Kingdom Monera: Archaebacteria & Eubacteria | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Classification of Bacteria on the basis of Shape |

|
| Classification of Kingdom Monera |

|
| Archaebacteria |

|
| Eubacteria |

|
Introduction
Bacteria are the only members of the Kingdom Monera and are the most abundant microorganisms on Earth. They can be found almost everywhere, with hundreds of bacteria present in just a handful of soil. Bacteria also survive in extreme environments such as hot springs, deserts, icy regions, and the deep ocean, where few other life forms can survive. Many bacteria live as parasites on or inside other organisms.

Classification of Bacteria on the basis of Shape
Bacteria are tiny, single-celled organisms that come in different shapes and sizes. Scientists group bacteria into four categories based on their shape.
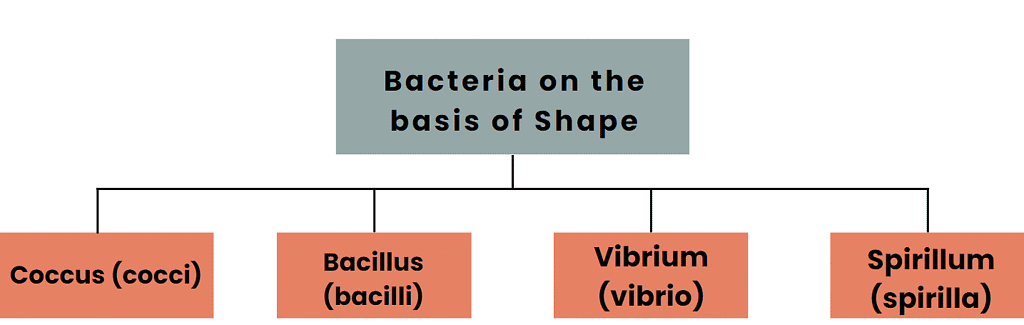
- The first category is Coccus (cocci): These bacteria are spherical or oval in shape. These can be micrococcus (single), diplococcus (in pairs), tetra coccus (in fours), streptococcus (in chains), and staphylococcus (in clusters like grapes)
- The second is the rod-shaped bacteria called Bacillus (bacilli): They can be with or without flagella.
- The third is the comma-shaped bacteria called Vibrium (vibrio): These are small bacteria with flagella at one end.
- The fourth is the spiral-shaped bacteria called Spirillum (spirilla): They are rigid forms due to the spiral structure and bear flagella at one or both ends.
 Bacterial Structure and Behaviour: Bacteria have a simple structure but exhibit complex behavior and they show the most extensive metabolic diversity compared to many other organisms.
Bacterial Structure and Behaviour: Bacteria have a simple structure but exhibit complex behavior and they show the most extensive metabolic diversity compared to many other organisms.
Modes of Nutrition in Bacteria
(a) Autotrophic Bacteria: These bacteria synthesize their own food from inorganic substances.
(b) Photosynthetic Autotrophic: These bacteria use light energy to synthesize food.
(c) Chemosynthetic Autotrophic: These bacteria obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic substances.
(d) Heterotrophic Bacteria: The vast majority of bacteria fall into this category. Heterotrophic bacteria depend on other organisms or dead organic matter for food.
Classification of Kingdom Monera
Now that you've understood Bacteria. It's time to understand how they are classified on the basis of their behaviour. Kingdom Monera is classified into two sub-kingdoms:
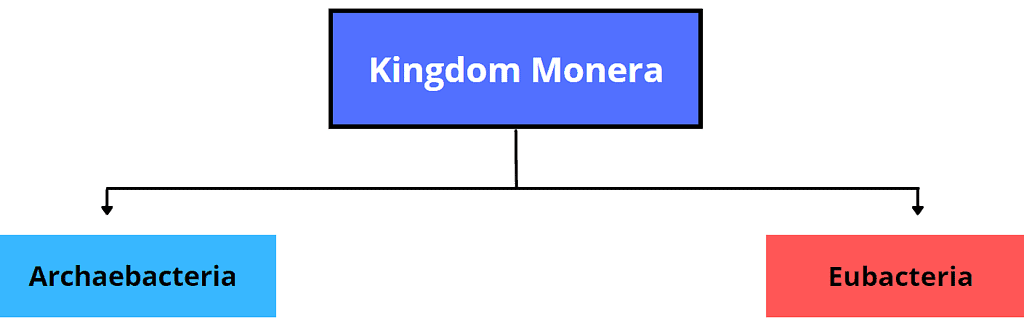
In Archaebacteria we will see the examples: Methanogens, Halophiles and Thermoacidophiles. In Eubacteria we will study Cyanobacteria, Chemosynthetic Bacteria, Heterotrophic Bacteria and Mycoplasma.
Archaebacteria
Archaebacteria are unique bacteria that thrive in extremely harsh environments. They can be found in places like:
(i) Super salty areas(halophiles)
(ii) Hot springs (thermoacidophiles)
(iii) Marshy regions (methanogens).

Do you know: What makes archaebacteria different from other bacteria is their unique cell wall structure, which helps them survive in these tough conditions.
Methanogens, a type of archaebacteria, are found in the guts of animals like cows and buffaloes. They play a crucial role in producing methane (biogas) from the dung of these animals.

Eubacteria
There are thousands of different eubacteria, also known as "true bacteria." Eubacteria are characterized by the presence of a rigid cell wall, and if they are motile (capable of movement), they have a flagellum.
Characteristics of Eubacteria
- Cyanobacteria, often called blue-green algae, are a type of eubacteria that contain chlorophyll a, similar to green plants. They are photosynthetic autotrophs, meaning they can produce their own food using sunlight.
- Cyanobacteria often form blooms in polluted water bodies. Some of these organisms, like Nostoc and Anabaena, can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialized cells called heterocysts.

- Cyanobacteria can be unicellular,colonial, or filamentous. They can live in freshwater, marine, or terrestrial environments. Their colonies are usually surrounded by a gelatinous sheath.

(a) Chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria oxidize various inorganic substances such as nitrates, nitrites, and ammonia, using the released energy to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is a form of energy used by cells. Chemosynthetic bacteria play a crucial role in recycling nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, iron, and sulphur.
(b) Heterotrophic bacteria are the most common type of bacteria found in nature and many of these bacteria play a crucial role as decomposers, breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Some heterotrophic bacteria have a significant impact on human activities. For example, they are involved in:
- Making curd from milk, which is a process used in dairy production.
- Producing antibiotics, which are important for treating bacterial infections.
- Fixing nitrogen in the roots of legume plants, which helps in enriching the soil.
Note: Bacteria can cause diseases in humans, plants, and animals. For example, diseases like cholera, typhoid, tetanus, and citrus canker are caused by different types of bacteria.
Mycoplasma are unique organisms that do not have a cell wall. They are the smallest known living cells and can live without oxygen. Some mycoplasma species can cause diseases in animals and plants.
 Mycoplasma
Mycoplasma
Mode of Reproduction
Bacteria are mainly reproduced by a process called fission. However, in harsh conditions, they can produce spores. They can also exchange genetic material through a primitive form of sexual reproduction.
 A Dividing Bacterium
A Dividing Bacterium
|
181 videos|361 docs|148 tests
|
FAQs on Kingdom Monera: Archaebacteria & Eubacteria - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main shapes of bacteria, and how are they classified based on shape? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between Archaebacteria and Eubacteria? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of Archaebacteria and their habitats? |  |
| 4. How do Eubacteria benefit humans and the environment? |  |
| 5. What are some characteristics used to classify bacteria within the Kingdom Monera? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















