Laxmikanth Summary: Union Territories | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Article 1 of the Constitution describes the territory of India as comprising three categories: territories of the states, union territories, and territories that may be acquired by the Government of India.
- Territories of the States: These are the territories that make up the individual states of India. There are currently twenty-eight states in India.
- Union Territories: These are regions that are directly governed by the Central government. There are currently eight union territories.
- Acquired Territories: These are territories that may be acquired by the Government of India in the future. As of now, there are no such acquired territories.
The states in India are part of a federal system, meaning they share power with the Central government. In contrast, union territories are under the direct control and administration of the Central government, which is why they are also called “centrally administered territories.” This arrangement shows a difference from federalism because the relationship between the Central government and these territories is more unitary.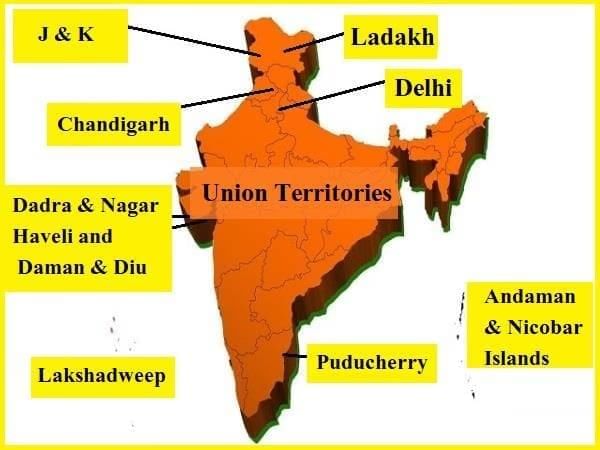 Union Territories of India
Union Territories of India
Creation of Union Territories
- During British Rule, certain areas were designated as 'scheduled districts' in 1874, later evolving into 'chief commissioners' provinces.'
- Post-independence, these areas were classified under Part 'C' States and Part 'D' Territories.
- In 1956, the 7th Constitutional Amendment Act and the States Reorganisation Act led to the establishment of 'union territories.'
- Over time, some union territories were granted statehood, including Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Tripura, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, and Goa.
- Territories acquired from the Portuguese (Goa, Daman and Diu, Dadra and Nagar Haveli) and the French (Puducherry) became union territories.
- Currently, there are eight Union Territories:
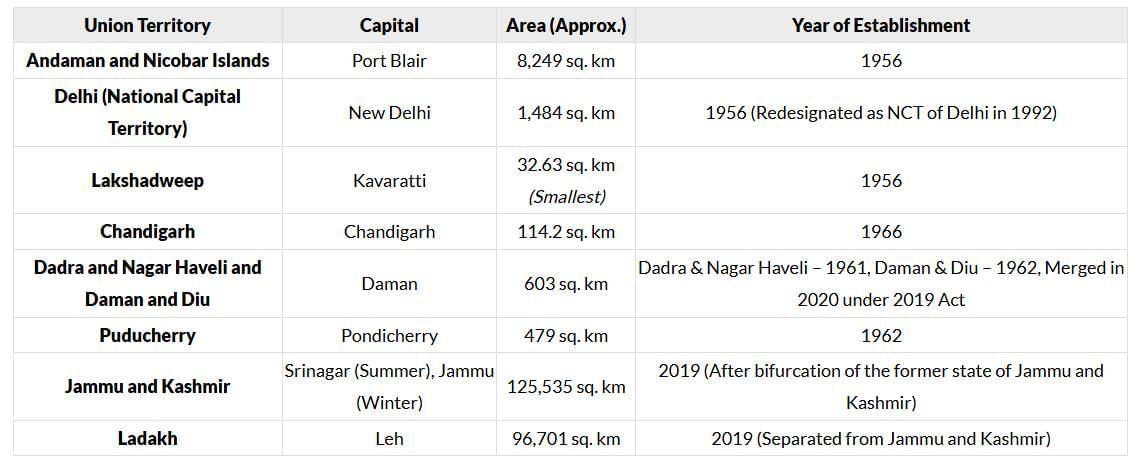
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands(1956),Delhi(1956),Lakshadweep(1956),Puducherry(1962),Chandigarh(1966),Jammu and Kashmir(2019),Ladakh(2019),Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu(2020).
- Until 1973, Lakshadweep was known as Laccadive, Minicoy, and Amindivi Islands. In 1992,Delhi became the National Capital Territory, and until 2006,Puducherry was called Pondicherry.
- In 1950, the Indian Constitution initially classified states and territories into Part A, Part B, Part C states, and Part D territories
Reasons for Creating Union Territories
- Political and Administrative Considerations: Examples include Delhi and Chandigarh.
- Cultural Distinctiveness: Puducherry and Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu are recognized for their unique cultural identities.
- Strategic Importance: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep are important for national security and strategic purposes.
- Special Treatment for Backward and Tribal People: Regions like Mizoram, Manipur, Tripura, and Arunachal Pradesh were created to address the needs of backward and tribal communities, eventually becoming states.
Administration of Union Territories
Articles 239 to 241 of the Constitution talk about how union territories in India are governed. Even though all union territories are similar, they are managed in different ways.
- Every union territory is run by the President of India, who acts through an administrator appointed by him or her.
- The administrator is like an agent of the President and is not the head of the state like a governor. The President can choose the title of the administrator, which could be a Lieutenant Governor, Chief Commissioner, or Administrator.
- Currently, the Lieutenant Governor administers Delhi, Puducherry, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Jammu and Kashmir, and Ladakh. Other areas like Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, and Lakshadweep are administered by an Administrator.
- The President can also appoint a governor of a state to act as an administrator for an adjoining union territory, and in this role, the governor operates independently of their council of ministers.
- Some union territories like Puducherry (1963), Delhi (1992), and Jammu and Kashmir (2019) have their own legislative assemblies and councils of ministers. The assembly of Puducherry has 30 members, Delhi has 70 members, and Jammu and Kashmir has 83 members.
- Parliament has the power to make laws on any subject for the union territories, including those with their own local legislatures like Puducherry, Delhi, and Jammu and Kashmir. Even with local legislatures, Parliament can legislate on subjects of the State List.
- The legislative assembly of Puducherry can make laws on subjects from both the State List and the Concurrent List.
- The legislative assembly of Delhi can make laws on any subject of the State List (except public order, police, and land) and the Concurrent List.
- The legislative assembly of Jammu and Kashmir can make laws on any subject of the State List (except public order and police) and the Concurrent List.
- The President can make regulations for the peace, progress, and good government of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, and Ladakh.
- In the case of Puducherry, the President can legislate by making regulations but only when the assembly is suspended or dissolved.
- A regulation made by the President has the same force and effect as an act of Parliament and can also repeal or amend any act of Parliament in relation to these union territories.
- The Parliament can establish a high court for a union territory or put it under the jurisdiction of the high court of an adjacent state.
- Delhi is the only union territory that has a high court of its own (since 1966).
- The Bombay High Court has jurisdiction over the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Lakshadweep, and Puducherry are placed under the Calcutta, Punjab and Haryana, Kerala and Madras High Courts respectively.
Special Provisions for Delhi
- 69th Constitutional Amendment Act (1991): This act gave Delhi a special status, redesignating it as the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi.
- Legislative Assembly: The act established a legislative assembly with 70 elected members.
- Law-Making Power: The assembly can make laws on State List and Concurrent List matters, except for public order, police, and land.
- Parliamentary Supremacy: Parliamentary laws take precedence over assembly laws.
- Council of Ministers: Comprises a chief minister and up to six ministers.
- Chief Minister: Appointed by the President, not the lieutenant governor.
- Ministerial Appointments: Other ministers are appointed by the President on the chief minister's advice.
- Governor's Role: The lieutenant governor acts on the advice of the council of ministers except in certain matters.
- Discretionary Powers: In case of disagreements, the governor refers matters to the President.
- Presidential Rule: The President can impose rule in case of constitutional failures, similar to Article 356 for states.
- Ordinance Power: The lieutenant governor can issue ordinances during assembly recess, which must be approved within six weeks.
- Ordinance Limitations: Ordinances cannot be issued or withdrawn without Presidential approval, and not during assembly dissolution or suspension.
Advisory Committees of Union Territories
- Under the Government of India (Allocation of Business) Rules 1961, the Ministry of Home Affairs is responsible for all matters related to Union Territories concerning legislation, finance and budget, services, and the appointment of Lieutenant Governors and Administrators.
- The five Union Territories without legislatures—Andaman and Nicobar Islands,Chandigarh,Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu,Lakshadweep, and Ladakh—have forums for advisory purposes.
- The Home Minister's Advisory Committee (HMAC) and the Administrator's Advisory Committee (AAC) are the two main forums for these Union Territories.
- The HMAC, chaired by the Union Home Minister, and the AAC, chaired by the Administrator of the respective Union Territory, discuss general issues related to social and economic development.
- Members of these committees include Members of Parliament and elected members from local bodies(such as District Panchayats and Municipal Councils) of the respective Union Territory, among others.
Creation of Union Territories in 2019 (Jammu and Kashmir)
- The state of Jammu and Kashmir was split into two Union Territories: Jammu and Kashmir (which has a legislative assembly) and Ladakh (which does not have a legislature), including the districts of Kargil and Leh.
- The first Lieutenant Governors for these territories were R.K. Mathur for Ladakh and Girish Chandra Murmu for Jammu and Kashmir.
- The Reorganisation Act removed Article 370 and Article 35A from the Constitution.
- The new Union Territories of Ladakh and Jammu and Kashmir officially started on the 144th birthday of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, which is October 31, 2019.
- This is the first instance of a state being divided into Union Territories.
- The flag and constitution of Jammu and Kashmir, along with the Ranbir Penal Code (RPC), are no longer in effect; instead, the Indian Penal Code (IPC) now applies to both Union Territories.
- The Parliament can create laws on any topic from the three lists for these Union Territories.
- The Lieutenant Governor has the authority to "act in his discretion" concerning matters related to the All India Services and the Anti-Corruption Bureau (ACB).
- The term for the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir is now set for five years, reduced from the previous six years.
- By area, Ladakh is now the largest Union Territory in India.
- The Legislative Council of Jammu and Kashmir has been abolished. There will be 107 seats filled through direct elections, increasing to 114 seats after a delimitation process.
Merger of Union Territories in 2020
- In 2020, the union territories of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu were merged to form a new union territory:
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli was originally created in 1961, and Daman and Diu was created in 1962.
Reasons for Merging Dadra and Nagar Haveli with Daman and Diu
- Administrative Similarities: Both Union territories share similar administrative setups, with common officials like Secretaries, Police Chiefs, and Forest Conservators. Development policies in sectors like Tourism and Education are also alike.
- Infrastructure Efficiency: Having parallel departments in each territory leads to wasted infrastructure and manpower. Key officials often work on alternate days in both areas, causing delays in public service.
- Reducing Duplication: Separate constitutional setups for each territory result in duplicate work and unnecessary financial strain on the government.
- Improving Governance: The merger aligns with the government's goal of "Minimum Government, Maximum Governance," aiming for efficient use of resources given the small populations and limited areas of the territories.
Concerns Associated with the Functioning of Union Territories in India
Several issues have been raised regarding the functioning of Union Territories (UTs) in India:
Democratic Deficit: Residents of UTs often lack mechanisms to hold their leaders accountable, leading to a gap in democratic representation when compared to states.
Population vs. Status: The designation of a region as a UT or a state should not be based merely on population size or geographical area. Interestingly, some former UTs like Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, and Sikkim, which were later granted statehood, still have smaller populations than current UTs like Puducherry or Dadra and Nagar Haveli.
Structural Weakness: The constitutional framework of UTs makes them more vulnerable to interference from the central government, which can disrupt their functioning and autonomy.
Legislative Composition: UT legislatures may be fully elected or partly elected and partly nominated. This arrangement, particularly the nomination process, is often politicized, as seen in Puducherry. In one case, the courts questioned the need for consulting the Union government during appointments to the Assembly.
Limited Autonomy: UTs generally lack the level of self-governance that states enjoy. The powers vested in the Administrator or Lieutenant Governor are often excessive, undermining democratic governance.
Thus, the Union government must respect the original intent behind granting certain UTs their own legislatures and Councils of Ministers—namely, to fulfill the democratic aspirations of their people.
As the Supreme Court has emphasized, just because the Union Territories are administered by the central government does not mean they are part of it. UTs, although centrally managed, are distinct entities and must function with a degree of autonomy.
|
162 videos|986 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikanth Summary: Union Territories - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is a Union Territory in India? |  |
| 2. How are Union Territories created in India? |  |
| 3. What are the special provisions for Delhi as a Union Territory? |  |
| 4. What is the role of the Lieutenant Governor in Union Territories? |  |
| 5. Can Union Territories have their own legislative assemblies? |  |






















