Irodov Solutions: Laws of Conservation of Energy, Momentum & Angular Momentum | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Q1: A particle has shifted along some trajectory in the plane xy from point 1 whose radius vector r1 = i + 2j to point 2 with the radius vector r2 = 2i — 3j. During that time the particle experienced the action of certain forces, one of which being F = 3i + 4j. Find the work performed by the force F. (Here r1, r2, and F are given in SI units).
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: As  is constant so the sought work done
is constant so the sought work done
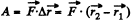
or, 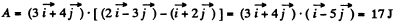
Q2: A locomotive of mass m starts moving so that its velocity varies according to the law 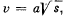 where a is a constant, and s is the distance covered. Find the total work performed by all the forces which are acting on the locomotive during the first t seconds after the beginning of motion.
where a is a constant, and s is the distance covered. Find the total work performed by all the forces which are acting on the locomotive during the first t seconds after the beginning of motion.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Differentiating v (s) with respect to time
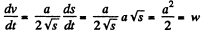
(As locomotive is in unidirectional motion)
Hence force acting on the locomotive 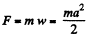
Let, at v = 0 at t = 0 then the distance covered during the first t seconds
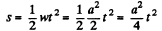
Hence the sought work, 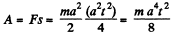
Q3: The kinetic energy of a particle moving along a circle of radius R depends on the distance covered s as T = as2, where a is a constant. Find the force acting on the particle as a function of S.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: We have
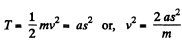 (1)
(1)
Differentiating Eq. (1) with respect to time
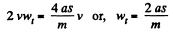 (2)
(2)
Hence net acceleration of the particle
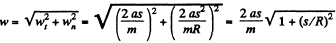
Hence the sought force, 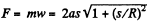
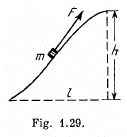
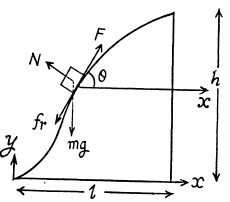
Q4: A body of mass m was slowly hauled up the hill (Fig. 1.29) by a force F which at each point was directed along a tangent to the trajectory. Find the work performed by this force, if the height of the hill is h, the length of its base l, and the coefficient of friction k.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let  makes an angle 0 with the horizontal at any instant of time (Fig.). Newton’s second law in projection form along the direction of the force, gives :
makes an angle 0 with the horizontal at any instant of time (Fig.). Newton’s second law in projection form along the direction of the force, gives :
F = Jang cos θ + mg sin θ (because there is no acceleration of the body.)
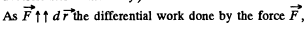
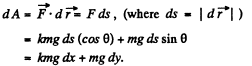
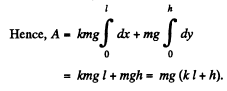
Q5: A disc of mass m = 50 g slides with the zero initial velocity down an inclined plane set at an angle α = 30° to the horizontal; having traversed the distance l = 50 cm along the horizontal plane, the disc stops. Find the work performed by the friction forces over the whole distance, assuming the friction coefficient k = 0.15 for both inclined and horizontal planes.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let 5 be the distance covered by the disc along the incline, from the Eq. of increment of M.E. of the disc in the field of gravity : 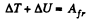
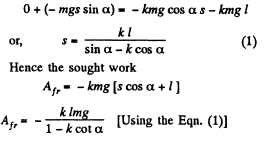
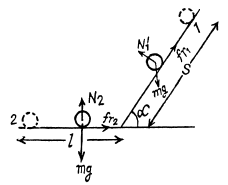
On putting the values Afr = -0.05 J
Q6: Two bars of masses m1 and m2 connected by a non-deformed light spring rest on a horizontal plane. The coefficient of friction between the bars and the surface is equal to k. What minimum constant force has to be applied in the horizontal direction to the bar of mass m1 in order to shift the other bar?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let x be the compression in the spring when the bar m2 is about to shift Therefore at this moment spring force on m2 is equal to the limiting friction between the bar m2 and horizontal floor. Hence
k x - k m2g [where k is the spring constant (say)] (1)
For the block m1 from work-eneigy theorem : A - ΔT = 0 for minimum force. (A here indudes the work done in stretching the spring.)
so, 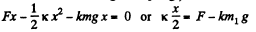 (2)
(2)
From (1) and (2),
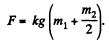
Q7: A chain of mass m = 0.80 kg and length l = 1.5 m rests on a rough-surfaced table so that one of its ends hangs over the edge. The chain starts sliding off the table all by itself provided the overhanging part equals η = 1/3 of the chain length. What will be the total work performed by the friction forces acting on the chain by the moment it slides completely off the table?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: From the initial condition of the problem the limiting friction between the chain lying on the horizontal table equals the weight of the over hanging part of the chain, i.e
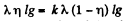 (where λis the linear mass density of the chain)
(where λis the linear mass density of the chain)
So, 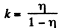 (1)
(1)
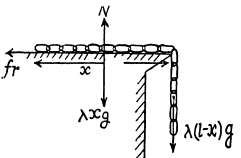
Let (at an arbitrary moment of time) the length of the chain on the table is x. So the net friction force between the chain and the table, at this moment :
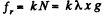 (2)
(2)
The differential work done by the friction forces :
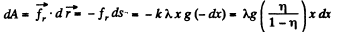 (3)
(3)
(Note that here we have written ds = - dx., because ds is essentially a positive term and as the length of the chain decreases with time, dx is negative) Hence, the sought work done
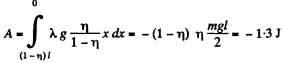
Q8: A body of mass m is thrown at an angle α to the horizontal with the initial velocity v0. Find the mean power developed by gravity over the whole time of motion of the body, and the instantaneous power of gravity as a function of time.
 View Answer
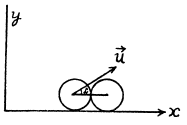
View Answer 
Ans: The velocity of the body, t seconds after the begining of the motion becomes 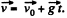 Thb power developed by the gravity
Thb power developed by the gravity 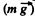 at that moment, is
at that moment, is 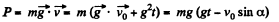 (1)
(1)
As 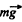 is a constant force, so the average power
is a constant force, so the average power
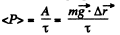
where 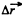 is the net displacement of the body during time of flight
is the net displacement of the body during time of flight
As, 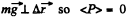
Q9: A particle of mass m moves along a circle of radius R with a normal acceleration varying with time as wn = at2, where a is a constant. Find the time dependence of the power developed by all the forces acting on the particle, and the mean value of this power averaged over the first t seconds after the beginning of motion.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: We have 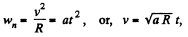
t is defined to start from the beginning of motion from rest
So, 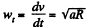
Instantaneous power, 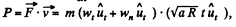
(where 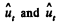 are unit vectors along the direction of tangent (velocity) and normal respectively)
are unit vectors along the direction of tangent (velocity) and normal respectively)
So , 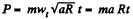
Hence the sought average power
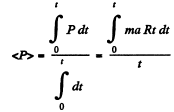
Hence 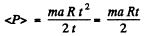
Q10: A small body of mass m is located on a horizontal plane at the point O. The body acquires a horizontal velocity v0. Find:
(a) the mean power developed by the friction force during the whole time of motion, if the friction coefficient k = 0.27, m = 1.0 kg, and v0 = 1.5 m/s;
(b) the maximum instantaneous power developed by the friction force, if the friction coefficient varies as k = αx, where α is a constant, and x is the distance from the point O.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let the body m acquire the horizontal velocity v0 along positive x - axis at the point O.
(a) Velocity of the body t seconds after the beginning of the motion,
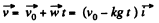 (1)
(1)
Instantaneous power 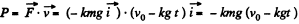
From Eq. (1), the time of motion τ - v0/kg
Hence sought average power during the time of motion
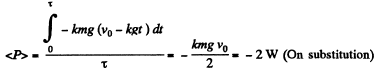
From 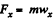
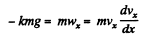
or, 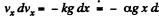
To find v (x), let us integrate the above equation
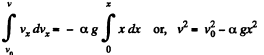 (1)
(1)
Now, 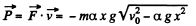 (2)
(2)
For maximum power, 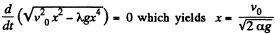
Putting this value of x , in Eq. (2) we get,
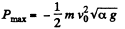
Q11: A small body of mass m = 0.10 kg moves in the reference frame rotating about a stationary axis with a constant angular velocity ω = 5.0 rad/s. What work does the centrifugal force of inertia perform during the transfer of this body along an arbitrary path from point 1 to point 2 which are located at the distances r1 = 30 cm and r2 = 50 cm from the rotation axis?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Centrifugal force of inertia is directed outward along radial line, thus the sought work
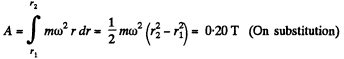
Q12: A system consists of two springs connected in series and having the stiffness coefficients k1 and k2. Find the minimum work to be performed in order to stretch this system by Δl.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Since the springs are connected in series, the combination may be treated as a single spring of spring constant
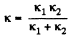
From the equation of increment of M.E., 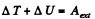
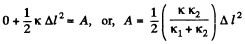
Q13: A body of mass m is hauled from the Earth's surface by applying a force F varying with the height of ascent y as F = 2 (ay - 1) mg, where a is a positive constant. Find the work performed by this force and the increment of the body's potential energy in the gravitational field of the Earth over the first half of the ascent.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: First, let us find the total height of ascent At the beginning and the end of the path of velocity of the body is equal to zero, and therefore the increment of the kinetic energy of the body is also equal to zero. On the other hand, in according with work-energy theorem ΔT is equal to the algebraic sum of the works A performed by all the forces, i.e. by the force F and gravity, over this path. However, since ΔT = 0 then A = 0. Taking into account that the upward direction is assumed to coincide with the positive direction of the y - axis, we can write
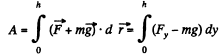
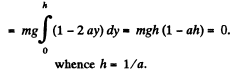
The work performed by the force F over the first half of the ascent is
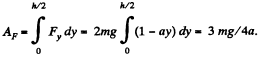
The corresponding increment of the potential energy is
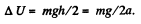
Q14: The potential energy of a particle in a certain field has the form U = a/r2 — blr, where a and b are positive constants, r is the distance from the centre of the field. Find:
(a) the value of r0 corresponding to the equilibrium position of the particle; examine whether this position is steady;
(b) the maximum magnitude of the attraction force; draw the plots U (r) and Fr (r) (the projections of the force on the radius vector r).
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: From the equation 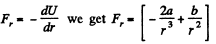
(a) we have at r - r0, the particle is in equilibrium position. 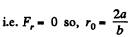
To check, whether the position is steady (the position of stable equilibrium), we have to satisfy
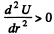
We have 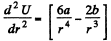
Putting the value of 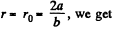
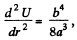 (as a and ft are positive constant)
(as a and ft are positive constant)
So, 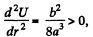
which indicates that the potential energy of the system is minimum, hence this position is steady.
(b) We have 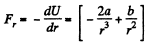
For F , to be maximum, 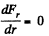
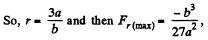
As Fr is negative, the force is attractive.
Q15: In a certain two-dimensional field of force the potential energy of a particle has the form U = αx2 + βy2, where α and β are positive constants whose magnitudes are different. Find out:
(a) whether this field is central;
(b) what is the shape of the equipotential surfaces and also of the surfaces for which the magnitude of the vector of force F = const.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) We have
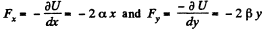
So, 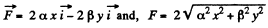 (1)
(1)
For a central force, 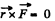
Here, 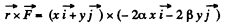
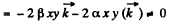
Hence the force is not a central force.
(b) 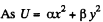
So, 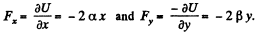
So, 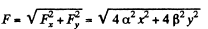
According to the problem
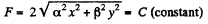
or, 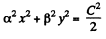
or, 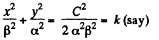 (2)
(2)
Therefore the surfaces for which F is constant is an ellipse. For an equipotential surface U is constant.
So, 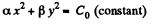
or, 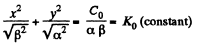
Hence the equipotential surface is also an ellipse.
Q16: There are two stationary fields of force F = ayi and F = axi + byj, where i and j are the unit vectors of the x and y axes, and a and b are constants. Find out whether these fields are potential.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let us calculate the work performed by the forces of each field over the path from a certain point 1 (x1, y1) to another certain point 2 (x2 , y2)
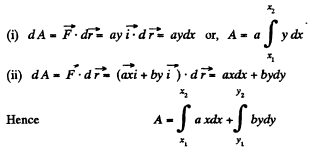
In the first case, the integral depends on the function of type y (x), i.e. on the shape of the path. Consequently, the first field of force is not potential. In the second case, both the integrals do not depend on the shape of the path. They are defined only by the coordinate of the initial and final points of the path, therefore the second field of force is potential.
Q17: A body of mass in is pushed with the initial velocity v0 up an inclined plane set at an angle α to the horizontal. The friction coefficient is equal to k. What distance will the body cover before it stops and what work do the friction forces perform over this distance?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let s be the sought distance, then from the equation of increment of M.E.
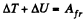
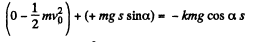
or, 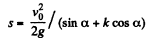
Hence 
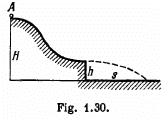
Q18: A small disc A slides down with initial velocity equal to zero from the top of a smooth hill of height H having a horizontal portion (Fig. 1.30). What must be the height of the horizontal portion h to ensure the maximum distance s covered by the disc? What is it equal to?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Velocity of the body at hight 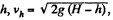 horizontally (from the figure given in the problem). Time taken in falling through the distance h.
horizontally (from the figure given in the problem). Time taken in falling through the distance h.
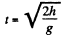 (as initial vertical component of the velocity is zero.)
(as initial vertical component of the velocity is zero.)
Now 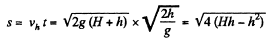
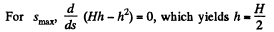
Putting this value of h in the expression obtained for s, we get,
smax = H
Q19: A small body A starts sliding from the height h down an inclined groove passing into a half-circle of radius h/2 (Fig. 1.31). Assuming the friction to be negligible, find the velocity of the body at the highest point of its trajectory (after breaking off the groove).
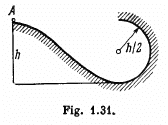
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: To complete a smooth vertical track of radius R, the minimum height at which a particle starts, must be equal to 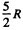 (one can proved it from energy conservation). Thus in our problem body could not reach the upper most point of the vertical track of radius R/2.
(one can proved it from energy conservation). Thus in our problem body could not reach the upper most point of the vertical track of radius R/2.
Let the particle A leave the track at some point O with speed v (Fig.). Now from energy conservation for the body A in the field of gravity :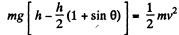
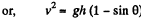 (1)
(1)
From Newton s second law for the particle at the point O; Fn = mwn,
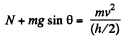
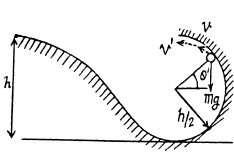
But, at the point O the normal reaction N = 0
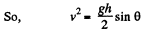 (2)
(2)
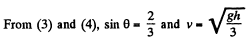
After leaving the track at O, the particle A comes in air and further goes up and at maximum height of it's trajectory in air, it’s velocity (say v') becomes horizontal (Fig.). Hence, the sought velocity of A at this point
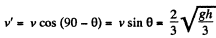
Q20: A ball of mass m is suspended by a thread of length l. With what minimum velocity has the point of suspension to be shifted in the horizontal direction for the ball to move along the circle about that point? What will be the tension of the thread at the moment it will be passing the horizontal position?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let, the point of suspension be shifted with velocity vA in the horizontal direction towards left then in the rest frame of point of suspension the ball starts with same velocity horizontally towards right Let us work in this, frame. From Newton’s second law in projection form towards the point of suspension at the upper most point (say B) :
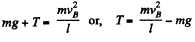 (1)
(1)
Condition required, to complete the vertical circle is that T > 0. But (2)
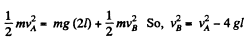 (3)
(3)
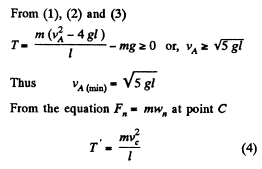
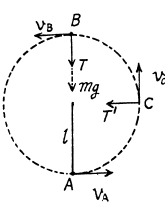
Again from energy conservation
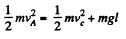 (5)
(5)
From (4) and (5)
T = 3 mg
Q21: A horizontal plane supports a stationary vertical cylinder of radius R and a disc A attached to the cylinder by a horizontal thread AB of length l0 (Fig. 1.32, top view). An initial velocity v0 is imparted to the disc as shown in the figure. How long will it move along the plane until it strikes against the cylinder? The friction is assumed to be absent.
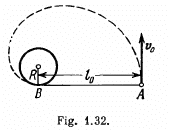
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Since the tension is always perpendicular to the velocity vector, the work done by the tension force will be zero. Hence, according to the work energy theorem, the kinetic eneigy or velocity of the disc will remain constant during it’s motion. Hence, the sought time 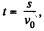 where s is the total distance traversed by the small disc during it's motion.
where s is the total distance traversed by the small disc during it's motion.
Now, at an arbitary position (Fig.)
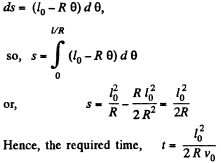
It should be clearly understood that the only uncompensated force acting on the disc A in this case is the tension T, of the thread. It is easy to see that there is no point here, relative to which the moment of force T is invariable in the process of motion. Hence conservation of angular momentum is not applicable here.
Q22: A smooth rubber cord of length l whose coefficient of elasticity is k is suspended by one end from the point O (Fig. 1.33). The other end is fitted with a catch B. A small sleeve A of mass m starts falling from the point O. Neglecting the masses of the thread and the catch, find the maximum elongation of the cord.
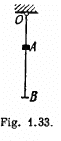
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Suppose that Δl is the elongation of the rubber cord. Then from energy conservation,
or, 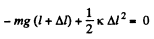
or, 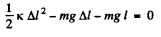
or. 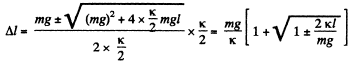
Since the value of 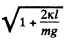 is certainly greater than 1, hence negative sign is a voided.
is certainly greater than 1, hence negative sign is a voided.
So, 
Q23: A small bar A resting on a smooth horizontal plane is attached by threads to a point P (Fig. 1.34) and, by means of a weightless pulley, to a weight B possessing the same mass as the bar itself. Besides, the bar is also attached to a point 0 by means of a light nondeformed spring of length l0 = 50 cm and stiffness x = 5 mg/l0, where m is the mass of the bar. The thread PA having been burned, the bar starts moving. Find its velocity at the moment when it is breaking off the plane.
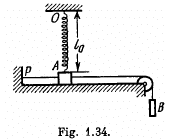
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: When the thread PA is burnt, obviously the speed of the bars will be equal at any instant of time until it breaks often. Let v be the speed of each block and θ be the angle, which the elongated spring makes with the vertical at the moment, when the bar A breaks off the plane. At this stage the elongation in the spring.
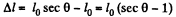 (1)
(1)
Since the problem is concerned with position and there are no forces other than conservative forces, the mechanical energy of the system (both bars + spring) in the field of gravity is conserved, i.e. ΔT + ΔU = 0
So, 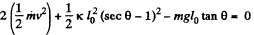 (2)
(2)
From Newton’s second law in projection form along vertical direction :
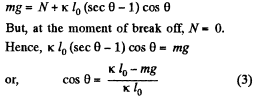
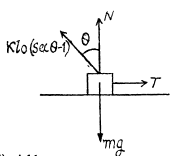
Taking 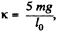 simultaneous solutions of (2) and (3) yields :
simultaneous solutions of (2) and (3) yields :
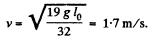
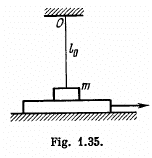
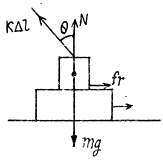
Q24: A horizontal plane supports a plank with a bar of mass m = 1.0 kg placed on it and attached by a light elastic non-deformed cord of length l0 = 40 cm to a point O (Fig. 1.35). The coefficient of friction between the bar and the plank equals k = 0.20. The plank is slowly shifted to the right until the bar starts sliding over it. It occurs at the moment when the cord deviates from the vertical by an angle θ = 30°. Find the work that has been performed by that moment by the friction force acting on the bar in the reference frame fixed to the plane.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Obviously the elongation in the cord, Δl = l0 (sec θ - 1), at the moment the sliding first starts and at the moment horizontal projection of spring force equals the limiting friction.
So, 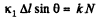 (1)
(1)
(where kx is the elastic constant)
From Newton's law in projection form along vertical direction :
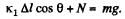
or, 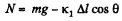 (2)
(2)
From (1) and (2),
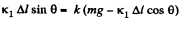

From the equation of the increment of mechanical energy : ΔU + ΔT = Afr
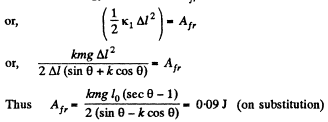
Q25: A smooth light horizontal rod AB can rotate about a vertical axis passing through its end A. The rod is fitted with a small sleeve of mass m attached to the end A by a weightless spring of length l0 and stiffness x. What work must be performed to slowly get this system going and reaching the angular velocity ω?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let the deformation in the spring be Δl, when the rod AB has attained the angular velocity ω.
From the second law of motion in projection form Fn = mwn .
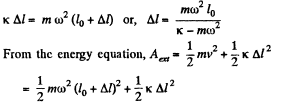
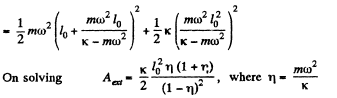
Q26: A pulley fixed to the ceiling carries a thread with bodies of masses m1 and m2 attached to its ends. The masses of the pulley and the thread are negligible, friction is absent. Find the acceleration wc of the centre of inertia of this system.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: We know that acceleration of centre of mass of the system is given by the expression.
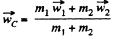
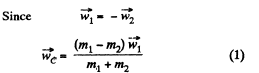
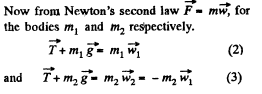
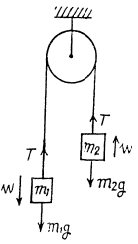
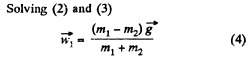
Thus from (1), (2) and (4),
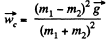
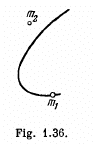
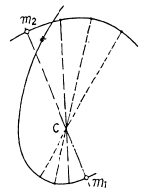
Q27: Two interacting particles form a closed system whose centre of inertia is at rest. Fig. 1.36 illustrates the positions of both particles at a certain moment and the trajectory of the particle of mass m1. Draw the trajectory of the particle of mass m2 if m2 = m1/2.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: As the closed system consisting two particles m 1 and of m2 is initially at rest the C.M. of the system will remain at rest. Further as m2 = m1/2, the C.M. of the system divides the line joining m1 and m2 at all the moments of time in the ratio 1 : 2. In addition to it the total linear momentum of the system at all the times is zero. So, 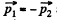 and therefore the velocities of m1 and m2 are also directed in opposite sense. Bearing in mind all these thing, the sought trajectory is as shown in the figure.
and therefore the velocities of m1 and m2 are also directed in opposite sense. Bearing in mind all these thing, the sought trajectory is as shown in the figure.
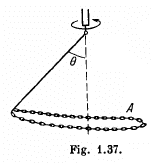
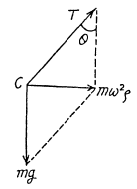
Q28: A closed chain A of mass m = 0.36 kg is attached to a vertical rotating shaft by means of a thread (Fig. 1.37), and rotates with a constant angular velocity ω = 35 rad/s. The thread forms an angle 0 = 45° with the vertical. Find the distance between the chain's centre of gravity and the rotation axis, and the tension of the thread.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: First of all, it is clear that the chain does not move in the vertical direction during the uniform rotation. This means that the vertical component of the tension T balances gravity. As for the horizontal component of the tension T, it is constant in magnitude and permanently directed toward the rotation axis. It follows from this that the C.M. of the chain, the point C, travels along horizontal circle of radius p (say). Therefore we have,
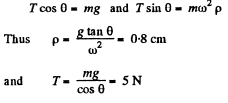
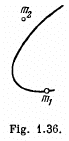
Q29: A round cone A of mass m = 3.2 kg and half angle α = 10° rolls uniformly and without slipping along a round conical surface B so that its apex O remains stationary (Fig. 1.38). The centre of gravity of the cone A is at the same level as the point O and at a distance l = 17 cm from it. The cone's axis moves with angular velocity ω. Find:
(a) the static friction force acting on the cone A, if ω = 1.0 rad/s;
(b) at what values of ω the cone A will roll without sliding, if the coefficient of friction between the surfaces is equal to k = 0.25.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Let us draw free body diagram and write Newton's second law in terms of projection along vertical and horizontal direction respectively.
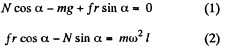
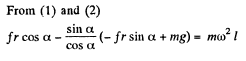
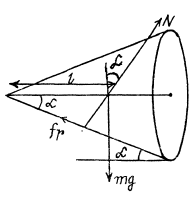
So, 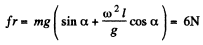 (3)
(3)
(b) For rolling, without sliding,
fr < kN
but, N = mg cos α - m ω2 l sin α
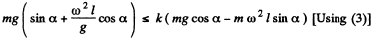
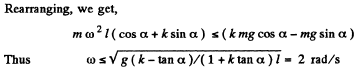
Q30: In the reference frame K two particles travel along the x axis, one of mass m1 with velocity v1, and the other of mass m2 with velocity v2. Find:
(a) the velocity V of the reference frame K' in which the cumulative kinetic energy of these particles is minimum;
(b) the cumulative kinetic energy of these particles in the K' frame.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Total kinetic energy in frame K ' is
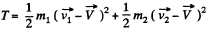
This is minimum with respect to variation in 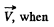 when
when
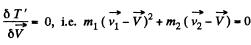
or 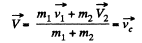
Hence, it is the frame of C.M. in which kinetic energy of a system is minimum.
(b) Linear momentum of the particle 1 in the K ' or C frame
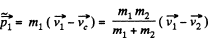
or, 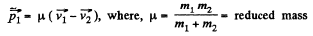
Similarly, 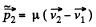
So, 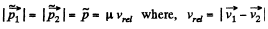 (3)
(3)
Now the total kinetic energy of the system in the C frame is
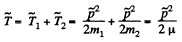
Hence 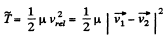
Q31: The reference frame, in which the centre of inertia of a given system of particles is at rest, translates with a velocity V relative to an inertial reference frame K. The mass of the system of particles equals m, and the total energy of the system in the frame of the centre of inertia is equal to 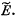 Find the total energy E of this system of particles in the reference frame K.
Find the total energy E of this system of particles in the reference frame K.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: To find the relationship between the values of the mechanical eneigy of a system in the K and C reference frames, let us begin with the kinetic eneigy T of the system. The velocity of the /-th particle in the K frame may be represented as 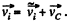 Now we can write
Now we can write
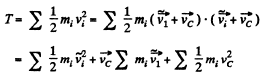
Since in the C frame 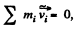 the previous expression takes the form
the previous expression takes the form
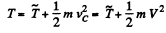 (since according to the problem vc = V) (1)
(since according to the problem vc = V) (1)
Since the internal potential energy U of a system depends only on its configuration, the magnitude U is the same in all reference frames. Adding U to the left and right hand sides of Eq. (1), we obtain the sought relationship
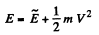
Q32: Two small discs of masses m1 and m2 interconnected by a weightless spring rest on a smooth horizontal plane. The discs are set in motion with initial velocities v1 and v2 whose directions are mutually perpendicular and lie in a horizontal plane. Find the total 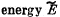 of this system in the frame of the centre of inertia.
of this system in the frame of the centre of inertia.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: As initially 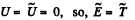
From the solution of 1.147 (b)
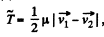
As 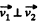
Thus 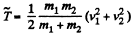
Q33: A system consists of two small spheres of masses m1 and m2 interconnected by a weightless spring. At the moment t = 0 the spheres are set in motion with the initial velocities v1 and v2 after which the system starts moving in the Earth's uniform gravitational field. Neglecting the air drag, find the time dependence of the total momentum of this system in the process of motion and of the radius vector of its centre of inertia relative to the initial position of the centre.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Velocity of masses m1 and m2, after t seconds are respectively.
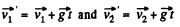
Hence the final momentum of the system,
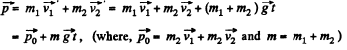
And radius vector,
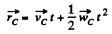
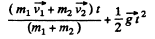

Q34: Two bars of masses m1 and m2 connected by a weightless spring of stiffness x (Fig. 1.39) rest on a smooth horizontal plane. Bar 2 is shifted a small distance x to the left and then released. Find the velocity of the centre of inertia of the system after bar 1 breaks off the wall.
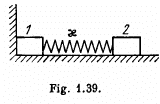
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: After releasing the bar 2 acquires the velocity v2, obtained by the energy, conservation :
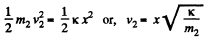 (1)
(1)
Thus the sought velocity of C.M.
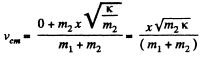
Q35: Two bars connected by a weightless spring of stiffness x and length (in the non-deformed state) l0 rest on a horizontal plane. A constant horizontal force F starts acting on one of the bars as shown in Fig. 1.40. Find the maximum and minimum distances between the bars during the subsequent motion of the system, if the masses of the bars are:
(a) equal;
(b) equal to m1 and m2, and the force F is applied to the bar of mass m2.
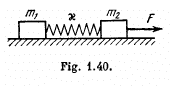
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let us consider both blocks and spring as the physical system. The centre of mass of the system moves with acceleration 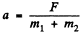 towards right Let us work in the frame of centre of mass. As this frame is a non-inertial frame (accelerated with respect to the ground) we have to apply a pseudo force m1 a towards left on the block m1 and m2 a towards left on the block m2
towards right Let us work in the frame of centre of mass. As this frame is a non-inertial frame (accelerated with respect to the ground) we have to apply a pseudo force m1 a towards left on the block m1 and m2 a towards left on the block m2
As the center of mass is at rest in this frame, the blocks move in opposite directions and come to instantaneous rest at some instant. The elongation of the spring will be maximum or minimum at this instant. Assume that the block m1 is displaced by the distance x1 and the block m2 through a distance x2 from the initial positions.
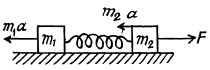
From the energy equation in the frame of C.M.
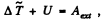
(where Aext also includes the work done by the pseudo forces)
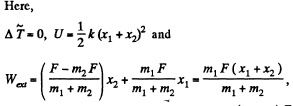
or, 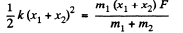
So, 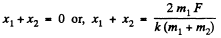
Hence the maximum separation between the blocks equals 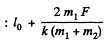
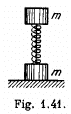
Q36: A system consists of two identical cubes, each of mass m, linked together by the compressed weightless spring of stiffness x (Fig. 1.41). The cubes are also connected by a thread which is burned through at a certain moment. Find:
(a) at what values of Δl, the initial compression of the spring, the lower cube will bounce up after the thread has been burned through:
(b) to what height h the centre of gravity of this system will rise if the initial compression of the spring Δl = 7 mg/x.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The initial compression in the spring Δl must be such that after burning of the thread, the upper cube rises to a height that produces a tension in the spring that is at least equal to the weight of the lower cube. Actually, the spring will first go from its compressed state to its natural length and then get elongated beyond this natural length. Let / be the maximum elongation produced under these circumstances.
Then
kl = mg (1)
Now, from energy conservation,
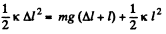 (2)
(2)
(Because at maximum elongation of the spring, the speed of upper cube becomes zero) From (1) and (2),
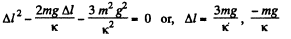
Therefore, acceptable solution of Δl equals 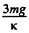
(b) Let v the velocity of upper cube at the position (say, at C) when the lower block breaks off the floor, then from energy conservation.
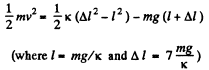
or, 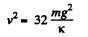 (2)
(2)
At the position C, the velocity of CM ; 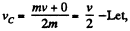 the C.M. of the system (spring + two cubes) further rises up to Δ yC2.
the C.M. of the system (spring + two cubes) further rises up to Δ yC2.
Now, from energy conservation,
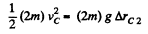
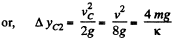
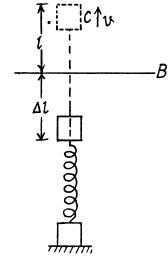
But, uptill position C, the C.M. of the system has already elevated by,
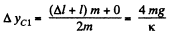
Hence, the net displacement of the C.M. of the system, in upward direction
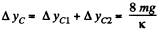
Q37: Two identical buggies 1 and 2 with one man in each move without friction due to inertia along the parallel rails toward each other. When the buggies get opposite each other, the men exchange their places by jumping in the direction perpendicular to the motion direction. As a consequence, buggy 1 stops and buggy 2 keeps moving in the same direction, with its velocity becoming equal to v. Find the initial velocities of the buggies v1 and v2 if the mass of each buggy (without a man) equals M and the mass of each man m.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Due to ejection of mass from a moving system (which moves due to inertia) in a direction perpendicular to it, the velocity of moving system does not change. The momentum change being adjusted by the forces on the rails. Hence in our problem velocities of buggies change only due to the entrance of the man coming from the other buggy. From the
Solving (1) and (2), we get
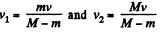
As 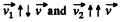
So, 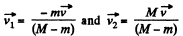
Q38: Two identical buggies move one after the other due to inertia (without friction) with the same velocity v0. A man of mass in rides the rear buggy. At a certain moment the man jumps into the front buggy with a velocity u relative to his buggy. Knowing that the mass of each buggy is equal to M, find the velocities with which the buggies will move after that.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: From momentum conservation, for the system “rear buggy with man”
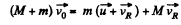 (1)
(1)
From momentum conservation, for the system (front buggy + man coming from rear buggy)
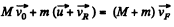
So, 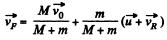
Putting the value of 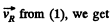
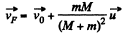
Q39: Two men, each of mass m, stand on the edge of a stationary buggy of mass M. Assuming the friction to be negligible, find the velocity of the buggy after both men jump off with the same horizontal velocity u relative to the buggy: (1) simultaneously; (2) one after the other. In what case will the velocity of the buggy be greater and how many times?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) 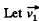 be the velocity of the buggy after both man jump off simultaneously. For the closed system (two men + buggy), from the conservation of linear momentum,
be the velocity of the buggy after both man jump off simultaneously. For the closed system (two men + buggy), from the conservation of linear momentum,
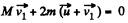
or, 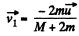 (1)
(1)
(ii) 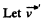 be the velocity of buggy with man, when one man jump off the buggy. For the closed system (buggy with one man + other man) from the conservation of linear momentum :
be the velocity of buggy with man, when one man jump off the buggy. For the closed system (buggy with one man + other man) from the conservation of linear momentum :
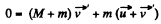 (2)
(2)
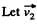 be the sought velocity of the buggy when the second man jump off the buggy; then from conservation of linear momentum of the system (buggy + one man) :
be the sought velocity of the buggy when the second man jump off the buggy; then from conservation of linear momentum of the system (buggy + one man) :
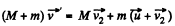 (3)
(3)
Solving equations (2) and (3) we get
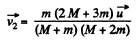 (4)
(4)
From (1) and (4)
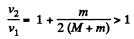
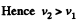
Q40: A chain hangs on a thread and touches the surface of a table by its lower end. Show that after the thread has been burned through, the force exerted on the table by the falling part of the chain at any moment is twice as great as the force of pressure exerted by the part already resting on the table.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The descending part of the chain is in free fall, it has speed 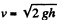 at the instant, all its points bave descended a distance y. The length of the chain which lands on the floor during the differential time interval dt following this instant is vdt.
at the instant, all its points bave descended a distance y. The length of the chain which lands on the floor during the differential time interval dt following this instant is vdt.
For the incoming chain element on the floor :
From 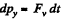 (where y - ax is is directed down)
(where y - ax is is directed down)
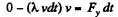
or 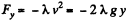
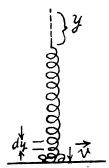
Hence, the force exerted on the falling chain equals λv2 and is directed upward. Therefore from third law the force exerted by the falling chain on the table at the same instant of time becomes λv2 and is directed downward.
Since a length of chain of weight (λyg) already lies on the table the total force on the floor is (2λyg) + (λyg) = (3λyg) or the weight of a length 3y of chain.
Q41: A steel ball of mass m = 50 g falls from the height h = 1.0 m on the horizontal surface of a massive slab. Find the cumulative momentum that the ball imparts to the slab after numerous bounces, if every impact decreases the velocity of the ball η = 1.25 times.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Velocity of the ball, with which it hits the slab, 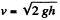
After first impact, v' = ev (upward) but according to the problem 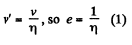 and momentum, imparted to the slab,
and momentum, imparted to the slab,
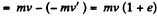
Similarly, velocity of the ball after second impact,
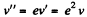
And momentum imparted 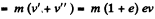
Again, momentum imparted during third impact,
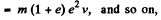
Hence, net momentum, imparted 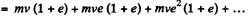
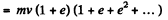
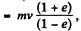 (from summation of G.P.)
(from summation of G.P.)
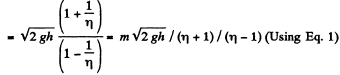
= 0.2 kg m/s. (On substitution)
Q42: A raft of mass M with a man of mass m aboard stays motionless on the surface of a lake. The man moves a distance 1' relative to the raft with velocity v'(t) and then stops. Assuming the water resistance to be negligible, find:
(a) the displacement of the raft 1 relative to the shore;
(b) the horizontal component of the force with which the man acted on the raft during the motion.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Since the resistance of water is negligibly small, the resultant of all external forces acting on the system “a man and a raft” is equal to zero. This means that the position of the C.M. of the given system does not change in the process of motion.
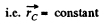
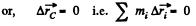
or, 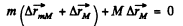
Thus, 
(b) As net external force on “man-raft” system is equal to zero, therefore the momentum of this system does not change,
So, 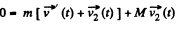
or, 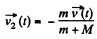 (1)
(1)
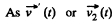 is along horizontal direction, thus the sought force on the raft
is along horizontal direction, thus the sought force on the raft
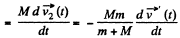
Note : we may get the result of part (a), if we integrate Eq. (1) over the time of motion of man or raft.
Q43: A stationary pulley carries a rope whose one end supports a ladder with a man and the other end the counterweight of mass M. The man of mass m climbs up a distance 1' with respect to the ladder and then stops. Neglecting the mass of the rope and the friction in the pulley axle, find the displacement 1 of the centre of inertia of this system.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In the reference frame fixed to the pulley axis the location of C.M. of the given system is described by the radius vector
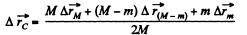
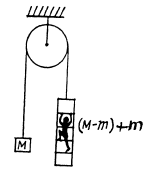
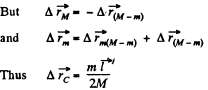
Note : one may also solve this problem using momentum conservation
Q44: A cannon of mass M starts sliding freely down a smooth inclined plane at an angle a to the horizontal. After the cannon covered the distance l, a shot was fired, the shell leaving the cannon in the horizontal direction with a momentum p. As a consequence, the cannon stopped. Assuming the mass of the shell to be negligible, as compared to that of the cannon, determine the duration of the shot.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Velocity of cannon as well as that of shell equals 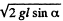 down the inclined plane taken as the positive x - axis. From the linear impulse momentum theorem in projection form along x - axis for the system (connon + shell) i.e. Δpx - Fx Δt :
down the inclined plane taken as the positive x - axis. From the linear impulse momentum theorem in projection form along x - axis for the system (connon + shell) i.e. Δpx - Fx Δt :
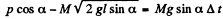 (as mass of the shell is negligible)
(as mass of the shell is negligible)
or, 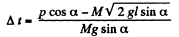
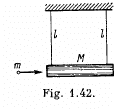
Q45: A horizontally flying bullet of mass m gets stuck in a body of mass M suspended by two identical threads of length l (Fig. 1.42). As a result, the threads swerve through an angle 0. Assuming m << M, find:
(a) the velocity of the bullet before striking the body;
(b) the fraction of the bullet's initial kinetic energy that turned into heat.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: From conservation of momentum, for the system (bullet + body) along the initial direction of bullet
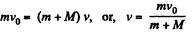
Q46: A body of mass M (Fig. 1.43) with a small disc of mass m placed on it rests on a smooth horizontal plane. The disc is set in motion in the horizontal direction with velocity v. To what height (relative to the initial level) will the disc rise after breaking off the body M? The friction is assumed to be absent.

 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: From conservation of momentum, along x-axis for the system (disc + body)
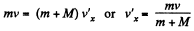 (1)
(1)
And from energy conservation, for the same system in the field of gravity :
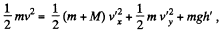
where h! is the height of break off point from initial level. So,
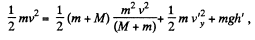 using (1)
using (1)
or, 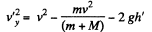
Also, if h" is the height of the disc, from the break-off point,
then, 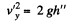
So, 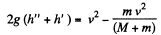
Hence, the total height, raised from the initial level
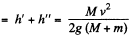
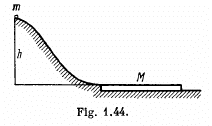
Q47: A small disc of mass m slides down a smooth hill of height h without initial velocity and gets onto a plank of mass M lying on the horizontal plane at the base of the hill (Fig. 1.44). Due to friction between the disc and the plank the disc slows down and, beginning with a certain moment, moves in one piece with the plank
(1) Find the total work performed by the friction forces in this process.
(2) Can it be stated that the result obtained does not depend on the choice of the reference frame?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) When the disc slides and comes to a plank, it has a velocity equal to 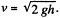 Due to friction between the disc and the plank the disc slows down and after some time the disc moves in one piece with the plank with velocity v' (say).
Due to friction between the disc and the plank the disc slows down and after some time the disc moves in one piece with the plank with velocity v' (say).
From the momentum conservation for the system (disc + plank) along horizontal towards right :
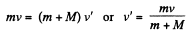
Now from the equation of the increment of total mechanical energy of a system :
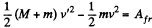
or, 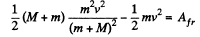
so, 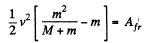
Hence, 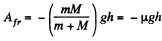
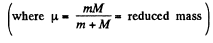
(b) We look at the problem from a frame in which the hill is moving (together with the disc on it) to the right with speed il Then in this frame the speed of the disc when it just gets onto the plank is, by the law of addition of velocities, 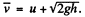 Similarly the common speed of the plank and the disc when they move together is
Similarly the common speed of the plank and the disc when they move together is
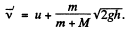
Then as above 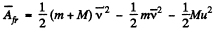
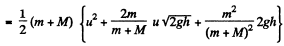
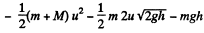
We see that 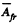 is independent of u and is in fact just - μ g h as in (a). Thus the result obtained does not depend on the choice of reference frame.
is independent of u and is in fact just - μ g h as in (a). Thus the result obtained does not depend on the choice of reference frame.
Do note however that it will be in correct to apply “conservation of energy” formula in the frame in which the hill is moving. The energy carried by the hill is not negligible in this frame. See also the next problem.
Q48: A stone falls down without initial velocity from a height h onto the Earth's surface. The air drag assumed to be negligible, the stone hits the ground with velocity 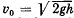 relative to the Earth. Obtain the same formula in terms of the reference frame "falling" to the Earth with a constant velocity v0.
relative to the Earth. Obtain the same formula in terms of the reference frame "falling" to the Earth with a constant velocity v0.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In a frame moving relative to the earth, one has to include the kinetic energy of the earth as well as earth’s acceleration to be able to apply conservation of energy to the problem. In a reference frame falling to the earth with velocity v0, the stone is initially going up with velocity v0 and so is the earth. The final velocity of the stone is 0 = v0 - gt and that of the earth is 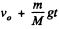 (M is the mass of the earth), from Newton’s third law, where t = time of fall. From conservation of energy
(M is the mass of the earth), from Newton’s third law, where t = time of fall. From conservation of energy
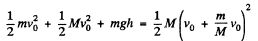
Hence 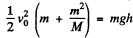
Negecting 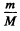 in comparison with 1, we get
in comparison with 1, we get
 The point is this in earth’s rest frame the effect of earth’s accleration is of order
The point is this in earth’s rest frame the effect of earth’s accleration is of order 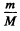 and can be neglected but in a frame moving with respect to the earth the effect of earth’s acceleration must be kept because it is of order one (i.e. large).
and can be neglected but in a frame moving with respect to the earth the effect of earth’s acceleration must be kept because it is of order one (i.e. large).
Q49: A particle of mass 1.0 g moving with velocity v1 = 3.0i - 2.0j experiences a perfectly inelastic collision with another particle of mass 2.0 g and velocity v2 = 4.0j — 6.0k. Find the velocity of the formed particle (both the vector v and its modulus), if the components of the vectors v1 and v2 are given in the SI units.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: From conservation of momentum, for the closed system “both colliding particles”
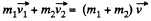
or, 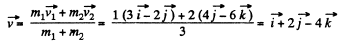
Hence 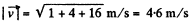
Q50: Find the increment of the kinetic energy of the closed system comprising two spheres of masses m1 and m2 due to their perfectly inelastic collision, if the initial velocities of the spheres were equal to v1 and v2.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: For perfectly inelastic collision, in the C.M. frame, final kinetic energy of the colliding system (both spheres) becomes zero. Hence initial kinetic energy of the system in C.M. frame completely turns into the internal energy (Q) of the formed body. Hence
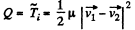
N ow from energy conservation 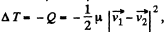
In lab frame the same result is obtained as
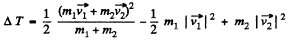
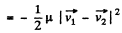
Q51: A particle of mass m1 experienced a perfectly elastic collision with a stationary particle of mass m2. What fraction of the kinetic energy does the striking particle lose, if
(a) it recoils at right angles to its original motion direction;
(b) the collision is a head-on one?
 View Answer
View Answer 
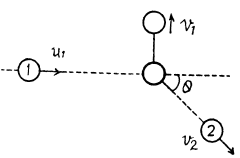
Ans: (a) Let the initial and final velocities of 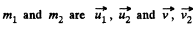 respectively.
respectively.
T hen from conservation o f momentum along horizontal and vertical directions, w e g et :
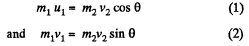
Squaring (1) and (2) and then adding them,
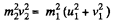
Now, from kinetic energy conservation,
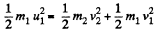 (3)
(3)
or, 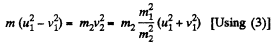
or, 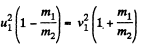
or, 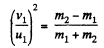 (4)
(4)
So, fraction of kinetic energy lost by the particle 1,
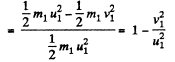
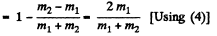 (5)
(5)
(b) When the collision occurs head on,
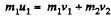
and from conservation of kinetic energy,
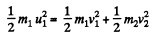
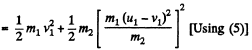
or, 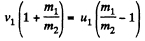
or, 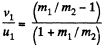 (6)
(6)
Fraction of kinetic energy, lost
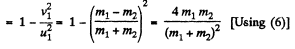
Q52: Particle 1 experiences a perfectly elastic collision with a stationary particle 2. Determine their mass ratio, if
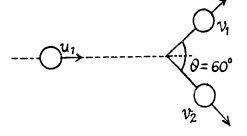
(a) after a head-on collision the particles fly apart in the opposite directions with equal velocities;
(b) the particles fly apart symmetrically relative to the initial motion direction of particle 1 with the angle of divergence θ = 60°.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) When the particles fly apart in opposite direction with equal velocities (say v), then from conservation of momentum,
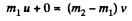 (1)
(1)
and from conservation of kinetic energy,
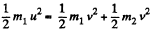
or, 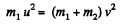 (2)
(2)
From Eq. (1) and (2),
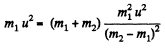
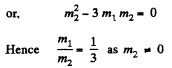
(b) When they fly apart symmetrically relative to the initial motion direction with the angle of divergence θ = 60°,
From conservation of momentum, along horizontal and vertical direction,
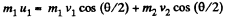 (1)
(1)
and 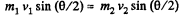
or, 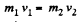 (2)
(2)
Now, from conservation of kinetic energy,
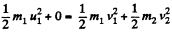 (3)
(3)
From (1) and (2),
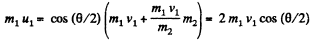
So, 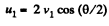 (4)
(4)
From (2), (3), and (4)
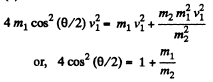
or, 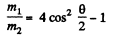
and putting the value of 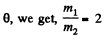
Q53: A ball moving translationally collides elastically with another, stationary, ball of the same mass. At the moment of impact the angle between the straight line passing through the centres of the balls and the direction of the initial motion of the striking ball is equal to α = 45°. Assuming the balls to be smooth, find the fraction η of the kinetic energy of the striking ball that turned into potential energy at the moment of the maximum deformation.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 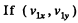 are the instantaneous velocity components of the incident ball and
are the instantaneous velocity components of the incident ball and 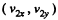 are the velocity components of the struck ball at the same moment, then since there are no external impulsive forces (i.e. other than the mutual interaction of the balls)
are the velocity components of the struck ball at the same moment, then since there are no external impulsive forces (i.e. other than the mutual interaction of the balls)
We have
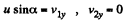

The impulsive force of mutual interaction satisfies
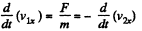
(F is along the x axis as the balls are smooth. Thus Y component of momentum is not transferred.) Since loss o f K.E. is stored as deformation energy D, we have
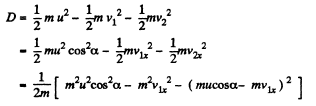
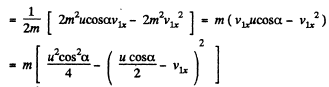
We see that D is maximum when
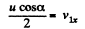
and 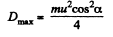
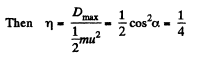
On subsituting α =45°
Q54: A shell flying with velocity v = 500 m/s bursts into three identical fragments so that the kinetic energy of the system increases η = 1.5 times. What maximum velocity can one of the fragments obtain?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: From the conservation of linear momentum of the shell just before and after its fragmentation
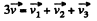 (1)
(1)
where 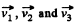 are the velocities of its fragments.
are the velocities of its fragments.
From the energy conservation 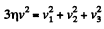 (2)
(2)
Now 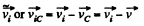 (3)
(3)
where 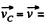 velocity of the C M . of the fragments the velocity of the shell. Obviously in the C.M. frame be linear momentum of a system is equal to zero, so
velocity of the C M . of the fragments the velocity of the shell. Obviously in the C.M. frame be linear momentum of a system is equal to zero, so
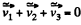 (4)
(4)
Using (3) and (4) in (2), we get
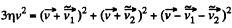
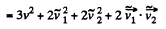
or, 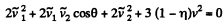 (5)
(5)
If we have had used 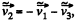 then Eq. 5 were contain
then Eq. 5 were contain  and so on.
and so on.
The problem being symmetrical we can look for the maximum of any one. Obviously it will be the same for each.
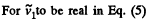
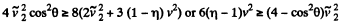
So, 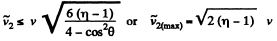
Hence 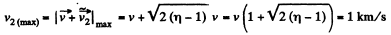
Thus owing to the symmetry
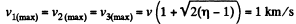
Q55: Particle 1 moving with velocity v = 10 m/s experienced a head-on collision with a stationary particle 2 of the same mass. As a result of the collision, the kinetic energy of the system decreased by η = 1.0%. Find the magnitude and direction of the velocity of particle 1 after the collision.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Since, the collision is head on, the particle 1 will continue moving along the same line as before the collision, but there will be a change in the magnitude of it’s velocity vector.
Let it starts moving with velocity v1 and particle 2 with v2 after collision, then from the conservation of momentum
mu = mv1 + mv2 or, u = v1 + v2 (1)
And from the condition, given,
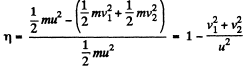
or, 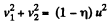 (2)
(2)
From (1) and (2),
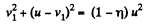
or, 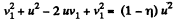
or, 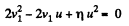
So, 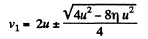
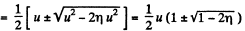
Positive sign gives the velocity of the 2nd particle which lies ahead. The negative sign is correct for v1.
So, 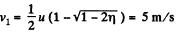 will continue moving in the same direction.
will continue moving in the same direction.
Note that 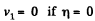 as it must.
as it must.
Q56: A particle of mass m having collided with a stationary particle of mass M deviated by an angle π/2 whereas the particle M recoiled at an angle θ = 30° to the direction of the initial motion of the particle tn. How much (in per cent) and in what way has the kinetic energy of this system changed after the collision, if M/m = 5.0?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Since, no external impulsive force is effective on the system “M + m”, its total momentum along any direction will remain conserved.
So from px = const.
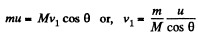 (1)
(1)
and from py = const
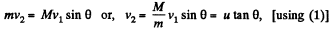
Final kinetic energy of the system
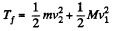
And initial kinetic energy of the system 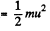
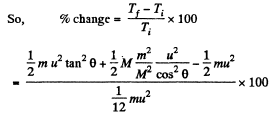
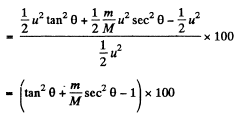
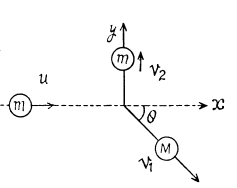
and putting the values of θ and m/M , we get % of change in kinetic energy = - 40 %
Q57: A closed system consists of two particles of masses m1 and m2 which move at right angles to each other with velocities v1 and v2. Find:
(a) the momentum of each particle and
(b) the total kinetic energy of the two particles in the reference frame fixed to their centre of inertia.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Let the particles m1 and m2 move with velocities 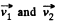 respectively. On the basis of solution of problem 1.147 (b)
respectively. On the basis of solution of problem 1.147 (b)
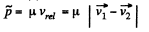
As 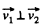
So, 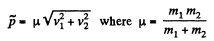
(b) Again from 1.147 (b)
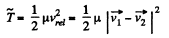
So, 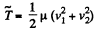
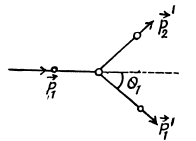
Q58: A particle of mass m1 collides elastically with a stationary particle of mass m2 (m1 > m2). Find the maximum angle through which the striking particle may deviate as a result of the collision.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: From conservation of momentum
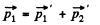
so 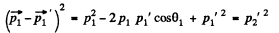
From conservation of energy
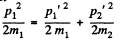
Eliminating p2’ we get
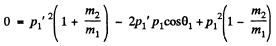
This quadratic equation for p1' has a real solution in terms of p1 and cos θ1 only if
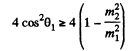
or 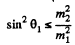
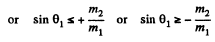
This clearly implies (since only + sign makes sense) that
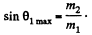
Q59: Three identical discs A, B, and C (Fig. 1.45) rest on a smooth horizontal plane. The disc A is set in motion with velocity v after which it experiences an elastic collision simultaneously with the discs B and C. The distance between the centres of the latter discs prior to the collision is η times greater than the diameter of each disc. Find the velocity of the disc A after the collision. At what value of η will the disc A recoil after the collision; stop; move on?
 View Answer
View Answer 
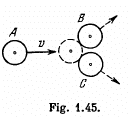
Ans: From the symmetry of the problem, the velocity of the disc A will be directed either in the initial direction or opposite to it just after the impact Let the velocity of the disc A after the collision be v' and be directed towards right after the collision. It is also clear from the symmetry of problem that the discs B and C have equal speed (say v") in the directions, shown. From the condition of the problem,
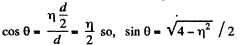 (1)
(1)
For the three discs, system, from the conservation of linear momentum in the symmetry direction (towards right)
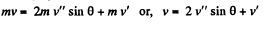 (2)
(2)
From the definition of the coefficient of restitution, we have for the discs A and B (or C)
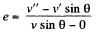
But e = 1, for perfectly elastic collision,
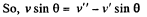 (2)
(2)
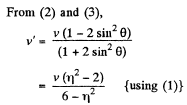
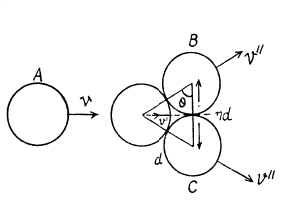
Hence we have,
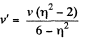
Therefore, the disc A will recoil if 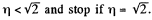
Note : One can write the equations of momentum conservation along the direction perpendicular to the initial direction of disc A and the consevation of kinetic energy instead of the equation of restitution.
Q60: A rocket ejects a steady jet whose velocity is equal to u relative to the rocket. The gas discharge rate equals μ kg/s. Demonstrate that the rocket motion equation in this case takes the form 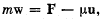
where m is the mass of the rocket at a given moment, w is its acceleration, and F is the external force.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Suppose that at time tf the rocket has the mass m and the velocity 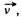 relative to the reference frame, employed. Now consider the inertial frame moving with the velocity that the rocket has at the given moment. In this reference frame, the momentum increment that the rocket & ejected gas system acquires during time dt is
relative to the reference frame, employed. Now consider the inertial frame moving with the velocity that the rocket has at the given moment. In this reference frame, the momentum increment that the rocket & ejected gas system acquires during time dt is
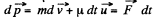
or, 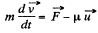
or, 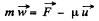
Q61: A rocket moves in the absence of external forces by ejecting a steady jet with velocity u constant relative to the rocket. Find the velocity v of the rocket at the moment when its mass is equal to m, if at the initial moment it possessed the mass m0 and its velocity was equal to zero. Make use of the formula given in the foregoing problem.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: According to the question, 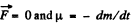 so the equation for this system becomes,
so the equation for this system becomes,
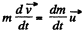
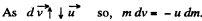
Integrating within the limits :
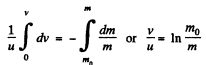
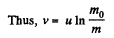
As 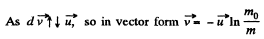
Q62: Find the law according to which the mass of the rocket varies with time, when the rocket moves with a constant acceleration w, the external forces are absent, the gas escapes with a constant velocity u relative to the rocket, and its mass at the initial moment equals m0.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: According to the question, 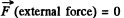
So, 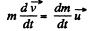
As 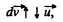
so, in scalar form, 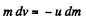
or,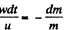
Integrating within the limits for m (t)
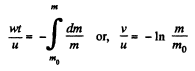
Hence, 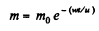
Q63: A spaceship of mass m0 moves in the absence of external forces with a constant velocity v0. To change the motion direction, a jet engine is switched on. It starts ejecting a gas jet with velocity u which is constant relative to the spaceship and directed at right angles to the spaceship motion. The engine is shut down when the mass of the spaceship decreases to m. Through what angle α did the motion direction of the spaceship deviate due to the jet engine operation?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 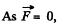 from the equation of dynamics of a body with variable mass;
from the equation of dynamics of a body with variable mass;
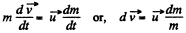 (1)
(1)
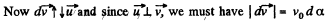 (because v0 is constant) Where d α is the angle by which the spaceship,turns in time dt.
(because v0 is constant) Where d α is the angle by which the spaceship,turns in time dt.
So, 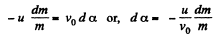
or, 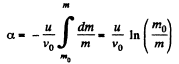
Q64: A cart loaded with sand moves along a horizontal plane due to a constant force F coinciding in direction with the cart's velocity vector. In the process, sand spills through a hole in the bottom with a constant velocity μ kg/s. Find the acceleration and the velocity of the cart at the moment t, if at the initial moment t = 0 the cart with loaded sand had the mass m0 and its velocity was equal to zero. The friction is to be neglected.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 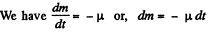
Integrating 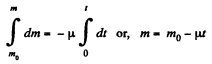
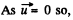 from the equation of variable mass system :
from the equation of variable mass system :
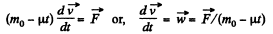
or, 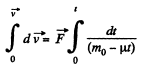
Hence 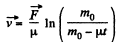
Q65: A flatcar of mass mo starts moving to the right due to a from a stationary hopper. The velocity of loading is constant and equal to p, kg/s. Find the time dependence of the velocity and the acceleration of the flatcar in the process of loading. The friction is negligibly small.
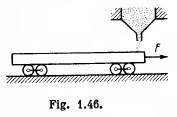
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let the car be moving in a reference frame to which the hopper is fixed and at any instant of time, let its mass be m and velocity
Then from the general equation, for variable mass system.
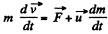
We write the equation, for our system as,
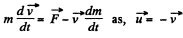 (1)
(1)
So 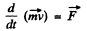
and 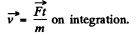
But 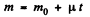
so, 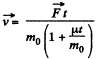
Thus the sought acceleration, 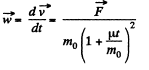
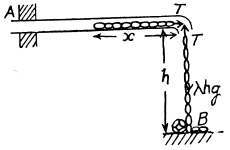
Q66: A chain AB of length l is located in a smooth horizontal tube so that its fraction of length h hangs freely and touches the surface of the table with its end B (Fig. 1.47). At a certain moment the end A of the chain is set free. With what velocity will this end of the chain slip out of the tube ?
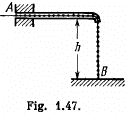
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let the length of the chain inside the smooth horizontal tube at an arbitrary instant is x. From the equation,
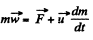
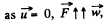 for the chain inside the tube
for the chain inside the tube
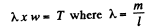 (1)
(1)
Similarly for the overhanging,
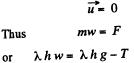 (2)
(2)
From (1) and (2
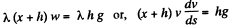
or, 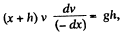
[As the length of the chain inside the tube decreases with time, ds = - dx.]
or, 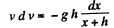
Integrating, 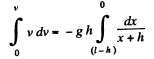
or, 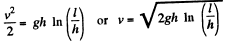
Q67: The angular momentum of a particle relative to a certain point 0 varies with time as M = a + bt2, where a and b are constant vectors, with a ⊥ b. Find the force moment N relative to the point O acting on the particle when the angle between the vectors N and M equals 45°.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Force moment relative to point O ;
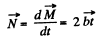
Let the angle between 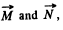
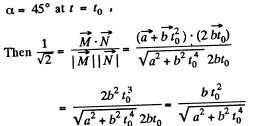
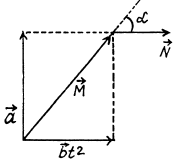
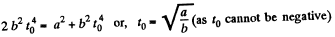
It is also obvious from the figure that the angle α is equal to 45° at the moment t0.
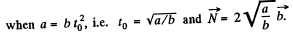
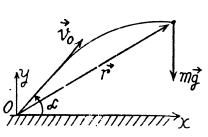
Q68: A ball of mass m is thrown at an angle α to the horizontal with the initial velocity v0. Find the time dependence of the magnitude of the ball's angular momentum vector relative to the point from which the ball is thrown. Find the angular momentum M at the highest point of the trajectory if m = 130 g, α = 45°, and v0 = 25 m/s. The air drag is to be neglected.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 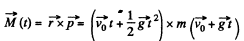
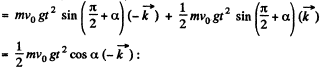
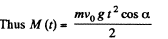
Thus angular momentum at maximum height
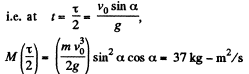
Alternate :
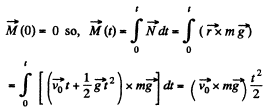
Q69: A disc A of mass m sliding over a smooth horizontal surface with velocity v experiences a perfectly elastic collision with a smooth stationary wall at a point O (Fig. 1.48). The angle between the motion direction of the disc and the normal of the wall is equal to α. Find:
(a) the points relative to which the angular momentum M of the disc remains constant in this process;
(b) the magnitude of the increment of the vector of the disc's angular momentum relative to the point O' which is located in the plane of the disc's motion at the distance l from the point O.
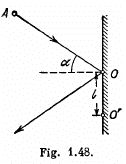
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The disc experiences gravity, the force of reaction of the horizontal surface, and the force  reaction of the wall at the moment of the impact against it. The first two forces counter-balance each other, leaving only the force
reaction of the wall at the moment of the impact against it. The first two forces counter-balance each other, leaving only the force 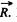 It’s moment relative to any point of the line along which the vector
It’s moment relative to any point of the line along which the vector 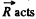 or along normal to the wall is equal to zero and therefore the angular momentum of the disc relative to any of these points does not change in the given process.
or along normal to the wall is equal to zero and therefore the angular momentum of the disc relative to any of these points does not change in the given process.
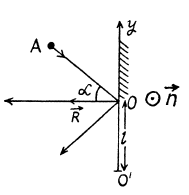
(b) During the course of collision with wall the position of disc is same and is equal to  Obviously the increment in linear momentum of the ball
Obviously the increment in linear momentum of the ball 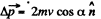
Here, 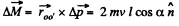 and directed normally emerging from the plane of figure
and directed normally emerging from the plane of figure
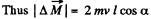
Q70: A small ball of mass m suspended from the ceiling at a point O by a thread of length l moves along a horizontal circle with a constant angular velocity ω. Relative to which points does the angular momentum M of the ball remain constant? Find the magnitude of the increment of the vector of the ball's angular momentum relative to the point O picked up during half a revolution.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The ball is under the influence of forces 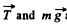 at all the moments of time, while moving along a horizontal circle. Obviously the vertical component of
at all the moments of time, while moving along a horizontal circle. Obviously the vertical component of 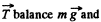 so the net moment of these two about any point becomes zero. The horizontal component of
so the net moment of these two about any point becomes zero. The horizontal component of 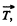 which provides the centripetal acceleration to ball is already directed toward the centre (C) of the horizontal circle , thus its moment about the point C equals zero at all the moments of time. Hence the net moment of the force acting on the ball about point C equals zero and that’s why the angular momentum of the ball is con served about the horizontal circle.
which provides the centripetal acceleration to ball is already directed toward the centre (C) of the horizontal circle , thus its moment about the point C equals zero at all the moments of time. Hence the net moment of the force acting on the ball about point C equals zero and that’s why the angular momentum of the ball is con served about the horizontal circle.
(b) Let a be the angle which the thread forms with the vertical.
Now from equation of particle dynamics :
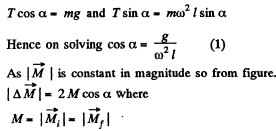
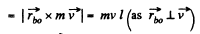
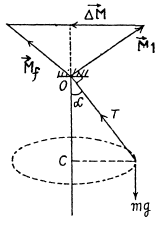
Q71: A ball of mass m falls down without initial velocity from a height h over the Earth's surface. Find the increment of the ball's angular momentum vector picked up during the time of falling (relative to the point O of the reference frame moving translationally in a horizontal direction with a velocity V). The ball starts falling from the point O. The air drag is to be neglected.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: During the free fall time 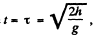 the reference point O moves in hoizontal direction (say tow ards right) b y the distance Vτ. In the translating fram e as
the reference point O moves in hoizontal direction (say tow ards right) b y the distance Vτ. In the translating fram e as 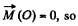
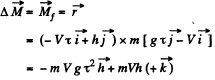
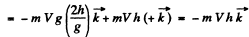
Hence 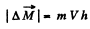
Q72: A smooth horizontal disc rotates with a constant angular velocity ω about a stationary vertical axis passing through its centre, the point O. At a moment t = 0 a disc is set in motion from that point with velocity v0. Find the angular momentum M (t) of the disc relative to the point 0 in the reference frame fixed to the disc. Make sure that this angular momentum is caused by the Coriolis force.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Coriolis force is. 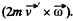
Here 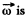 along the z-axis (vertical). The moving disc is moving with velocity v0 which is constant. The motion is along the x-axis say. Then the Coriolis force is along y-axis and has the m agnitude
along the z-axis (vertical). The moving disc is moving with velocity v0 which is constant. The motion is along the x-axis say. Then the Coriolis force is along y-axis and has the m agnitude 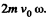 At time t, the distance of the centre of moving disc from
At time t, the distance of the centre of moving disc from 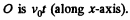 Thus the torque N due to the coriolis force is
Thus the torque N due to the coriolis force is
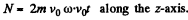
Hence equating this to 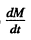
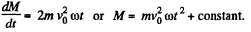
The constant is irrelevant and may be put equal to zero if the disc is originally set in motion from the point O.
This discussion is approximate. The Coriolis force will cause the disc to swerve from straight line motion and thus cause deviation from the above formula which will be substantial for large t.
Q73: A particle moves along a closed trajectory in a central field of force where the particle's potential energy U = kr2 (k is a positive constant, r is the distance of the particle from the centre O of the field). Find the mass of the particle if its minimum distance from the point O equals r1 and its velocity at the point farthest from 0 equals v2.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: If r = radial velocity of the particle then the total .energy of the particle at any instant is
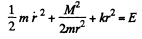 (1)
(1)
where the second term is the kinetic energy of angular motion about the centre O. Then the extreme values of r are determined by r = 0 and solving the resulting quadratic equation
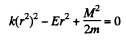
we get
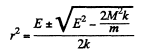
From this we see that
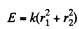 (2)
(2)
where r1 is the minimum distance from O and r2 is the maximum distance. Then
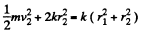
Hence, 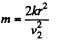
Note : Eq. (1) can be derived from the standard expression for kinetic energy and angular momentum in plane poler coordinates :
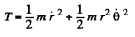
M = angular momentum = mr2θ
Q74: A small ball is suspended from a point O by a light thread of length l. Then the ball is drawn aside so that the thread deviates through an angle θ from the vertical and set in motion in a horizontal direction at right angles to the vertical plane in which the thread is located. What is the initial velocity that has to be imparted to the ball so that it could deviate through the maximum angle π/2 in the process of motion?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The swinging sphere experiences two forces : The gravitational force and the tension of the thread. Now, it is clear from the condition, given in the problem, that the moment of these forces about the vertical axis, passing through the point of suspension Nz = 0. Consequently, the angular momentum Mz of the sphere relative to the given axis (z) is constant.
Thus 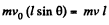 (1)
(1)
where m is the mass of the sphere and v is it s velocity in the position, when the thread 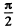 forms an angle with the vertical. Mechanical energy is also conserved, as the sphere is under the influence if only one other force, i.e. tension, which does not perform any work, as it is always perpendicular to the velocity.
forms an angle with the vertical. Mechanical energy is also conserved, as the sphere is under the influence if only one other force, i.e. tension, which does not perform any work, as it is always perpendicular to the velocity.
So,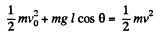 (2)
(2)
From (1) and (2), we get,
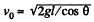
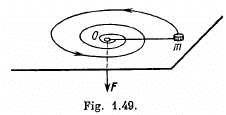
Q75: A small body of mass m tied to a non-stretchable thread moves over a smooth horizontal plane. The other end of the thread is being drawn into a hole O (Fig. 1.49) with a constant velocity. Find the thread tension as a function of the distance r between the body and the hole if at r = r0 the angular velocity of the thread is equal to ω.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Forces, acting on the mass m are shown in the figure. As 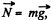 the net torque of these two forces about any tixed point must be equal to zero. Tension T, acting on the mass m is a central force, which is always directed towards the centre O. Hence the moment of force T is also zero about the point 0 and therefore the angular momentum of the particle m is conserved about O.
the net torque of these two forces about any tixed point must be equal to zero. Tension T, acting on the mass m is a central force, which is always directed towards the centre O. Hence the moment of force T is also zero about the point 0 and therefore the angular momentum of the particle m is conserved about O.
Let, the angular velocity of the particle be to, when the separation between hole and particle m is r, then from the conservation of momentum about the point O, : 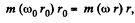
or 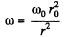
Now, from the second law of motion for m,

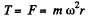
Hence the sought tension;
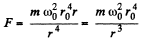
Q76: A light non-stretchable thread is wound on a massive fixed pulley of radius R. A small body of mass m is tied to the free end of the thread. At a moment t = 0 the system is released and starts moving. Find its angular momentum relative to the pulley axle as a function of time t.
Ans: On the given system the weight of the body m is the only force whose moment is effective about the axis of pulley. Let us take the sense of co of the pulley at an arbitrary instant 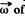 the pulley at an arbitrary instant as the positive sense of axis of rotation (z - axis)
the pulley at an arbitrary instant as the positive sense of axis of rotation (z - axis)
As 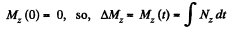
So, 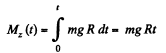
Q77: A uniform sphere of mass m and radius R starts rolling without slipping down an inclined plane at an angle α to the horizontal. Find the time dependence of the angular momentum of the sphere relative to the point of contact at the initial moment. How will the obtained result change in the case of a perfectly smooth inclined plane?
 View Answer
View Answer 
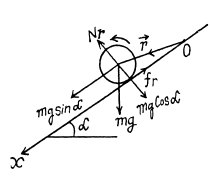
Ans: Let the point of contact of sphere at initial moment (t = 0) be at O. At an arbitrary moment, the forces acting on the sphere are shown in the figure. We have normal reaction Nr = mg sin a and both pass through same line and the force of static friction passes through the point O, thus the moment about point O becomes zero. Hence mg sin a is the only force which has effective torque about point 0, and is given by 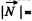 mgR sin α normally emerging from the plane of figure.
mgR sin α normally emerging from the plane of figure.
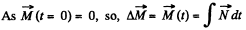
Hence , 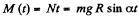
Q78: A certain system of particles possesses a total momentum p and an angular momentum M relative to a point O. Find its angular momentum M' relative to a point O' whose position with respect to the point O is determined by the radius vector r0. Find out when the angular momentum of the system of particles does not depend on the choice of the point O.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let position vectors of the particles of the system be 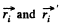 with respect to the points O and O' respectively. Then we have,
with respect to the points O and O' respectively. Then we have,
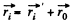 (1)
(1)
where 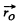 is the radius vector of O' with respect to O.
is the radius vector of O' with respect to O.
Now, the angular momentum of the system relative to the point O can be written as follows;
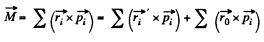 [using (1)]
[using (1)]
or, 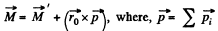 (2)
(2)
From (2), if the total linear momentum of the system, 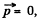 then its angular momen tum does not depend on the choice of the point O.
then its angular momen tum does not depend on the choice of the point O.
Note that in the C M . frame, the system of particles, as a whole is at rest.
Q79: Demonstrate that the angular momentum M of the system of particles relative to a point 0 of the reference frame K can be represented as 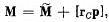
where 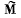 is its proper angular momentum (in the reference frame moving translationally and fixed to the centre of inertia), rc is the radius vector of the centre of inertia relative to the point O, p is the total momentum of the system of particles in the reference frame K.
is its proper angular momentum (in the reference frame moving translationally and fixed to the centre of inertia), rc is the radius vector of the centre of inertia relative to the point O, p is the total momentum of the system of particles in the reference frame K.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: On the basis of solution of problem 1.196, we have concluded that; “in the C.M. frame, the angular momentum of system of particles is independent of the choice of the point, relative to which it is determined” and in accordance with the problem, this is denoted by 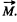
We denote the angular momentum of the system of particles, relative to the point O, by 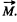 Since the internal and proper angular momentum
Since the internal and proper angular momentum 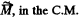 frame, does not depend on the choice of the point O', this point may be taken coincident with the point O of the A-frame, at a given moment of time. Then at that moment, the radius vectors of all the particles, in both reference frames, are equal
frame, does not depend on the choice of the point O', this point may be taken coincident with the point O of the A-frame, at a given moment of time. Then at that moment, the radius vectors of all the particles, in both reference frames, are equal 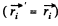 and the velocities are related by the equation,
and the velocities are related by the equation,
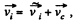 (1)
(1)
where 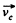 is the velocity of C.M. frame, relative to the A-frame. Consequently, we may write,
is the velocity of C.M. frame, relative to the A-frame. Consequently, we may write,
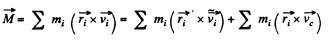
or, 
or, 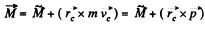
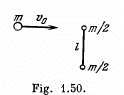
Q80: A ball of mass m moving with velocity v0 experiences a head-on elastic collision with one of the spheres of a stationary rigid dumbbell as whown in Fig. 1.50. The mass of each sphere equals m/2, and the distance between them is l. Disregarding the size of the spheres, find the proper angular momentum 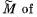 the dumbbell after the collision, i.e. the angular momentum in the reference frame moving translationally and fixed to the dumbbell's centre of inertia.
the dumbbell after the collision, i.e. the angular momentum in the reference frame moving translationally and fixed to the dumbbell's centre of inertia.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: From conservation of linear momentum along the direction of incident ball for the system consists with colliding ball and sphere
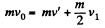
where v' and v1 are the velocities of ball and sphere 1 respectively after collision. (Remember that the collision is head on).
As the collision is perfectly elastic, from the definition of co-efficient of restitution,
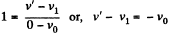 (2)
(2)
Solving (1) and (2), we get,

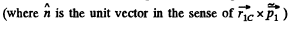
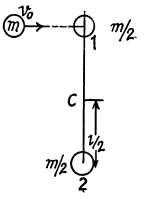
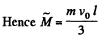
Q81: Two small identical discs, each of mass m, lie on a smooth horizontal plane. The discs are interconnected by a light non-deformed spring of length l0 and stiffness x. At a certain moment one of the discs is set in motion in a horizontal direction perpendicular to the spring with velocity v0. Find the maximum elongation of the spring in the process of motion, if it is known to be considerably less than unity.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In the C.M. frame of the system (both the discs + spring), the linear momentum of the discs are related by the relation, 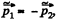 at all the moments of time.
at all the moments of time.
where, 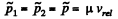
And the total kinetic energy of the system,
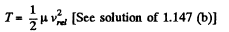
Bearing in mind that at the moment of maximum deformation of the spring, the projection of 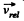 along the length of the spring becomes zero, i.e.
along the length of the spring becomes zero, i.e. 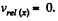
The conservation of mechanical energy of the considered system in the C.M. frame gives.
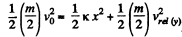 (1)
(1)
Now from the conservation of angular momentum of the system about the C.M.,
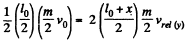
or, 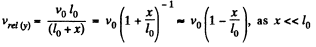 (2)
(2)
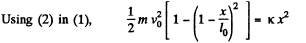
or, 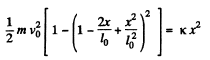
or, 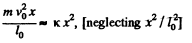
As 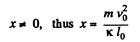
|
96 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Laws of Conservation of Energy, Momentum & Angular Momentum - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the law of conservation of energy? |  |
| 2. How does momentum conservation apply in collisions? |  |
| 3. What is angular momentum conservation and when does it apply? |  |
| 4. How can the conservation laws of energy, momentum, and angular momentum be used in physics problems? |  |
| 5. Are there any real-world examples where conservation laws of energy, momentum, and angular momentum are violated? |  |






















