Krebs Cycle or Citric Acid Cycle: Steps, Products & Significance | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Krebs or Citric Acid Cycle? |

|
| Steps of Krebs Cycle |

|
| Summary of Kreb Cycle |

|
| Significance of Krebs Cycle |

|
| Important Questions on Krebs Cycle |

|
What is Krebs or Citric Acid Cycle?
- The Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle is a series of enzyme catalysed reactions occurring in the mitochondrial matrix, where acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced, which generate ATP in the electron transport chain.
- Krebs cycle was named after Hans Krebs, who postulated the detailed cycle. He was awarded the Nobel prize in 1953 for his contribution.
- It is a series of eight-step processes, where the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form two molecules of CO2 and in the process, one ATP is produced. Reduced high energy compounds, NADH and FADH2 are also produced.
- Two molecules of acetyl-CoA are produced from each glucose molecule so two turns of the Krebs cycle are required which yields four CO2, six NADH, two FADH2 and two ATPs.
Krebs Cycle: Part of Cellular Respiration
- Cellular respiration is a catabolic reaction taking place in the cells. It is a biochemical process by which nutrients are broken down to release energy, which gets stored in the form of ATP and waste products are released. In aerobic respiration, oxygen is required.
- Cellular respiration is a four-stage process. In the process, glucose is oxidised to carbon dioxide and oxygen is reduced to water. The energy released in the process is stored in the form of ATPs. 36 to 38 ATPs are formed from each glucose molecule.
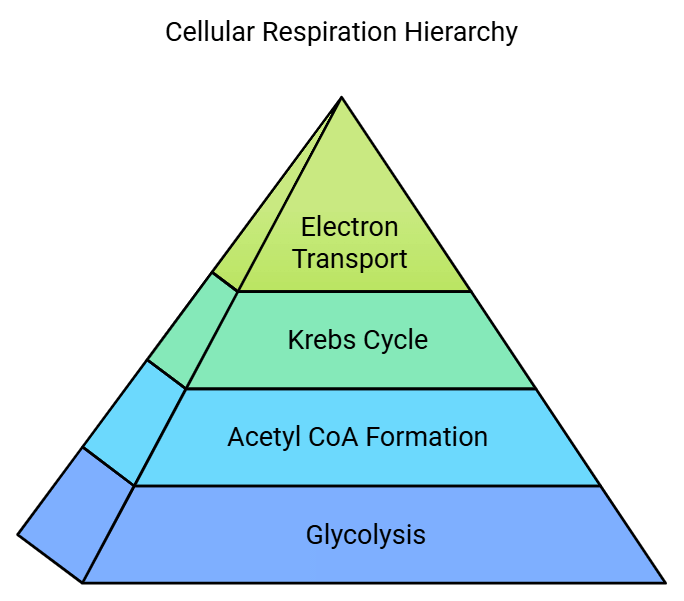
The four stages are:
- Glycolysis: Partial oxidation of a glucose molecule to form 2 molecules of pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytosol.
- Formation of Acetyl CoA: Pyruvate formed in glycolysis enters the mitochondrial matrix. It undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to form two molecules of Acetyl CoA. The reaction is catalysed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase enzyme.
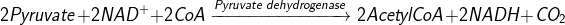
- Krebs Cycle (TCA or Citric Acid Cycle): It is the common pathway for complete oxidation of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids as they are metabolised to acetyl coenzyme A or other intermediates of the cycle. The Acetyl CoA produced enters the Tricarboxylic acid cycle or Citric acid cycle. Glucose is fully oxidized in this process. The acetyl CoA combines with 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate to form 6C citrate. In this process, 2 molecules of CO2 are released and oxaloacetate is recycled. Energy is stored in ATP and other high energy compounds like NADH and FADH2.
- Electron Transport System and Oxidative Phosphorylation: ATP is generated when electrons are transferred from the energy-rich molecules like NADH and FADH2, produced in glycolysis, citric acid cycle and fatty acid oxidation to molecular O2 by a series of electron carriers. O2 is reduced to H2O. It takes place in the inner membrane of mitochondria.
Steps of Krebs Cycle
It is an eight-step process. Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of mitochondria under aerobic condition.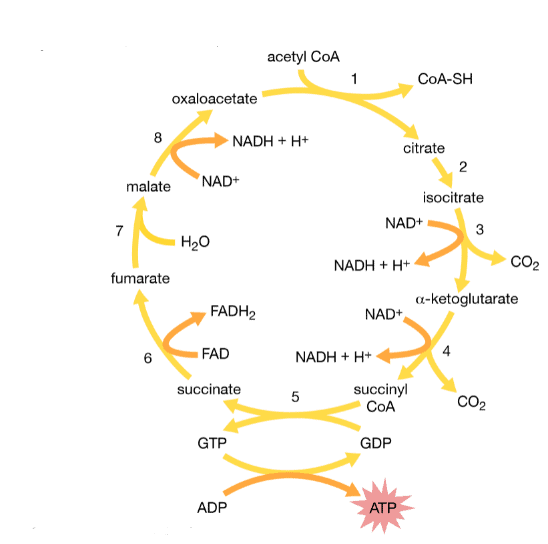 Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
Step 1: The first step is the condensation of acetyl CoA with 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate to form 6C citrate, coenzyme A is released. The reaction is catalysed by citrate synthase.
Step 2: Citrate is converted to its isomer, isocitrate. The enzyme aconitase catalyses this reaction.
Step 3: Isocitrate undergoes dehydrogenation and decarboxylation to form 5C 𝝰-ketoglutarate. A molecular form of CO2 is released. Isocitrate dehydrogenase catalyses the reaction. It is an NAD+ dependent enzyme. NAD+ is converted to NADH.
Step 4: 𝝰-ketoglutarate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to form succinyl CoA, a 4C compound. The reaction is catalyzed by the 𝝰-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase enzyme complex. One molecule of CO2 is released and NAD+ is converted to NADH.
Step 5: Succinyl CoA forms succinate. The enzyme succinyl CoA synthetase catalyses the reaction. This is coupled with substrate-level phosphorylation of GDP to get GTP. GTP transfers its phosphate to ADP forming ATP.
Step 6: Succinate is oxidised by the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase to fumarate. In the process, FAD is converted to FADH2.
Step 7: Fumarate gets converted to malate by the addition of one H2O. The enzyme catalysing this reaction is fumarase.
Step 8: Malate is dehydrogenated to form oxaloacetate, which combines with another molecule of acetyl CoA and starts the new cycle. Hydrogens removed, get transferred to NAD+ forming NADH. Malate dehydrogenase catalyses the reaction.
Summary of Kreb Cycle
(i) Location: Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
(ii) Krebs Cycle Reactants: Acetyl CoA, which is produced from the end product of glycolysis, i.e. pyruvate and it condenses with 4 carbon oxaloacetate, which is generated back in the Krebs cycle.
(iii) Krebs Cycle Products: Each citric acid cycle forms the following products:
- 2 molecules of CO2 are released. Removal of CO2or decarboxylation of citric acid takes place at two places:
- In the conversion of isocitrate (6C) to 𝝰-ketoglutarate (5C)
- In the conversion of 𝝰-ketoglutarate (5C) to succinyl CoA (4C)
- 1 ATP is produced in the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinate
- 3 NAD+ are reduced to NADH and 1 FAD+ is converted to FADH2in the following reactions:
- Isocitrate to 𝝰-ketoglutarate → NADH
- 𝝰-ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA → NADH
- Succinate to fumarate → FADH2
- Malate to Oxaloacetate → NADH
Note that 2 molecules of Acetyl CoA are produced from oxidative decarboxylation of 2 pyruvates so two cycles are required per glucose molecule.
To summarize, for complete oxidation of a glucose molecule, Krebs cycle yields 4 CO2, 6NADH, 2 FADH2 and 2 ATPs.
Each molecule of NADH can form 2-3 ATPs and each FADH2 gives 2 ATPs on oxidation in the electron transport chain.
(iv) Krebs Cycle Equation: To Sum up
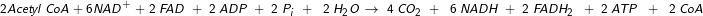
Significance of Krebs Cycle
- Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle is the final pathway of oxidation of glucose, fats and amino acids.
- Many animals are dependent on nutrients other than glucose as an energy source.
- Amino acids (metabolic product of proteins) are deaminated and get converted to pyruvate and other intermediates of the Krebs cycle. They enter the cycle and get metabolised e.g. alanine is converted to pyruvate, glutamate to 𝝰-ketoglutarate, aspartate to oxaloacetate on deamination.
- Fatty acids undergo 𝞫-oxidation to form acetyl CoA, which enters the Krebs cycle.
- It is the major source of ATP production in the cells. A large amount of energy is produced after complete oxidation of nutrients.
- It plays an important role in gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis and interconversion of amino acids.
- Many intermediate compounds are used in the synthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, cytochromes and chlorophylls, etc.
- Vitamins play an important role in the citric acid cycle. Riboflavin, niacin, thiamin and pantothenic acid as a part of various enzymes cofactors (FAD, NAD) and coenzyme A.
- Regulation of Krebs cycle depends on the supply of NAD+ and utilization of ATP in physical and chemical work.
- The genetic defects of the Krebs cycle enzymes are associated with neural damage.
- As most of the biological processes occur in the liver to a significant extent, damage to liver cells has a lot of repercussions. Hyperammonemia occurs in liver diseases and leads to convulsions and coma. This is due to reduced ATP generation as a result of the withdrawal of 𝝰-ketoglutarate and formation of glutamate, which forms glutamine.
Important Questions on Krebs Cycle
Q1. What is the Kreb Cycle?
Ans: Also known as the citric acid cycle, the Krebs cycle is a chain of reactions occurring in the mitochondria, through which almost all living cells produce energy in aerobic respiration. It uses oxygen and gives out water and carbon dioxide as products. Here, ADP is converted into ATP. This cycle renders electrons and hydrogen required for electron chain transport.
Q2. How Many ATPs are Produced In the Krebs Cycle?
Ans: 2 ATPs are produced in one Krebs Cycle.
For complete oxidation of a glucose molecule, the Krebs cycle yields 4 CO2, 6NADH, 2 FADH2 and 2 ATPs.
Q3. Where Does Krebs Cycle Occur?
Ans: Mitochondrial matrix.
In all eukaryotes, mitochondria are the site where the Krebs cycle takes place. The cycle takes place in a mitochondrial matrix producing chemical energy in the form of NADH, ATP, FADH2. These are produced as a result of oxidation of the end product of glycolysis – pyruvate.
Q4. How The Krebs Cycle Works?
Ans: It is an eight-step process:
i) Condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate (4C) forming citrate (6C), coenzyme A is released.
ii) Conversion of Citrate to its isomer, isocitrate.
iii) Isocitrate is subjected to dehydrogenation and decarboxylation forming 𝝰-ketoglutarate (5C).
iv) 𝝰-ketoglutarate (5C) experiences oxidative decarboxylation forming succinyl CoA (4C).
v) Conversion of Succinyl CoA to succinate by succinyl CoA synthetase enzyme along with substrate-level phosphorylation of GDP forming GTP.
vi) Oxidation of Succinate to fumarate by the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase.
vii) Fumarate gets converted to malate by the addition of one H2O.
viii) Malate is dehydrogenated to form oxaloacetate, which combines with another molecule of acetyl CoA and starts the new cycle.
Q5. Why Is Krebs Cycle Called As Amphibolic Pathway?
Ans: It is called amphibolic as in the Krebs cycle both catabolism and anabolism take place. The amphibolic pathway indicates the one involving both catabolic and anabolic procedures.
Q6. How Many NADH are Produced In The Krebs Cycle?
Ans: 3 NADH molecules.
- In one turn of the Krebs cycle, 3 molecules of NADH are produced.
- For complete oxidation of a glucose molecule, Krebs cycle yields 4 CO2, 6NADH, 2 FADH2 and 2 ATPs.
Q7. What Is The Krebs Cycle Also Known As?
Ans: Krebs cycle is also known as Citric acid cycle (CAC) or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle).
Q8. Why Krebs Cycle Is Called the Citric Acid Cycle?
Ans: Krebs cycle is also referred to as the Citric Acid Cycle. Citric acid is the first product formed in the cycle.
|
150 videos|398 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Krebs Cycle or Citric Acid Cycle: Steps, Products & Significance - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the Krebs Cycle and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the main steps of the Krebs Cycle? |  |
| 3. What are the products of the Krebs Cycle? |  |
| 4. How does the Krebs Cycle contribute to cellular respiration? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the Krebs Cycle in metabolism? |  |





















