Languages, Religions & Secularisation | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Language |

|
| Religion |

|
| Secularization |

|
| Issues in Languages, Religions, and Secularization |

|
| Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Languages, Religions & Secularisation |

|
Language
- Language is the means by which ideas are conveyed through spoken sounds, words, and symbols. It is a system of conventional spoken, manual (signed), or written symbols that humans use to express themselves as members of a social group and participants in its culture. Language serves various functions, including communication, expression of identity, play, creative expression, and emotional release.
- The importance of language lies in its role as a key component of cultural understanding. Cultural practices, moral values, and literature, among other aspects, are passed down from generation to generation through language. In this way, language helps preserve and transmit cultural heritage.
- Additionally, language plays a significant role in defining regional boundaries. For instance, many Indian states were formed based on linguistic divisions. This highlights the importance of language in shaping our world and our understanding of the people and cultures within it.
Dialect
Dialect refers to a unique form of language that is specific to a particular geographical area or social group.
Languages of the World
There are approximately 6,500 languages spoken across the globe today. Identifying the most widely spoken languages can be a challenging task.
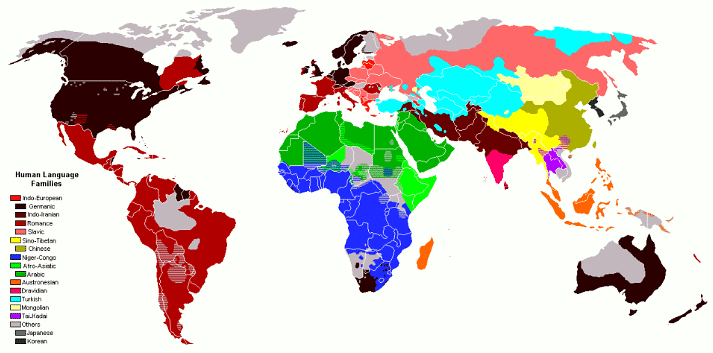
Here is a list of some of the most spoken languages in the world:
- English: spoken by 1,132 million people
- Mandarin Chinese: spoken by 1,117 million people
- Hindi: spoken by 615 million people
- Spanish: spoken by 534 million people
- French: spoken by 280 million people
- Arabic: spoken by 274 million people
- Bangla/Bengali: spoken by 265 million people
- Russian: spoken by 258 million people
- Portuguese: spoken by 234 million people
- Indonesian: spoken by 199 million people
- Urdu: spoken by 170 million people
- German: spoken by 132 million people
These figures offer a general understanding of the most common languages spoken around the world.
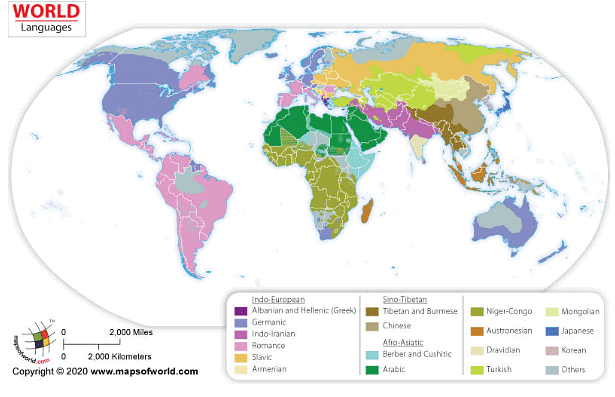
Religion
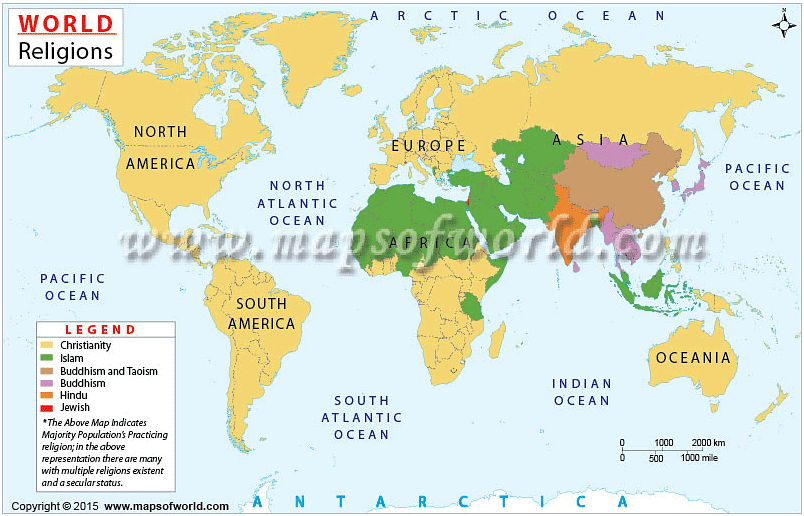
Religion can be described as a system of shared supernatural beliefs and moral values that connect people within a community. The cultural geography of our world is incredibly intricate, with language and religion being two essential aspects that contribute to the richness, diversity, and complexity of human experience. As nations worldwide become more culturally, religiously, and linguistically diverse, the concept of "diversity" is gaining increasing attention. Religions that once remained confined to their places of origin have now spread to other regions, in some cases causing religious wars and persecution, while in others fostering cultural tolerance and respect.
- The mingling of diverse religious and linguistic backgrounds is often the result of historical migratory trends and demographic changes. While geography may not be able to answer specific questions about language structure or theological perspectives, it can provide insights by studying these cultural traits in a spatial context. By understanding the spread of cultural traits and the role of geographic factors in this process, we can appreciate how geography has influenced the distribution and practice of different belief systems and spiritual traditions.
- Geographers classify religions into two main categories: universalizing religions, which actively seek new members, and ethnic religions, which are associated with particular ethnic or national groups. Understanding these different classifications can help us appreciate the cultural richness of various religious traditions around the world.
- Many of the world's universalizing religions have specific hearths or places of origin, often linked to events in the life of a key individual. The largest universalizing religions, including Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism, originated in Asia and have since spread to other regions of the world, amassing over 2.5 billion adherents combined.
- The major world religions (Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, Confucianism, Christianity, Taoism, and Judaism) differ in several ways, including the organization of each religion, the belief systems they uphold, the nature of belief in a higher power, the history of how the world and the religion began, and the use of sacred texts and objects.
- Studying religion in the context of geography is important for several reasons. Religious festivals, food, and ceremonies are often shaped by the physical environment. It also helps to examine the relationship between religion and the environment, as religion can support sustainable development, environmental conservation, and the overall welfare of the population. By understanding the geographical aspects of religion, we can better appreciate the diverse beliefs and traditions that contribute to our world's rich cultural tapestry.
Diffusion of Religion
The major religions of the world, despite originating in limited geographic regions, have spread across vast areas through various means. These include invasion, as seen in the case of Islam, where conquest played a significant role in its dissemination. Similarly, missionary activities have facilitated the spread of religions such as Buddhism and Christianity, with followers traveling to different regions to share their beliefs. Political imperialism has also contributed to the expansion of religious influence, as imperial powers often imposed their religion on the territories they controlled. Additionally, the growth and movement of political boundaries enabled the diffusion of religious beliefs, as did the migration of populations who carried their faith with them to new locations.
Secularization
- Secularization refers to the historical process in which religion loses its social and cultural significance in a society. This leads to a decrease in the influence of religion on people's everyday lives, and religious organizations lose their social power. In secularized societies, faith lacks cultural authority, and public life proceeds without reference to the supernatural. This long-term societal change has consequences for religion itself, particularly in Western countries, where the connection to their Christian heritage becomes more tenuous. However, secularization is important beyond the formerly Christian West, as many of the forces that initially drove secularization in those societies also affect other regions.
- The term secularism initially denoted a distinction between sacred and mundane aspects of life within Christianity. In the Catholic Church, secular priests were those who served society at large rather than belonging to a religious order. The term secularization was later used to describe the transfer of territories controlled by the church to the authority of political entities, particularly after the 1648 Treaty of Westphalia, which ended the European wars of religion.
- By the late 19th century, secularization began to refer to the changing role of religion in society, often associated with modernization. This concept has been at the center of controversies between traditional advocates of strong public religion and secularist intellectuals who sought to reduce religion's role in society. More recently, scholars have debated the validity of secularization interpretations, with some prominent sociologists of religion charting its course, partly guided by the work of Max Weber (1864–1920), while others question their conclusions.
Secularization aims to:
- Encourage logical thinking among people.
- Promote the study of science and empirical evidence.
- Reduce the dominance of religious institutions and symbols in society.
- Separate religion from the state, ensuring that political decisions are not influenced by religious beliefs.
- Facilitate cultural shifts that free society from superstition and supernatural beliefs.
- Foster communal harmony by reducing religious tensions and conflicts.
Issues in Languages, Religions, and Secularization
- Cultural Appropriation: Cultural appropriation is a significant issue in the study of languages and religions. The use of language and religious practices outside of their original cultural context can be seen as disrespectful and can lead to misunderstandings and misrepresentations.
- Conflicts: Languages and religions have been the source of many conflicts throughout human history. Conflicts over language and religious differences have been a significant factor in many wars and ongoing conflicts around the world.
- Marginalization: Language and religious minorities can be marginalized in society, facing discrimination and a lack of representation in political and cultural institutions.
- Strategies for Effective Understanding of Languages, Religions, and Secularization
- Multiculturalism: Multiculturalism involves recognizing and valuing the diversity of cultures and promoting a society that is inclusive and respectful of all cultures.
- Interfaith Dialogue: Interfaith dialogue involves promoting communication and understanding between different religious communities. This can help to reduce conflicts and promote a more peaceful and harmonious society.
- Education and Awareness: Education and awareness about different languages, religions, and cultures can help to promote understanding and reduce stereotypes and biases. This can be achieved through educational programs, cultural events, and media representation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, language and religion are integral aspects of human culture and play a significant role in shaping our world. With thousands of languages spoken globally and diverse religious traditions practiced, understanding the geographical context of these cultural traits offers valuable insights into the richness, diversity, and complexity of human experience. The study of languages, dialects, and religious diffusion, as well as secularization, helps us appreciate the ways in which history, migration, and geography have influenced and continue to shape societies across the globe. Ultimately, fostering a better understanding of language and religion contributes to building cultural tolerance, respect, and harmony in our increasingly interconnected world.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Languages, Religions & Secularisation
What is the difference between language and dialect?
Language is a system of spoken, written, or signed symbols used by humans to communicate, express themselves, and participate in a culture. Dialect, on the other hand, refers to a unique form of language that is specific to a particular geographical area or social group.
Why is it important to study the geography of religion?
Studying religion in the context of geography helps us understand how the physical environment shapes religious festivals, food, and ceremonies. It also helps us examine the relationship between religion and the environment, as religion can support sustainable development, environmental conservation, and the overall welfare of the population.
What are the main categories of religions, and how do they differ?
Geographers classify religions into two main categories: universalizing religions, which actively seek new members, and ethnic religions, which are associated with particular ethnic or national groups. Universalizing religions, such as Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism, originated in specific regions and have since spread globally, while ethnic religions are primarily practiced by specific cultural groups.
How have major religions diffused throughout the world?
Major religions have spread across vast areas through various means, including invasion, missionary activities, political imperialism, and migration. Examples include the conquests that led to the spread of Islam, the missionary work that facilitated the dissemination of Buddhism and Christianity, and the migration of populations who carried their faith with them to new locations.
What is secularization, and why is it important?
Secularization refers to the historical process in which religion loses its social and cultural significance in a society. This leads to a decrease in the influence of religion on people's everyday lives, and religious organizations lose their social power. Secularization is important because it encourages logical thinking, promotes scientific study, reduces the dominance of religious institutions, separates religion from the state, facilitates cultural shifts, and fosters communal harmony by reducing religious tensions and conflicts.
|
303 videos|635 docs|252 tests
|
FAQs on Languages, Religions & Secularisation - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the relationship between language and culture? |  |
| 2. How do religions shape societies? |  |
| 3. What is secularization and its impact on religious practices? |  |
| 4. How does language influence identity formation? |  |
| 5. What are the factors contributing to the global spread of religions? |  |















