Laxmikanth Summary: Preamble of the Constitution | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Text of the Preamble |

|
| Ingredients of the Preamble |

|
| Key Words in the Preamble |

|
| Significance of the Preamble |

|
| Preamble as Part of the Constitution |

|
| Amendability of the Preamble |

|
The American Constitution was the first to begin with a Preamble. The Preamble to the Indian Constitution is based on the "Objectives Resolution', drafted and moved by Pandit Nehru, and adopted by the Constituent Assembly. It has been amended by the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act t.1976), which added three new words - socialist, secular and integrity.
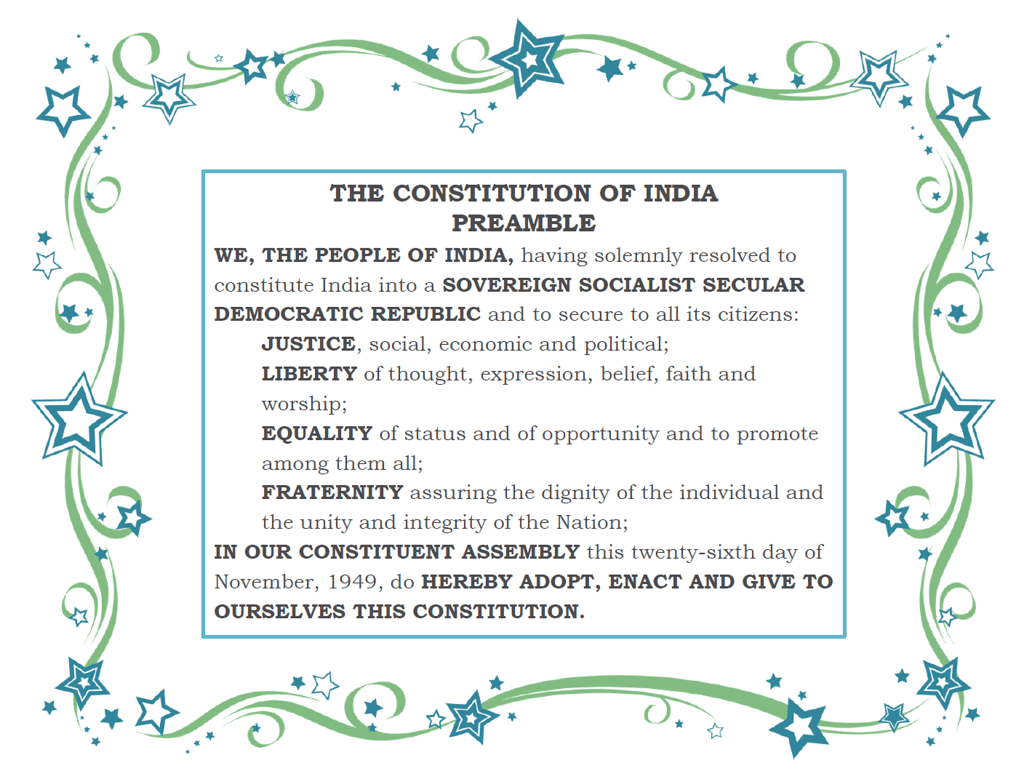
Text of the Preamble
The Preamble in its present form reads:
We, THE PEOPLE OF INDIA, having solemnly resolved to constitute India into a SOVEREIGN SOCIALIST SECULAR DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC and to secure to all its citizens: JUSTICE', Social, Economic and Political; LIBERTY of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship; EQUALITY of status and of opportunity; and to promote among them all; FRATERNITY assuring the dignity of the individual and the unity and integrity of the Nation;
IN OUR CONSTITUENT ASSEMBLY this twenty-sixth day of November, 1949, do HEREBY ADOPT, ENACT AND GIVE TO OURSELVES THIS CONSTITUTION”.
Ingredients of the Preamble
- Source of Authority of the Constitution: The Preamble explains that the Constitution gets its power from the people of India.
- Nature of the Indian State: It describes India as a sovereign, socialist, secular democratic, and republican system.
- Objectives of the Constitution: It outlines justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity as its goals.
- Date of Adoption of the Constitution: It designates November 26, 1949, as the official adoption date.
Key Words in the Preamble
Certain key words—Sovereign, Socialist, Secular, Democratic, Republic, Justice, Liberty, Equality and Fraternity—are explained as follows:
1. Sovereign
- The word "sovereign’ implies that India is neither a dependency nor a dominion of any other nation, but an independent state.
- There is no authority above it, and it is free to conduct its own affairs (both internal and external).
2. Socialist
- Even before the term was added by the 42nd Amendment in 1976, the Constitution had a socialist content in the form of certain Directive Principles of State Policy.
- Democratic socialism, on the other hand, holds faith in a "mixed economy’ where both public and private sectors co-exist side by side. As the Supreme Court says, ‘Democratic socialism aims to end poverty, ignorance, disease and inequality of opportunity.
3. Secular
- The term "secular’ too was added by the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act of 1976. However, as the Supreme Court said in 1974, although the words "secular state’ were not expressedly mentioned in the Constitution, there can be no doubt that Constitution-makers wanted to establish such a state and accordingly Articles 25 to 28 (guaranteeing the fundamental right to freedom of religion) have been included in the constitution.
- The Indian Constitution all religions in our country have the same status and support from the state.
4. Democratic
- A democratic system, as mentioned in the Preamble, is built on the idea of power belonging to the people.
- States can be categorized based on their stance towards religion:
- Atheistic State: Opposes all religions.
- Theocratic State: Favors one religion as the state religion (e.g., Bangladesh, Burma, Sri Lanka, Pakistan).
- Secular State: Neutral on religion, does not endorse any specific religion as the state religion (e.g., USA, India).
- Democracy is of two types-direct and indirect. In direct democracy, the people exercise their supreme power directly as is the case in Switzerland. There are four devices of direct democracy, namely, Referendum, Initiative, Recall and Plebiscite.
- In indirect democracy, on the other hand, the representatives elected by the people exercise the supreme power and thus carry on the government and make the laws. This type of democracy, also known as representative democracy, is of two kinds-parliamentary and presidential.
- The term ‘democratic' is used in the Preamble in the broader sense embracing not only political democracy but also social and economic democracy.
5. Republic
- The term ‘republic' in our Preamble indicates that India has an elected head called the president. He is elected indirectly for a fixed period of five years.
- A republic also means two more things: one, vesting of political sovereignty in the people and not in a single individual like a king; second, the absence of any privileged class and hence all public offices being opened to every citizen without any discrimination.
6. Justice: Social, Economic, and Political
- The objective of ensuring justice in Indian society is to create a fair, impartial, and equal system for all citizens.
- Social justice aims to provide equal opportunities and treatment to all individuals, regardless of their caste, religion, gender, or economic status.
- Economic justice focuses on providing equal opportunities for all citizens to participate in the economy and enjoy the benefits of economic growth.
- Lastly, political justice ensures that all citizens have the right to participate in the political process and decision-making, as well as equal protection under the law.
7. Liberty: of thought, expression, belief, faith, and worship
- The Indian state aims to guarantee the freedom of thought, expression, belief, faith, and worship to all its citizens.
- This objective promotes a diverse and tolerant society where individuals have the right to express their opinions, practice their religion, and follow their beliefs without fear of discrimination or persecution.
- By ensuring these liberties, the Indian state fosters an environment in which the free exchange of ideas and knowledge can flourish, contributing to the nation's progress.
8. Equality
- The objective of equality in the Indian state focuses on providing equal status and opportunities to all citizens, regardless of their social, economic, or cultural background.
- This means that all individuals should have equal access to resources, education, and employment, and that discrimination based on caste, religion, gender, or economic status should be eliminated.
- The Indian state works to promote policies and programs that address inequalities and provide support to marginalized communities to ensure that they have equal opportunities to succeed.
9. Fraternity
- The objective of fraternity in the Indian state is to create a sense of unity among the diverse population while maintaining the dignity of each individual.
- By promoting brotherhood and understanding among its citizens, the Indian state fosters social cohesion and ensures that the nation remains unified in its pursuit of progress.
- This objective also emphasizes the importance of respecting each individual's dignity and rights, which contributes to a harmonious and inclusive society.
Significance of the Preamble
- The Preamble holds the core beliefs and essential principles—political, moral, and religious—on which the Constitution is built. It showcases the grand vision and noble ideals of the Constituent Assembly, reflecting the hopes and ambitions of the founding figures of the Constitution.
- In the words of Sir Alladi Krishnaswami Iyer, a member of the Constituent Assembly who played a significant role in shaping the Constitution, the Preamble represents what they had long envisioned and desired.
- According to K.M. Munshi, a member of the Drafting Committee of the Constituent Assembly, the Preamble acts as the 'horoscope' of our independent democratic republic.
- Pandit Thakur Das Bhargava, another member of the Constituent Assembly, emphasized the significance of the Preamble, calling it the most valuable part of the Constitution, the essence of the Constitution, and a crucial measure of its value.
- Sir Ernest Barker, a renowned English political scientist, praised the political acumen of the creators of the Preamble, labeling it as the 'keynote' to the Constitution and even incorporating it in his work, Principles Of Social and Political Theory.
- M. Hidayatullah, a former Chief Justice of India, noted that the Preamble resembles the Declaration of Independence of the United States but goes beyond a mere declaration. It stands as the essence of our Constitution, outlining the structure of our political society and embodying an unyielding determination that only a revolution could change.
Preamble as Part of the Constitution

- In the Berubari Union case (1960), the Supreme Court said that the Preamble shows the general purposes behind the several provisions in the Constitution, the Supreme Court specifically opined that Preamble is not a part of the Constitution.
- In the Kesavananda Bharati case 17 (1973), the Supreme Court rejected the earlier opinion and held that Preamble is a part of the Constitution.
- In the LIC of India case(1995) also, the Supreme Court again held that the Preamble is an integral part of the Constitution. Like any other part of the Constitution.
- However, two things should be noted:
- The Preamble is neither a source of power to legislature nor a prohibition upon the powers of legislature.
- It is non-justiciable, that is, its provisions are not enforceable in courts of law.
Amendability of the Preamble
- Preamble can be amended under Article 368 of the Constitution arose for the first time in the historic case of Kesavananda Bharati (1973).
- The Preamble has been amended only once so far, in 1976, by the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act, which has added three new words Socialist, Secular and Integrity to the Preamble. This amendment was held to be valid.
|
162 videos|986 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikanth Summary: Preamble of the Constitution - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the objectives of the Indian State mentioned in the Preamble of the Constitution? |  |
| 2. Is the Preamble considered as a part of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 3. Can the Preamble of the Indian Constitution be amended? |  |
| 4. How does the Preamble reflect the aspirations of the people of India? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the Preamble in the Indian Constitution? |  |





















