Kidney: Clinical Anatomy | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Kidney - Gross Anatomy |

|
| Kidney - Relations |

|
| Kidney - Arterial Supply/Vascular Segments |

|
| Nephron |

|
Kidney - Gross Anatomy
The kidney, characterized by its bean-shaped structure, exhibits distinct features, including upper and lower poles, medial and lateral borders, and anterior and posterior surfaces.
With regard to the two poles, the upper one is broad and closely associated with the corresponding suprarenal gland, while the lower pole is pointed. Regarding the two surfaces, the anterior surface is noted for its irregularity, while the posterior surface is flat.
The kidney also possesses two borders, with the lateral border being convex and the medial border concave. The hilum, found in the middle part of the medial border, contains the renal vein, renal artery, and renal pelvis in anterior to posterior order.
From a locational perspective:
(a) Kidneys are retroperitoneal organs, partially covered by peritoneum anteriorly.
(b) They occupy the epigastric, hypochondriac, lumbar, and umbilical regions.
(c) Vertically, their extension ranges from the upper border of the twelfth thoracic vertebra to the center of the body of the third lumbar vertebra.
(d) The right kidney is slightly lower than the left, and the left kidney is somewhat closer to the median plane than the right.
(e) The long axis of the kidney points downward and laterally, positioning the upper poles nearer to the median plane than the lower poles.
Kidney - Relations

Relations Common to the Two Kidneys
Each kidney's upper pole is associated with the corresponding suprarenal gland, while the lower poles are positioned approximately 2.5 cm above the iliac crests.
The medial border of each kidney shares connections with:
(a) The suprarenal gland above the hilus.
(b) The ureter below the hilus.Regarding posterior relationships, the posterior surfaces of both kidneys are connected to:
(a) The diaphragm.
(b) The medial and lateral arcuate ligaments.
(c) The psoas major.
(d) The quadratus lumborum.
(e) The transversus abdominis.
(f) The subcostal vessels.
(g) The subcostal, iliohypogastric, and ilioinguinal nerves.
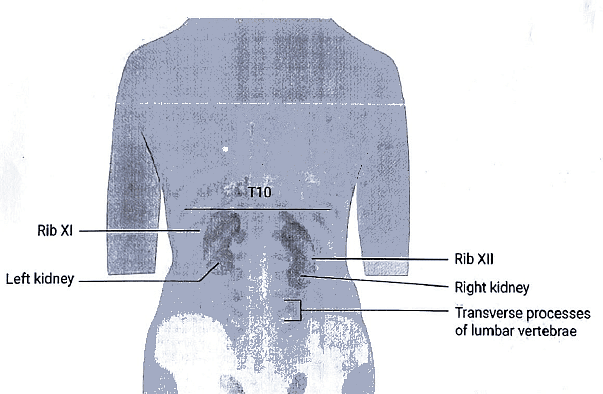
Furthermore, the right kidney has a relationship with the twelfth rib, while the left kidney is associated with the eleventh and twelfth ribs.

Kidney - Arterial Supply/Vascular Segments
Typically, there exists a single renal artery on each side, originating from the abdominal aorta. Near or at the hilus, the renal artery bifurcates into anterior and posterior divisions. Subsequent branching of these divisions leads to the formation of segmental arteries, each responsible for supplying a distinct vascular segment. Five such segments are identified: (1) Apical, (2) Upper, (3) Middle, (4) Lower, and (5) Posterior.




Nephron


- Surgical exposure of the kidney: Caution is warranted to avoid inadvertent opening of the pleural cavity.
- Renal angle
- Pyelonephritis: The infection is hindered from spreading to the opposite kidney by the presence of a fascial septum and midline attachment of the renal fascia.
- Renal stones - Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): This non-invasive approach involves directing shockwaves from outside the body onto urinary tract stones for effective treatment.


Clinical Anatomy - Repeats
- Describe in short the normal and anomalous development of urinary bladder (2007).
- Describe microscopic anatomy and fine structure of NEPHRON. Add a note on its applied anatomy (2004).
- Describe the gross anatomical features and relations of kidney. Explain its arterial supply and vascular segments. Add a note on the development of kidney. (2010)
- Describe the morphological features of kidney. Add a note on relations of right kidney. (2013)
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Kidney: Clinical Anatomy - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the gross anatomy of the kidney? |  |
| 2. What are the relations of the kidney? |  |
| 3. How is the kidney supplied with blood? |  |
| 4. What are the vascular segments of the kidney? |  |
| 5. How does the kidney function within the nephron? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















