Laxmikanth Summary: Salient Features of the Constitution | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
The Indian Constitution is special because it takes ideas from around the world but still has its own unique qualities. Over time, there have been important changes, especially with the 42nd Amendment in 1976, which had a big impact on many parts of the Constitution. The courts, in a case called Kesavananda Bharati in 1973, said that while Parliament can make changes, it can't touch the Constitution's fundamental structure. So, despite these changes, the Constitution keeps its special identity, showing how it can adapt and grow while staying true to its core.
Salient Features of the Constitution
The Salient features of the constitution are as follows:
1. Lengthiest Written Constitution
- Constitutions are classified into written (like the American) or unwritten (like the British).
- Indian Constitution is the world's lengthiest written constitution.
- Original (1949): Preamble, 395 Articles (22 Parts), 8 Schedules.
- Current: Preamble, about 470 Articles (25 Parts), 12 Schedules.
- Amendments since 1951: Deleted 20 Articles, one Part (VII), added 95 Articles, four Parts (IVA, IXA, IXB, XIVA), four Schedules (9, 10, 11, 12).
- Factors contributing to size: Geographical diversity, historical influence, single constitution for Center and states, legal luminaries' dominance.
- Comprehensive content includes fundamental principles and detailed administrative provisions.
- Jammu and Kashmir had special status until 2019 (Article 370).
- Abolishment of special status in 2019, extending all provisions of the Constitution of India to Jammu and Kashmir.
- Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019, created two Union territories: Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
2. Drawn From Various Sources
- The Constitution of India incorporates provisions from various countries and the Government of India Act of 1935.
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar emphasized the exhaustive study of global constitutions during the framing.
- Structural elements, largely from the Government of India Act of 1935.
- Philosophical aspects (Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles) inspired by American and Irish Constitutions respectively.
- Political components (Cabinet Government principle, Executive-Legislature relations) drawn from British Constitutions.
- Other provisions borrowed from the constitutions of Canada, Australia, Germany, USSR (now Russia), France, South Africa, Japan, and more.
- The Government of India Act, 1935, holds significant influence, serving as a major source.
- Federal Scheme, Judiciary, Governors, Emergency Powers, Public Service Commissions, and administrative details mainly drawn from the 1935 Act.
- Over half of the Constitution's provisions are identical or closely resemble those in the 1935 Act.
3. Blend of Rigidity and Flexibility
- Constitutions are classified as rigid or flexible.
- Rigid Constitution: Requires a special procedure for amendment (e.g., American Constitution).
- Flexible Constitution: Amended like ordinary laws (e.g., British Constitution).
- Indian Constitution: Neither rigid nor flexible, a synthesis of both.
- Article 368 outlines two types of amendments:
(a) Special majority of Parliament (two-thirds of members present and voting, and majority of total membership).
(b) Special majority of Parliament with ratification by half of the total states. - Some Constitution provisions are amendable by a simple majority in the manner of the ordinary legislative process.
- These amendments do not fall under Article 368.
4. Federal System with Unitary Bias
- Indian Constitution: Establishes a federal system of Government.
- Usual federal features include two Governments, division of powers, a written Constitution, supremacy, rigidity, an independent judiciary, and bicameralism.
- Unitary/non-federal features include a strong Center, single Constitution, single citizenship, flexibility, integrated judiciary, Center-appointed state governor, all-India services, emergency provisions, etc.
- Parliamentary government features:
- Federal in form but unitary in spirit.
- Described as 'Union of States' in Article 1.
- Implies the Indian Federation is not a result of a state agreement.
- No state has the right to secede from the federation.
- Descriptive terms for the Indian Constitution:
- 'Quasi-federal' by K.C. Wheare.
- 'Bargaining federalism' by Morris Jones.
- 'Co-operative federalism' by Granville Austin.
- 'Federation with a centralizing tendency' by Ivor Jennings.
5. Parliamentary Form of Government
- Constitution of India: Adopts the British Parliamentary System over the American Presidential System.
- The parliamentary system emphasizes cooperation between legislative and executive, contrary to the American separation of powers.
- Also known as 'Westminster Model,' 'Responsible Government,' and 'Cabinet Government.'
- Features of Parliamentary Government in India:
- Presence of nominal and real executives.
- Majority party rule.
- Collective responsibility of the executive to the legislature.
- Membership of ministers in the legislature.
- Leadership of the Prime Minister or Chief Minister.
- Dissolution of the lower House (Lok Sabha or Assembly).
- Westminster: Symbol/synonym for the British Parliament.
- Differences from the British Parliamentary System:
- Indian Parliament is not sovereign, unlike the British.
- Indian State has an elected head (republic), while the British State has a hereditary head (monarchy).
- In both Indian and British parliamentary systems, the role of the Prime Minister is significant, termed as 'Prime Ministerial Government.'
6. Synthesis of Parliamentary Sovereignty and Judicial Supremacy
- Sovereignty of Parliament:
- Associated with the British Parliament.
- Principle of judicial supremacy linked to the American Supreme Court.
- Judicial Review in India:
- Differs from the British system and is narrower than the U.S.
- American Constitution's 'due process of law' vs. Indian Constitution's 'procedure established by law' (Article 21).
- Indian Constitutional Synthesis:
- A balance between British parliamentary sovereignty and American judicial supremacy.
- Supreme Court can declare parliamentary laws unconstitutional through judicial review.
- Parliament can amend a major portion of the Constitution through its constituent power.
7. Integrated and Independent Judiciary
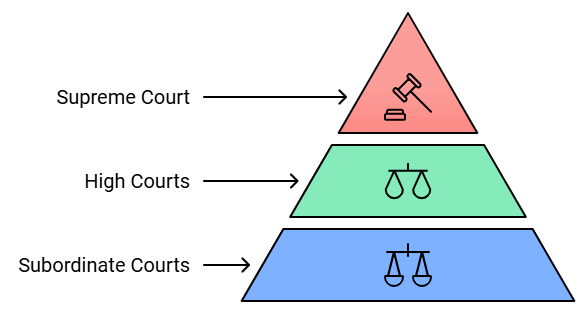
- Indian Judicial System: Integrated and independent.
- Hierarchy:
- Supreme Court: Apex of the integrated system.
- High Courts: At the state level.
- Subordinate Courts: Hierarchy includes district courts and lower courts.
- Enforcement of Laws:
- Single system of courts enforces both central and state laws.
- In the USA, federal laws by federal judiciary, state laws by state judiciary.
- Supreme Court's Role: Federal court, highest appeal court, guardian of fundamental rights, and Constitution.
- Provisions for Independence:
- Security of tenure for judges.
- Fixed service conditions.
- Supreme Court expenses from Consolidated Fund of India.
- Prohibition on discussing judge conduct in legislatures.
- Ban on practice after retirement.
- Contempt of court power vested in the Supreme Court.
- Separation of judiciary from the executive.
8. Fundamental Rights
- Fundamental Rights in Indian Constitution (Part III):
- Right to Equality (Articles 14-18)
- Right to Freedom (Articles 19-22)
- Right against Exploitation (Articles 23-24)
- Right to Freedom of Religion (Articles 25-28)
- Cultural and Educational Rights (Articles 29-30)
- Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32)
- Original Fundamental Rights:
- Seven initially, with the Right to Property (Article 31).
- Removed by the 44th Amendment Act of 1978.
- Right to Property became a legal right under Article 300-A in Part XII.
- Purpose of Fundamental Rights:
- Promote political democracy.
- Limit executive tyranny and arbitrary laws.
- Enforceable by courts; justiciable in nature.
- Limitations on Fundamental Rights:
- Not absolute, subject to reasonable restrictions.
- Can be curtailed or repealed by Parliament through Constitutional Amendment Act.
- Suspended during National Emergency, except rights under Articles 20 and 21.
9. Directive Principles of State Policy
- Directive Principles of State Policy (Part IV):
- Termed a 'novel feature' by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar.
- Three categories: socialistic, Gandhian, liberal-intellectual.
- Purpose:
- Aim to promote social and economic democracy.
- Establish a 'welfare state' in India.
- Enforceability:
- Unlike Fundamental Rights, not justiciable.
- Not enforceable by courts for violation.
- Moral Obligation:
- Constitution declares them fundamental.
- State duty to apply these principles in making laws.
- Imposes a moral obligation on state authorities.
- Force Behind Principles:
- Political force, primarily public opinion.
- Not legally binding but carry moral weight.
- Minerva Mills Cases (1980): The Supreme Court emphasized the balance between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles in the Indian Constitution.
10. Fundamental Duties
- Fundamental Duties (Part IV-A):
- Not in the original constitution.
- Added during the internal emergency (1975-77) by the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act of 1976.
- One more duty added by the 86th Constitutional Amendment Act of 2002.
- Specification:
- Part IV-A, Article 51-A lists eleven Fundamental Duties.
- Includes respecting the Constitution, national flag, and national anthem.
- Involves protecting the sovereignty, unity, and integrity of the country.
- Promotes common brotherhood and preserves the rich heritage of composite culture.
- Purpose of Fundamental Duties:
- Serve as a reminder to citizens about their responsibilities while enjoying rights.
- Consciousness of duties to country, society, and fellow citizens.
- Enforceability:
- Like Directive Principles, non-justiciable in nature.
- Not legally binding but highlight the moral and ethical responsibilities of citizens.
11. A Secular State
- Secular Character of the Indian State:
- The Constitution stands for a secular state, with no official religion.
- Provisions indicating secularism:
- 'Secular' was added to Preamble by the 42nd Amendment Act of 1976.
- The preamble ensures liberty of belief, faith, and worship for all citizens.
- Equality before the law and non-discrimination on the grounds of religion (Articles 14-15).
- Equality of opportunity in public employment (Article 16).
- Freedom of conscience and the right to profess, practice, and propagate any religion (Article 25).
- Right of religious denominations to manage their religious affairs (Article 26).
- No compelled taxes for promoting a particular religion (Article 27).
- No religious instruction in state-maintained educational institutions (Article 28).
- Right to conserve distinct language, script, or culture (Article 29).
- Minorities' right to establish and administer educational institutions (Article 30).
- State's endeavour for a Uniform Civil Code (Article 44).
- Indian Secularism:
- Positive concept: Equal respect and protection to all religions.
- Inapplicability of the Western concept of complete separation due to the multi-religious nature of Indian society.
- Abolishment of Communal Representation:
- Abolished old communal representation system.
- Temporary reservation of seats for scheduled castes and tribes for adequate representation.
12. Universal Adult Franchise
- Basis for Lok Sabha and state legislative assembly elections.
- Every citizen 18 years or older has the right to vote without discrimination.
- Voting Age: Reduced to 18 from 21 in 1989 by the 61st Constitutional Amendment Act of 1988.
- Bold Experiment:
- Constitution-makers introduced universal adult franchise.
- Remarkable considering vast size, huge population, high poverty, social inequality, and overwhelming illiteracy.
- Impact of Universal Adult Franchise:
- Broadens democracy, making it inclusive.
- Enhances self-respect and prestige of common people.
- Upholds the principle of equality.
- Enables minorities to protect their interests.
- Opens new opportunities for weaker sections.
13. Single Citizenship
- Indian Constitution and Citizenship:
- Federal structure with a dual polity (Centre and states).
- Provides for a single citizenship, i.e., Indian citizenship.
- Comparison with the USA:
- In the USA, individuals are citizens of both the country and the state they belong to.
- Dual allegiance and rights conferred by both the national and state governments.
- Indian Citizenship:
- All citizens, regardless of their state of birth or residence, enjoy the same political and civil rights throughout the country.
- No discrimination based on regional factors.
- Challenges despite Single Citizenship:
- Communal riots, class conflicts, caste wars, linguistic clashes, and ethnic disputes persist.
- The Constitution's goal of building a united and integrated Indian nation not fully realized.
14. Independent Bodies
- Independent Bodies in the Indian Constitution:
- Complement legislative, executive, and judicial organs.
- Crucial for the democratic system in India.
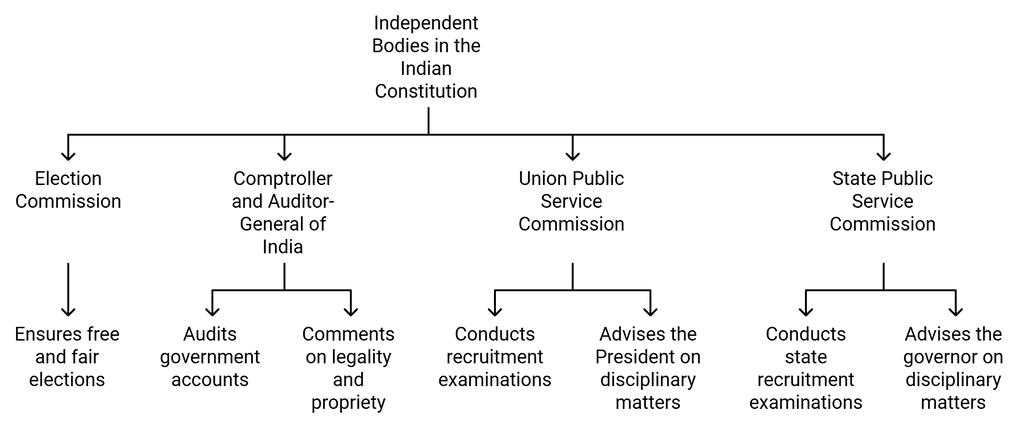
- Election Commission: Ensures free and fair elections for Parliament, state legislatures, President, and Vice President.
- Comptroller and Auditor-General of India:
- Audits accounts of Central and state governments.
- Guardian of the public purse, comments on legality and propriety of government expenditure.
- Union Public Service Commission:
- Conducts examinations for recruitment to All-India services and higher Central services.
- Advises the President on disciplinary matters.
- State Public Service Commission:
- Every state conducts examinations for recruitment to state services.
- Advises the governor on disciplinary matters.
- Independence Assurance: The Constitution ensures independence through provisions like security of tenure, fixed service conditions, and expenses charged to the Consolidated Fund of India.
15. Emergency Provisions
- Emergency Provisions in the Indian Constitution: Included to safeguard sovereignty, unity, integrity, and security of the country, democratic political system, and the Constitution.
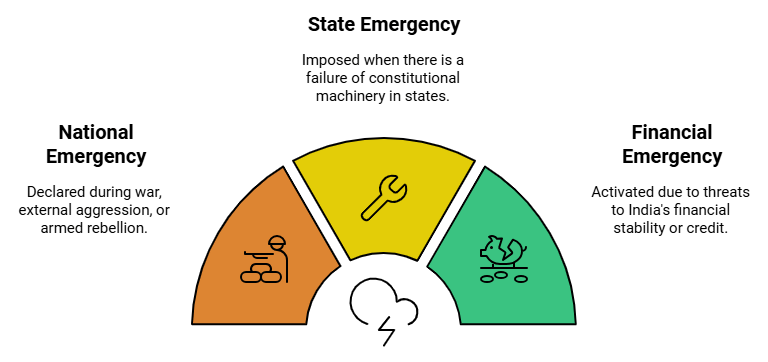
- Types of Emergencies:
- National Emergency (Article 352): Grounds: War, external aggression, armed rebellion.
- State Emergency (President's Rule) (Article 356): Grounds: Failure of Constitutional machinery in states.
- Financial Emergency (Article 360): Grounds: Threat to financial stability or credit of India.
- Central Government's Powers During Emergency:
- All-powerful during an emergency.
- States come under the total control of the Centre.
- Federal structure transforms into a unitary one without a formal constitutional amendment.
- Unique Feature of the Indian Constitution: Transformation from federal (normal times) to unitary (during emergencies) is distinctive and unique.
16. Three-tier Government
- Originally, the Indian Constitution focused on a dual polity—Centre and states, like other federal constitutions.
- Later, the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act (1992) added a third tier of government, not present in other world constitutions.
- The 73rd Amendment recognized panchayats, adding Part IX and Schedule 11, instituting a three-tier panchayati raj system in every state.
- The 74th Constitutional Amendment Act (1992) added Part IX-A and Schedule 12, recognizing municipalities and introducing three types in every state—nagar panchayat, municipal council, and municipal corporation.
17. Co-operative Societies
The 97th Constitutional Amendment Act of 2011 conferred constitutional status and protection to co-operative societies, bringing about three key changes:
- Elevated the formation of co-operative societies to a fundamental right under Article 19.
- Introduced a new Directive Principle of State Policy focused on the promotion of cooperative societies (Article 43-B).
- Added a new section, Part IX-B, titled "The Co-operative Societies" (Articles 243-ZH to 243-ZT), containing provisions to ensure the democratic, professional, autonomous, and economically sound functioning of co-operative societies. Empowers Parliament and state legislatures to legislate appropriately for multi-state and other cooperative societies, respectively.
Criticism of the Constitution
The Constitution of India, as framed and adopted by the Constituent Assembly of India, has been criticized on the following grounds:
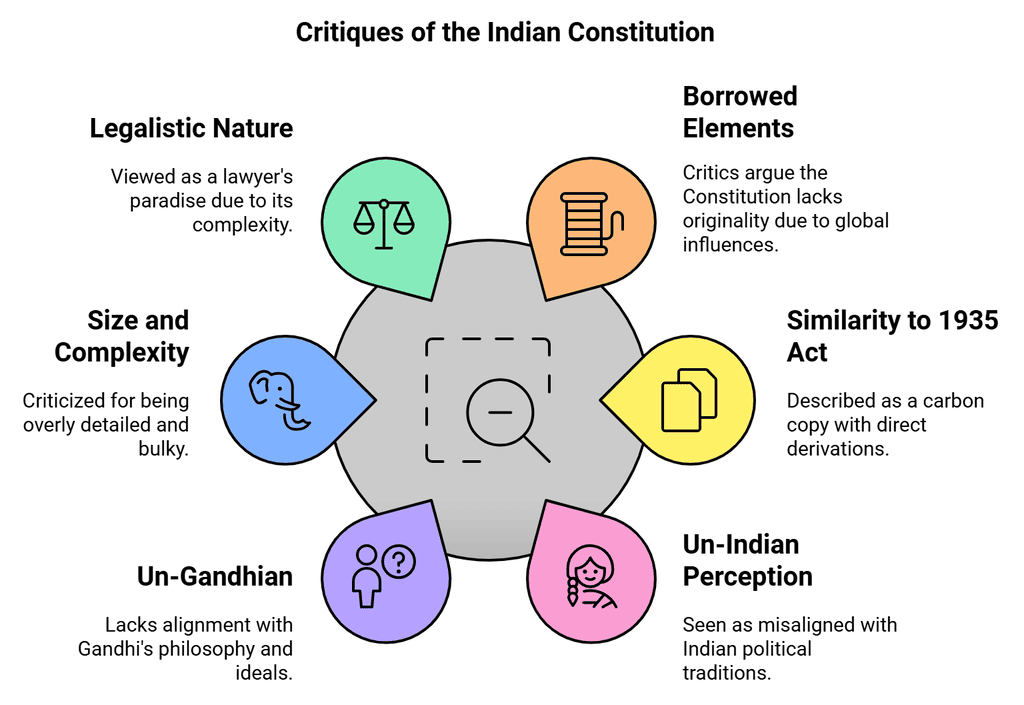
1. A Borrowed Constitution
- Labelled as a 'borrowed Constitution,' 'bag of borrowings,' 'hotch-potch Constitution,' or 'patchwork' of world constitutions by critics.
- Critics argue that it lacks originality.
- Critics' views are deemed unfair and illogical.
- Framers made necessary modifications to borrowed features, adapting them to Indian conditions and avoiding faults.
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar defended the Constitution in the Constituent Assembly.
- Highlighted the inevitability of similarities in main provisions among constitutions globally.
- Stressed that variations to address faults and accommodate national needs are the only novel aspects.
- Dismissed the charge of blindly copying other countries' constitutions as based on inadequate study.
2. A Carbon Copy of the 1935 Act
- Critics: Raised concerns about extensive borrowing from the Government of India Act of 1935.
- "Carbon Copy" and "Amended Version": Terms used by critics to characterize the Constitution's relationship with the 1935 Act.
- N. Srinivasan: Described the Constitution as closely resembling the 1935 Act in language and substance.
- Sir Ivor Jennings: Noted direct derivations and textual similarities between the Constitution and the 1935 Act.
- P.R. Deshmukh: Commented that the Constitution added adult franchise to the 1935 Act.
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar: Defended the borrowing, emphasizing that fundamental constitutional ideas are not patentable.
- Administrative Details: Dr. Ambedkar expressed regret that the borrowed provisions mainly related to administrative details.
3. Un-Indian or Anti-Indian
- Described the Indian Constitution as 'un-Indian' or 'anti-Indian.'
- Claimed that it does not align with India's political traditions and spirit.
- K. Hanumanthaiya: Expressed dissatisfaction, comparing the desired music of Veena or Sitar to the perceived English band music in the Constitution.
- Lokanath Misra: Criticized the Constitution as a "slavish imitation of the west" and a "slavish surrender to the west."
- Lakshminarayan Sahu:
- Observed that the ideals in the draft Constitution lacked a manifest relation to the fundamental spirit of India.
- Predicted that the Constitution would not be suitable and would break down soon after implementation.
4. An Un-Gandhian Constitution
- Labelled the Indian Constitution as un-Gandhian.
- Argued that it lacks Mahatma Gandhi's philosophy and ideals.
- K. Hanumanthaiya: Stated that the Constitution was not in line with what Mahatma Gandhi wanted or envisaged.
- T. Prakasam: Attributed the perceived lapse to Ambedkar's non-participation in the Gandhian movement and his antagonism towards Gandhian ideas.
5. Elephantine Size
- Described the Indian Constitution as too bulky and detailed.
- Sir Ivor Jennings suggested that the borrowed provisions were not always well-selected.
- H.V. Kamath:
- Compared the constitution to an elephant, symbolizing its bulkiness.
- Urged against making the Constitution overly extensive.
6. Paradise of the Lawyers
- Described the Indian Constitution as too legalistic and complicated.
- Sir Ivor Jennings labeled it a "lawyer's paradise."
- H.K. Maheswari: Suggested that the legal language might lead to increased litigation.
- P.R. Deshmukh:
- Criticized the draft for being too ponderous, resembling a law manual.
- Desired a more dynamic and concise socio-political document.
|
170 videos|999 docs|259 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikanth Summary: Salient Features of the Constitution - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the salient features of the Constitution? |  |
| 2. What are some criticisms of the Constitution? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Constitution's length and detail? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between fundamental rights and directive principles? |  |
| 5. How does the Constitution ensure a federal system of government? |  |

















