Part XVII of the Constitution deals with the official language in Articles 343 to 351. Its provisions are divided into four heads—Language of the Union, Regional languages, Language of the judiciary and texts of laws and Special directives.
Language of the Union
- Official Language: Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, is to be the official language of the Union. However, the form of numerals to be used for official purposes is the international form of Indian numerals, not Devanagari numerals.
- Use of English: For 15 years (from 1950 to 1965), English would continue to be used for all official purposes of the Union, as it was before 1950.
- Post-1965: After 15 years, Parliament may decide whether to continue using English for specific purposes.
- Presidential Commissions: Every five years (and again after ten years), the President is to appoint a commission to make recommendations on the progressive use of Hindi, restrictions on the use of English, and other related issues.
- Parliamentary Committee: A committee of Parliament is formed to examine the recommendations of the commission and report its views to the President.
Historical Steps Taken:
- 1955: The President appointed the Official Language Commission under B.G. Kher, which submitted its report in 1956.
- 1957: A Parliamentary committee, chaired by Gobind Ballabh Pant, examined the report.
- 1960: No further Official Language Commission was appointed.
Official Languages Act, 1963:
- Continued Use of English: The Act provided for the continued use of English, along with Hindi, for all official purposes of the Union.
- Amendment in 1967: The Act was amended to make the use of English, in addition to Hindi, compulsory in certain cases, and there was no time limit for using English.
Regional Languages
The Constitution does not specify the official language of different states. In this regard, it makes the following provisions: . The legislature of a state may adopt any one or more of the languages in use in the state or Hindi as the official language of that state. Until that is done, English is to continue as official language of that state.
State's Official Language:
- The legislature of a state may adopt one or more of the languages used in the state or Hindi as the official language.
- If no decision is made, English continues to be the official language of the state.
- Most states have adopted their major regional language as the official language, and the choice is not limited to the languages in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution.
Communication Between the Union and States:
- English remains the link language for communication between the Union and states or between states.
- However, two or more states can agree to use Hindi for communication between themselves instead of English.
- The Official Languages Act, 1963 specifies that English should be used for communication between the Union and non-Hindi states.
- If Hindi is used for communication between a Hindi and a non-Hindi state, it must be accompanied by an English translation.
Recognition of Languages for Official Use:
- If a significant portion of the population in a state demands recognition of a language, the President may direct that such a language be officially recognized in the state.
- This provision ensures the protection of linguistic interests of minorities in states.
Question for Laxmikanth Summary: Official Language
Try yourself:
Which language is the official language of the Union according to Part XVII of the Constitution?Explanation
- Hindi is designated as the official language of the Union according to the provisions of Part XVII of the Constitution.
Report a problem
Language of the Judiciary and Text Laws
The constitutional provisions dealing with the language of the courts and legislation are as follows:

Proceedings in Courts: English is to be used in all proceedings in the Supreme Court and in every High Court, unless Parliament provides otherwise.
Language for Legislation: The authoritative texts of all bills, acts, ordinances, orders, rules, regulations, and bylaws at both the Central and State levels are to be in English.
Use of Hindi or Other State Languages in High Courts:
- The Governor of a state, with the President’s consent, can authorize the use of Hindi or any other official language of the state for proceedings in the state's High Court.
- However, judgements, decrees, and orders of the High Court must continue to be in English, unless Parliament provides otherwise.
State Legislation:
- A state legislature can prescribe the use of any language (other than English) for bills, acts, ordinances, orders, rules, regulations, or bylaws.
- A translation of these documents in English must be published.
Official Languages Act, 1963:
- Hindi translation of acts, ordinances, orders, regulations, and bylaws published under the authority of the President is considered the authoritative text.
- Every bill introduced in Parliament must be accompanied by a Hindi translation.
- Similarly, a Hindi translation of state acts or ordinances must be provided in certain cases.
Governor's Authority: The Governor of a state, with the President's consent, can authorize the use of Hindi or any other official language of the state for judgements, decrees, and orders passed by the state’s High Court, but they must also be accompanied by an English translation.
Supreme Court: The Supreme Court has not made provisions for the use of Hindi. Therefore, it only hears petitions or appeals in English.
Authorised Translations (Central Laws) Act, 1973: This Act states that a translation of any Central Act, ordinance, order, rule, regulation, or bylaw published in the Official Gazette under the authority of the President in any regional language specified in the Eighth Schedule (other than Hindi) is considered the authoritative text in that language.
Special Directives
The Constitution contains certain special directives to protect the interests of linguistic minorities and to promote the development of the Hindi language. There are:
Protection of Linguistic Minorities
Right to Submit Representations:
- Every aggrieved person has the right to submit a representation to any officer or authority of the Union or a state in any of the languages used in the Union or the state.
- A representation cannot be rejected on the ground that it is not in the official language of the Union or the state.
Facilities for Instruction in Mother-Tongue:
- Every state and local authority in the state is required to provide adequate facilities for instruction in the mother-tongue at the primary stage of education for children belonging to linguistic minority groups.
- The President can issue necessary directions for ensuring these facilities.
Special Officer for Linguistic Minorities:
- The President should appoint a special officer for linguistic minorities to investigate matters related to constitutional safeguards for linguistic minorities.
- The special officer is tasked with reporting findings to the President, who must then place the reports before Parliament and send them to the relevant state governments.
These provisions aim to safeguard the interests of linguistic minorities and promote their development within the framework of the Indian Constitution.
Question for Laxmikanth Summary: Official Language
Try yourself:
Which language must be used in all proceedings in the Supreme Court and every High Court, unless stated otherwise?Explanation
- English is the language to be used in all proceedings in the Supreme Court and every High Court unless specified otherwise.
Report a problem
Development of Hindi Language

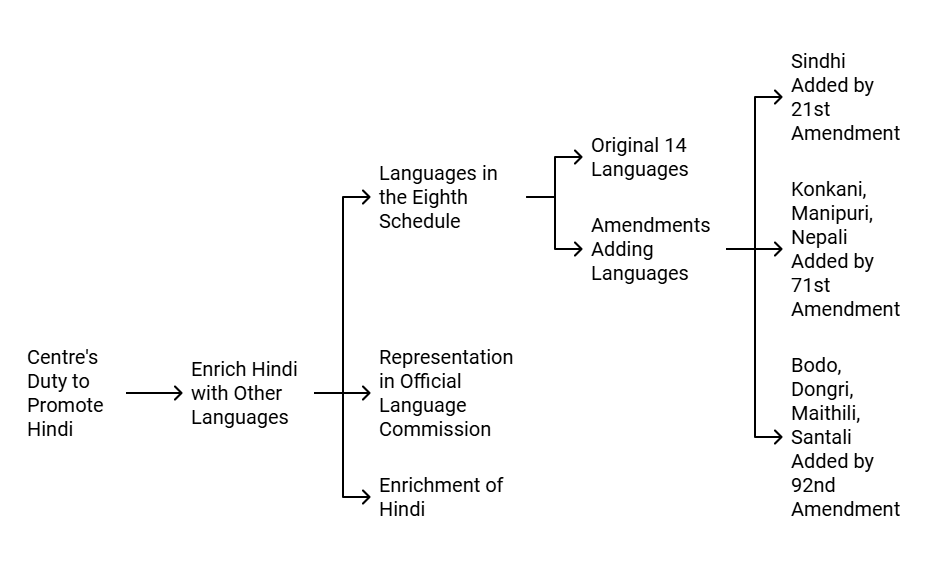
Duty to Promote Hindi:
- The Centre is mandated to promote the spread and development of Hindi so that it becomes a linguistic link in the composite culture of India.
- The Centre is also directed to enrich Hindi by assimilating forms, styles, and expressions from Hindustani and other languages specified in the Eighth Schedule.
- The vocabulary of Hindi should primarily be drawn from Sanskrit and secondarily from other languages.
Languages in the Eighth Schedule:
- Currently, the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution specifies 22 languages, which were originally 14 languages. These languages are: Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri (Dongri), Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu
Amendments to the Eighth Schedule:
- Sindhi was added by the 21st Amendment Act of 1967.
- Konkani, Manipuri, and Nepali were added by the 71st Amendment Act of 1992.
- Bodo, Dongri, Maithili, and Santali were added by the 92nd Amendment Act of 2003.
Objectives Behind the Specification of Languages:
- Representation in the Official Language Commission: Members of these languages are to be represented in the Official Language Commission.
- Enrichment of Hindi: The forms, styles, and expressions of these languages are to be used for the enrichment of the Hindi language, making it more comprehensive and diverse.
Committee of Parliament on Official Language
The Official Languages Act (1963) aims to promote the use of Hindi for official purposes in the Union Government. To ensure its effective implementation, a Parliamentary Committee on Official Language was formed to review the progress and recommend necessary changes.
Purpose of the Committee:
- The Committee reviews the use of Hindi for official work in the Union Government.
- It was set up 10 years after the Act’s implementation on 26th January 1976.
- Committee Composition: 30membersofParliament:
- 20 from Lok Sabha (Lower House).
- 10 from Rajya Sabha (Upper House).
Functions and Duties:
- The Committee evaluates the progress in using Hindi for official purposes and submits a report to the President with recommendations.
- The President shares the report with Parliament and State Governments for feedback.
Recommendations and Directions: After considering the views of the State Governments, the President may issue directions based on the report.
Chairmanship: The Chairman is elected by the Committee members, with the Union Home Minister traditionally serving as the Chairman.
Review Process:
- The Committee monitors the use of Hindi in Central Government offices, guided by the Official Languages Act and related rules.
- It reviews instructions, circulars, and other official documents issued by the Government.
Additional Areas of Focus: The Committee also examines the use of Hindi in schools, colleges, and universities, as well as in the recruitment process for Central Government services and departmental exams.
Secretariat: The Secretary heads the Committee’s Secretariat, which is part of the Department of Official Language, Ministry of Home Affairs.
Question for Laxmikanth Summary: Official Language
Try yourself:
Which languages were added to the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution by the 71st Amendment Act of 1992?Explanation
- The 71st Amendment Act of 1992 added Konkani, Manipuri, and Nepali to the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution.
Report a problem
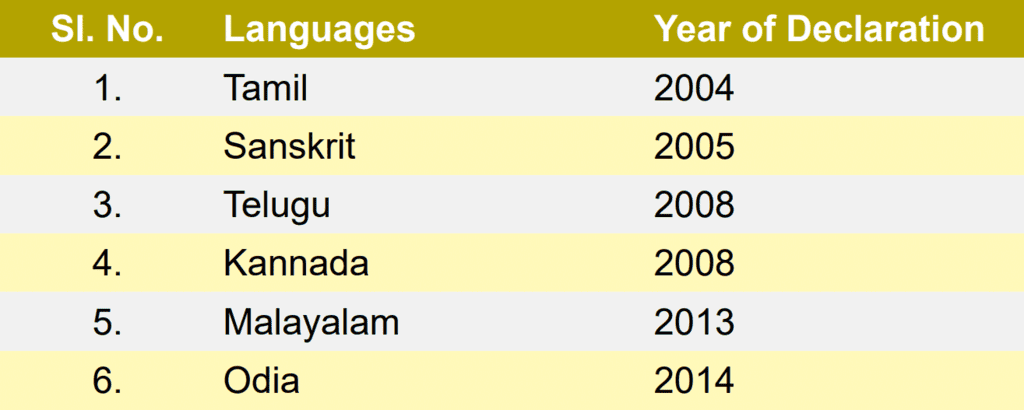
Classical Language Status
In 2004, the Government of India introduced a new category called Classical Languages to recognize and promote languages with rich historical and cultural significance. Six languages have been granted this status so far.
Benefits of Classical Language Status:
- Annual international awards are given to scholars for their work in Classical Indian Languages.
- A Centre of Excellence for studies in Classical Languages is set up to promote research and scholarship.
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) encourages the establishment of Professorial Chairs for Classical Languages in Central Universities to promote advanced studies.
Criteria for Classical Language Status:
The government set out specific criteria to determine whether a language can be classified as Classical:
- The language must have a history or early texts spanning 1500-2000 years.
- The language should have a body of ancient literature that is regarded as a valuable heritage by generations of its speakers.
- The language's literary tradition should be original, not borrowed from another community.
- The classical language and its literature should be distinct from its modern forms, with discontinuity between classical and later versions or offshoots of the language.