Class 7 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answers - Environment
Q1. Explain with examples the different components of environment.
Ans:
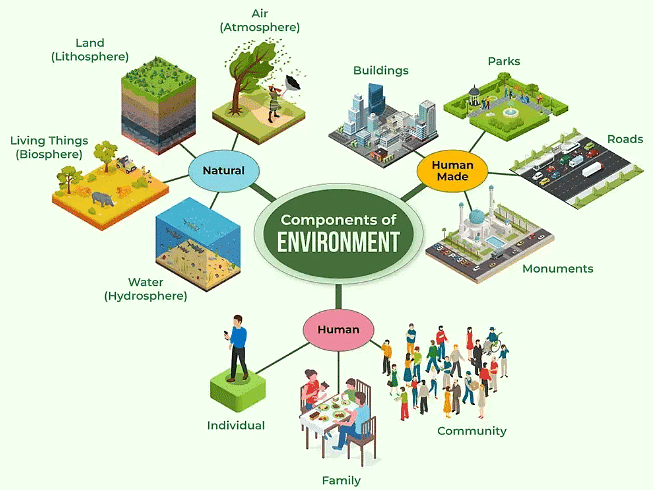
Major Components of environment are – Man-made, natural and Human beings.
Major Components of the Environment:
Natural Components:
- Land (Lithosphere).
- Water (Hydrosphere).
- Air (Atmosphere).
- Living things (Organisms).
Human-made Components
- Buildings.
- Parks.
- Bridges.
- Roads.
- Monuments.
- Industries.
Humans
- Individuals
- Family
- Community
- Religion
- Education
- Economic
- Political situation
Examples of Human-made Environment:
- Buildings
- Parks
- Bridges
- Roads
- Monuments
- Industries
Q2. What is environment?
Ans:
The surrounding in which we live forms environment. It is the basic life support system having natural and man-made components.
- The people, the place, the things, the nature and the living organisms that surround us are called environment.
- It is a combination of natural and human made phenomena.
- The natural environment refers to both biotic and abiotic conditions existing on the earth.
- Human environment reveals the activities, creations and interactions among human beings.
Q3. Describe lithosphere and hydrosphere.
Ans:
Lithosphere
- is the solid crust or the hard top layer of the earth.
- It is made up of rocks and minerals.
- It is covered by a thin layer of soil.
- It is an irregular surface with various landforms like mountains, plateaus, plains, valleys etc.
- Landforms spread over the continents and also on the ocean floors.
Lithosphere provides us the following:
- Forests.
- Grasslands for grazing.
- Land for agriculture and
- Human settlements.
- It is also a source of mineral wealth.
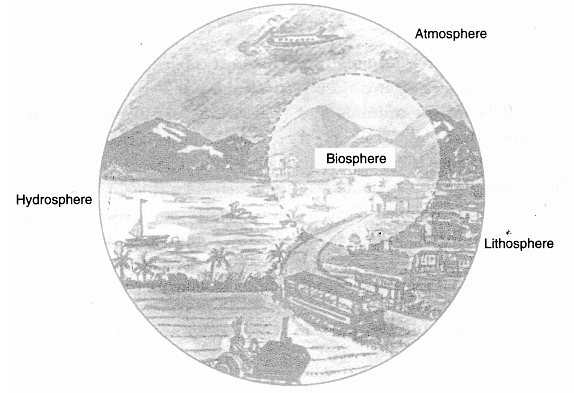 Domains of Environment
Domains of Environment
Hydrosphere is the domain of water.
- It comprises various sources of water.
- The different types of water bodies like rivers, lakes, seas, oceans, etc. are its major components.
- It is essential for all living organisms.
Q4. Give an account of the atmosphere.
Ans:
- The atmosphere is the thin layer of air that surrounds the earth.
- The gravitational force of the earth holds the atmosphere around it.
- It protects us from the harmful rays and scorching heat of the sun.
- It consists of numerous gases, dust and water vapour.
- The changes in the atmosphere produce changes in the weather and climate.
Q5. What has brought a change in interaction between humans and their surroundings?
Ans:
- Human being modifies nature according to their need. Early humans adapted themselves to their natural surroundings. They led a simple life fulfilling their needs from nature.
- With changes in needs new methods and technologies were invented. Settled life brought agriculture domestication of animals. Invention of wheel, surplus food led to development of trade and commerce. Barter system emerged.
- Industrial revolution, changes in transportation increased production. Growth in communication system made life easier and speedy. Humans learned new ways to use and change the surroundings.
Q6. Why do the animals and vegetation vary from place to place?
Ans:
Animals and vegetation vary from place to place because
- They are dependent on their immediate surroundings.
- They depend on the environmental conditions like climate, soil, water etc.
- All of them sire interdependent on each other.
Q7. What made Ravi sad while going to school after vacation?
Ans:
- After the long vacation while going to school Ravi noticed that the only play-ground next to the school is dug up.
- He was told that a multi storey building would be constructed there.
- This made him sad as the big playground with grass, marigolds and butterflies would be gone forever.
- He shared his feelings with his classmates.
Q8. Distinguish between biotic and abiotic environments.
Ans:
Biotic Environment
- The world of living organisms is called biotic environment.
Examples: Plants and animals. - Abiotic Environment
- The world of non-living elements is called abiotic environment.
Example: Land.
Q9. Define barter system.
Ans:
The barter system is an ancient form of trade and exchange. In this system, goods and services are exchanged directly for other goods and services without the use of money as a medium of exchange. It was prevalent in early human societies and played a significant role in facilitating trade before the advent of a standardized monetary system.
- In a barter system, individuals or communities exchange surplus goods they produce for other items they need. For example, a farmer who has an excess of grains might exchange some of his grains with a potter for a clay pot. The exchange is based on mutual consent and the perceived value of the goods being traded.
- However, the barter system had its limitations, as it required a double coincidence of wants. This means that both parties involved in the exchange must have something the other desires. For instance, if the potter in the above example did not want grains, the exchange would not take place.
- The barter system gradually became impractical for more extensive and complex trade. As societies evolved and trade increased, the need for a more efficient medium of exchange led to the development of money. Money serves as a universal medium that can be easily exchanged for goods and services, overcoming the limitations of the barter system.
Q10. What do you understand by the term “Ecosystem”?
Ans:
An ecosystem refers to a dynamic and complex community of living organisms (plants, animals, and microorganisms) and their physical environment (which includes soil, water, air, and various non-living elements). It is a functional unit where both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components interact and depend on each other for survival and sustenance.
Key features of an ecosystem:
- Biotic Components: These include all living organisms present in the ecosystem, such as plants, animals, insects, and microorganisms. They play various roles, including producers (plants), consumers (herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores), and decomposers (bacteria and fungi).
- Abiotic Components: These are the non-living factors that influence the ecosystem, such as sunlight, temperature, water, air, soil, rocks, and minerals. These abiotic factors play a crucial role in shaping the structure and functioning of the ecosystem.
- Energy Flow: Ecosystems operate based on the flow of energy. Producers (plants) capture energy from the sun through photosynthesis and convert it into food. This energy is then transferred through different trophic levels as consumers eat plants or other animals.
- Nutrient Cycling: Nutrients, such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and others, are cycled within the ecosystem. Decomposers break down dead organic matter and release nutrients back into the soil, which are taken up by plants, starting the cycle again.
- Interdependence: Organisms in an ecosystem are interdependent, meaning they rely on each other for resources and support. Disruptions to one species or element can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem.
- Stability and Adaptation: Ecosystems exhibit resilience and stability, adapting to environmental changes over time. Some ecosystems may be more resilient to disturbances, while others are more fragile.
|
63 videos|554 docs|46 tests
|

















