Kingdom Monera- 2 | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Archaebacteria |

|
| Eubacteria |

|
| Rickettsia |

|
| Chlamydia |

|
| Myxobacteria |

|
Archaebacteria
"Group of ancient bacteria"
- They are primitive organisms. They were the first to be born on our planet and they are present even today with their primitive characters. They are the"Oldest living fossils".
- They are different from eubacteria in many ways.
 Archaebacteria
Archaebacteria - All archaebacteria are obligate anaerobes.
- Thermococcus, Methanococcus and Methanobacterium exemplify archaebacteria that contain proteins homologous to eukaryotic core histones.
- Their cell wall is not made up of peptidoglycan like that of eubacteria. Their cell wall is made up of complex polysaccharides and polypeptide.
- Their cell membrane is not a unit membrane, while in eubacteria, the cell membrane is a unit membrane.
 Eubacteria
Eubacteria
 View Answer
View AnswerNote: Cell membrane of archaebacteria is composed of a single layer of branched chain molecules of lipids while the lipids present in the cell membrane of eubacteria are straight chain molecules. Due to the branched chain structure, archaebacteria are more resistant to extreme environmental conditions as compared to eubacteria. i.e. Archaebacteria are not affected by high temperature, high salinity, radiations and change in pH. So, that is why Archaebacteria are found in highly unfavourable habitats.
- In archaebacteria sequence of nucleotide in 16S – r RNA is different from other prokaryotes.
➢ Archaebacteria include the following Bacteria
1. Methanogens
"Methane producing bacteria"
- These bacteria convert CO2 of swampy areas (Marshy) into methane (CH4).
Example: Methanobacterium, Methanococcus, Methanomicrobium - These bacteria convert the organic substance (cellulose) present in cow dung into methane by fermentation (Gobar gas fermenter).
Example: Methanobacterium, Methanococcus, Methanomicrobium - An archaebacterium is found in cattle's rumen, where it digests the cellulose by fermentation and converts it into methane.
Example: Ruminococcus
 Ruminococcus
Ruminococcus
2. Halophiles
- These archaebacteria are found in highly saline areas.
Example: Halobacterium Halophiles- Halobacterium
Halophiles- Halobacterium - Halococcus Halophiles are surrounded by a purple membrane. This membrane absorbs the bright light and directly forms ATP i.e. they cannot prepare food (carbohydrates) like eubacteria. Instead, they directly produce ATP.
- Therefore, Halophiles are non-photosynthetic.
3. Thermo Acidophiles
- These archaebacteria are found at places where the temperature is approx 80°C and the medium is acidic [pH = 2].
- They are found in hot sulphur springs. These can also survive at 100°C temperature.
- They oxidise sulphur to H2SO4 and obtain energy. This is used to prepare food. Due to the conversion of sulphur to H2SO4, the medium (water) becomes acidic in nature.
- These are chemoautotrophs.
- Hot water sulphur springs are found in the Himalayan region.
- Exceptionally these archaebacteria are facultative aerobes.
Example: Thermus, Sulpholobus, Thermoplasma
Eubacteria
- Eubacteria are also known as “true bacteria”.
- The cell wall is rigid and made up of peptidoglycans.
- It moves with the help of flagella.
- A few bacteria contain short appendages on the cell surface, known as pili which help the bacteria during sexual reproduction. Pili also helps a pathogen to attach to the host.
- They are divided into two categories; gram-positive and gram-negative, depending upon the nature of the cell wall and the stain they take.
- Rhizobium and Clostridium are two eubacteria.
Rickettsia
- They are also called as bacteria because they are similar to eubacteria in structure.
- These are intracellular endoparasite.
- These are non-motile.
 Rickettsia
Rickettsia
- Diseases caused by rickettsia in humans:
(i) Typhus fever: Rickettsia prowazekii
(ii) Rocky Mountain spotted fever: R. rickettsii
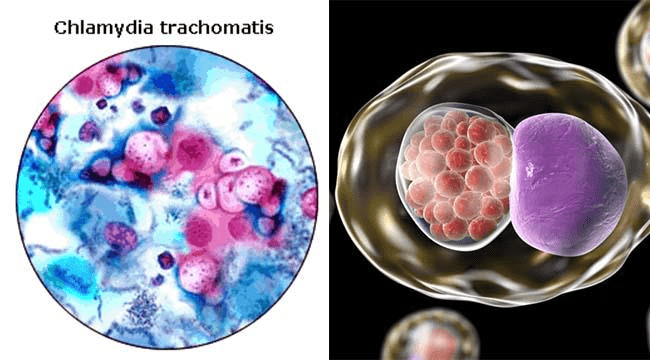
Chlamydia
- The chlamydiae are a group of microbes classified as a type of rickettsiae. They also have the characteristics of rickettsiae, like very small in size, having both DNA & RNA and a number of enzymes.
- They can be treated with some antibiotics.
- They are obligate intracellular energy parasites of animals. They form the elementary body, initial body or reticulate body, during their reproductive cycle. They divide by binary fission.
Example: Chlamydia trachomatis, C.psittaci
Disease caused by chlamydia are:
(i) Trachoma (eye disease)
(ii) Non-gonococcal urethritis (reproductive system disease)
(iii) Chlamydial ophthalmia
Myxobacteria
- They are gram –ve coccus like or rod-shaped bacteria, having mucilage on their cell wall, so they form slimy colonies and are usually called as swarm stage or pseudoplasmodium.
- They multiply by transverse binary fission and form non-motile fruiting bodies called cysts or microcysts or myxospores.
 Myxobacteria
Myxobacteria
- They do not form flagella, pili and endospores. They are bacteriolytic and cellulolytic.
- Some myxobacteria show gliding movement.
Example: Myxococcus, Cystobacter, Flexibacter, Stigmatella
|
26 videos|287 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Kingdom Monera- 2 - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What are the characteristics of Archaebacteria? |  |
| 2. How do Eubacteria differ from Archaebacteria? |  |
| 3. What diseases are caused by Rickettsia? |  |
| 4. Can Chlamydia be cured? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of Myxobacteria in nature? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|