Magnetic Properties of Solids | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Magnetic properties:
The macroscopic magnetic properties of material are consequence of magnetic moments associated with the individual electron. Each electron in an atom has magnetic moment due to two reasons. The first one is due to the orbital motion around the nucleus, and the second is due to the spin of electron around its own axis. A moving electron may be considered to be a small current loop, generating a small magnetic field, and having a magnetic moment along its axis of rotation.
The other type of magnetic moment originates from electron spin which is directed along the spin axis. Each electron in an atom may be thought of as being a small magnet having permanent orbital and spin magnetic moments. The fundamental magnetic moment is Bohr Magneton, ms equal to 9.27 × 10-24 Am2 . For each electron in an atom, the spin magnetic moment is ± mB (depending upon the two possibilities of the spin). The contribution of the orbital magnetic moment is equal to mi mB, where mi is the magnetic quantum number of the electron.
Based on the behaviour in the external magnetic field, the substances are divided different categories.
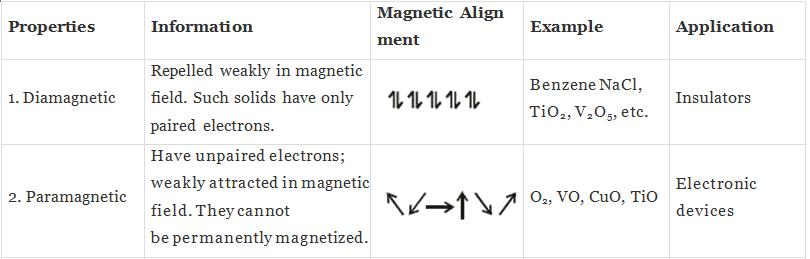
(i) Diamagnetic substances: 
Substances which are weakly repelled by the external magnetic field are called diamagnetic substances,
Example: TiO2, NaCl, Benzene.
(ii) Paramagnetic substances: Substances which are attracted by the external magnetic field are called paramagnetic substances,
Example: O2, Cu2+, Fe3+.
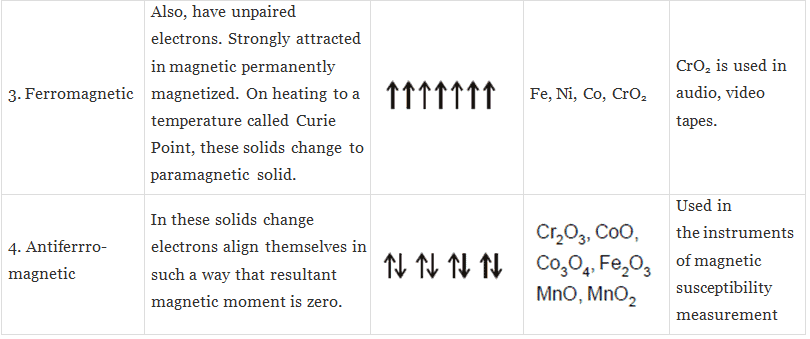
(iii) Ferromagnetic substances: Substances which show permanent magnetism even in the absence of the magnetic field are called ferromagnetic substances.
Example:, Fe, Ni, Co, CrO2.
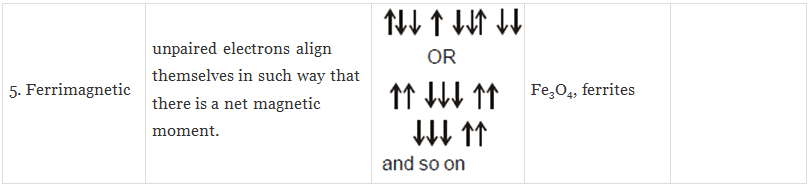
(iv) Ferrimagnetic Substances: Substances which are expected to possess large magnetism on the basis of the unpaired electrons but actually have small net magnetic moment are called ferrimagnetic substances.
Example: Fe3O4.
(v) Anti-ferromagnetic substances: Substances which are expected to posses paramagnetic behaviour, ferromagnetism on the basis of unpaired electron but actually they possess zero not magnetic moment are called anti-ferromagnetic substances.
Example: MnO2
Note : Ferromagnetic, Anti-ferromagnetic and Ferrimagnetic solids change into paramagnetic at some temperature. It may be further pointed out here that each ferromagnetic substance has a characteristic temperature above which no ferromagnetism is observed. This is known as Curie Temperature.
Dielectric Properties:
Insulators do not conduct electricity because the electrons present in them are held tightly to the individual atoms or ions and are not free to move. however, when electric field is applied, polarization takes place because nuclei are attracted to one side and the electron cloud to the other side. Thus dipoles are formed. In addition to these dipoles, there may also be permanent dipoles in the crystal. These dipoles may align themselves in an ordered manner so that such crystals have a net dipole moment.
Such polar crystals show the following interesting properties:
(i) Piezoelectricity or Pressure - electricity: When mechanical stress is applied on such crystals so as to deform them, electricity is produced due to displacement of ions. The electricity thus produced is called piezoelectricity and the crystals are called piezoelectric crystals. A few examples of piezoelectric crystals include Titanates of Barium and Lead, Lead zirconate (PbZrO3), Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (NH4H2PO4) and Quarts. These crystals are used as pick-ups in record players where they produce electrical signals by application of pressure. They are also used in microphones, ultrasonic generators and sonar detectors.
(ii) Ferroelectricity: In some of the piezoelectric crystals, the dipoles are permanently polarized even in the absence of the electric field. However, on applying, electric field, the direction of polarization changes, this phenomenon is called ferroelectricity due to analogy with ferromagnetism. Some examples of the ferroelectric solids are barium titanate (BaTiO3), Sodium potassium tartarate (Rochelle salt) and Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4)
Note : All ferroelectric solids are piezoelectric but the reverse is not true.
(iii) Anti-ferroelectricity: In some crystals, the dipoles align themselves in such a way that alternately, they point up and down so that the crystal does not posses any net dipole moment. Such crystals are said to be anti-ferroelectric. A typical example of such crystals is Lead zirconate (PbZrO3)
Superconductivity:
A substance is said to be superconducting when it offers no resistance to the flow of electricity.
Isomorphism:
The property shown by crystals of different chemical substances which exhibit the same crystalline form is known as isomorphism.
Such substances have similar chemical formula,
Example: Na2HPO4. 12H2O and Na3ASO4. 12H2O
Chemically substances having same type of formulae are not necessarily Isomorphous.
Magnetic Properties of Crystals
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|
FAQs on Magnetic Properties of Solids - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the magnetic properties of solids? |  |
| 2. How do magnetic properties of solids differ from those of liquids? |  |
| 3. What factors determine the magnetic properties of solids? |  |
| 4. Can all solids exhibit magnetic properties? |  |
| 5. How can the magnetic properties of solids be measured? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















