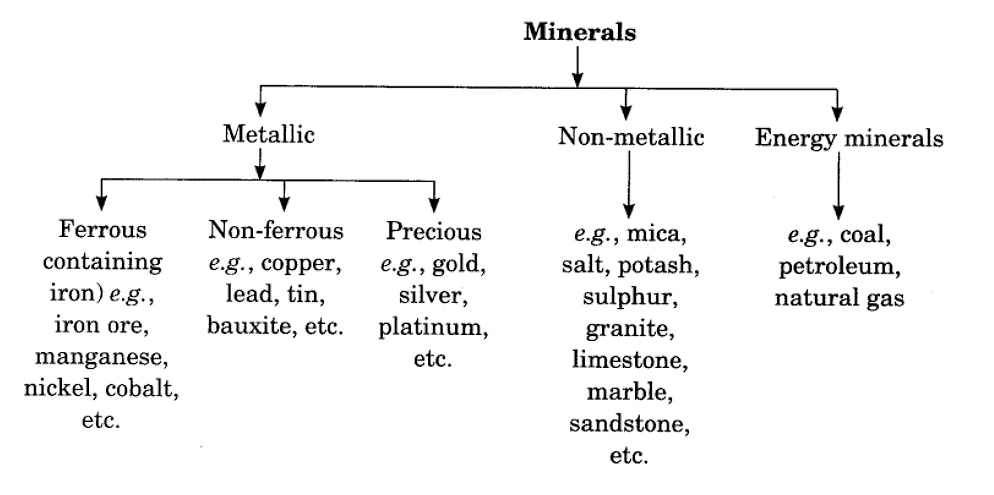 Metallic Minerals : further sub-divided into ferrous and non-ferrous-
Metallic Minerals : further sub-divided into ferrous and non-ferrous-
(i) Ferrous (containing iron) are iron ore, manganese ore, chromite, pyrite, nickel and cobalt.
(ii) Non-ferrous (containing metals other than iron) — gold, silver, copper, lead, bauxite, tin and magnesium.
Non-metallic Minerals : They are limestone, nitrate, potash, mica, gypsum, coal, petroleum.
Distribution of Minerals
- Iron Ore : Basic mineral, backbone of industrial development. There are four varieties of iron ore (a) Limonite (contains 40% to 60% iron)
(b)Hematite (contains 60% to 70% iron) – Most important industrial iron ore.
(c) Magnetite (contains 70% iron) — Finest quality, with magnetic properties.
(d) Siderite (contains 40% to 50% iron)
Magnetite and Haematite:
These are found in Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Orissa, Karnataka and Maharashtra.
Well-known iron ore mines:
Durgs and Bastar districts of Chhattisgarh, Paschimi and Purbi Singhbhum districts of Jharkhand, Sundargarh, Keonjhar and Mayurbhanj districts of Orissa,North Goa, Chikmagalur and Bellary districts of Karnataka, Ratnagiri of Maharashtra. - Manganese Ore :
(a) Use : Manganese ore is used for making iron and steel and preparing alloys. It is used to manufacture bleaching powder, insecticides, paints and batteries.
(b) Reserves : The main reserves of manganese ore are found in Karnataka, Orissa, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Jharkhand, Maharashtra and Goa. 97% of India’s manganese ore is mined in the states of Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. - Copper :
Use — Copper is used for making utensils, electric wires and alloys .
Distribution — 90% of the copper reserves are concentrated in Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Jharkhand, Gujarat, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. - Bauxite :
It is an ore from which aluminium is obtained. Aluminium is used in manufacturing of aeroplanes, utensils and other household goods.
(a)Distribution : Jharkhand, Orissa, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh
(b) Tamil Nadu: Orissa is the largest producer (45%) Panchpatmali deposits in Koraput, Orissa and Amarkantak, Maikal hills, Bilaspur-Katni plateau regions are important. - Mica :
(a) Use — It is used in electrical and electronic industries.
(b) Distribution — Jharkhand, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan. - Limestone:
Composed of calcium carbonate or calcium and magnesium carbonates.
(a) Use — Limestone is used in the cement industry, smelting of iron and in chemical industries.
(b) Distribution — Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Karnataka and Himachal Pradesh
Conservation of Minerals

They are non-renewable — should be conserved.
- Wastage in the process of mining and processing has to be reduced to the minimum.
- Export of minerals should be minimised.
- Substitutes should be used in order to save minerals.
Energy Resources
The sources of energy are — Coal, Petroleum, Natural Gas, Solar Energy, Wind Energy, Hydel Energy. Conventional Energy — Coal, petroleum, natural gas and electricity.
Non-Conventional Energy — Solar, wind, tidal, geothermal, atomic energy and biogas.
Commercial Sources of Energy — Coal, petroleum, natural gas, hydroelectricity and nuclear energy.
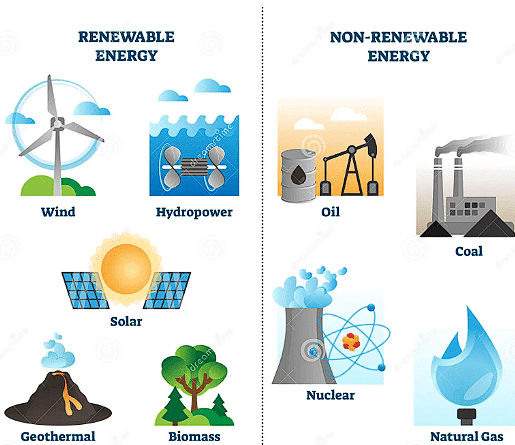
Non-Commercial Sources of Energy — Firewood, charcoal, cow dung and agricultural wastes.
- Coal
(a) Use — Coal is the main source of power generation in India. 67% of the country’s requirements of power is met by coal. It is used in the manufacture of iron and steel. It is also used as a raw material for the chemical industry.
(b) Four Types of Coal — Anthracite, bituminous, lignite and peat. - Petroleum : Second most important energy source, raw materials for a number of industries.
(a) Distribution : 63% of crude petroleum is produced from Mumbai High, 18% from Gujarat and 16% from Assam.
(b) Small quantity of oil is also produced in Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Arunachal Pradesh.
(c) Important offshore oilfields — Mumbai High, Bassein and Aliabet.
(d) Important oilfields in Gujarat — Ankleshwar, Lunej, Kalol.
(e) Oil Refineries — Trombay, Koyali, Lunej and Kalol.
(f) Important oilfields in Assam — Digboi, Naharkatiya, Moran, Hygrijan. Oil from these fields is refined at Digboi, Guwahati, Bongaigaon in Assam and Barauni in Bihar. - Natural Gas : Environment friendly fuel, raw material in petrochemical industry.
(a) Distribution — Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Assam and Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Krishna-Godavari Basin.
(b) Over 3/4th of the production comes from Mumbai High, 10% form Gujarat, 7% from Assam and the rest from Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Tripura and Rajasthan. - Electricity :
(a) Installed Capacity of India — 137500 MW. Per capita consumption of electricity — 379 kwh.
(b) Thermal Electricity : It is obtained by using coal, petroleum and natural gas.
(c) Distribution : Assam, Jharkhand, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal.
(d) Other Significant Producers: Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Karnataka, Orissa and Delhi.
(e) Hydroelectricity : It is produced from water released at a great force from a high head.
(f) Distribution: Important hydel power-producing states are Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Orissa, and Punjab.
(g) Nuclear Electricity : It is produced from uranium and thorium.
There are seven nuclear power stations in the country.
They are located at — Tarapur (Maharashtra), Kalpakkam (Tamil Nadu), Rawatbhata (Rajasthan), Narora (Uttar Pradesh), Kakrapara (Gujarat), Kaiga (Karnataka).
- Non-Conventional Sources of Energy : The potential of non-conventional sources of energy is large. They use renewable resources for energy generation.
(a) Solar Energy — Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight directly into electricity.
(b) Use — Solar energy is used for cooking, pumping, heating of water, refrigerator and street lighting.
(c) Biggest Solar Power House of India : Thar desert.
(d) Largest Solar Plant of India : Madhapur near Bhuj.
(e) Wind Energy — India has a wind power potential of 20,000 MW.
(f) Distribution — Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Kerala, Maharashtra and Lakshadweep.
(g) Largest Wind Farm Cluster — It is of 150 MW and located in Tamil Nadu. Gujarat is very favourable for wind farm.
(h) Biogas — Shrubs, farm wastes, animal and human wastes are used to produce biogas for domestic consumption in the rural areas.
(i) Improved Chulhas — The chulhas used in the rural areas use wood and cow dung which emits smoke. The improved chulhas do not emit smoke and use less wood.
(j) Other Non-Conventional Sources : include geo-thermal energy, tidal energy and wave energy.
- Conservation of Energy Resources :
In order to conserve energy, we must —
(a) Use the public transport system more frequently.
(b) Switch off electricity whenever not required.
(c) Use power-saving devices.
(d) Check the power equipments regularly.
(e) Use non-conventional sources of energy more frequently.
|
95 videos|815 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Geography Key Concepts - Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy
| 1. What are minerals? |  |
| 2. What are energy resources? |  |
| 3. How are minerals and energy resources important for human life? |  |
| 4. What are the effects of overexploitation of minerals and energy resources? |  |
| 5. What are the measures that can be taken to conserve minerals and energy resources? |  |





















