Managerial Functions (Planning, Organizing, Controlling) | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Planning |

|
| Organizing |

|
| Controlling |

|
Introduction
Management operates through various functions, often classified as planning, organizing, staffing, leading/directing, controlling/monitoring and Motivation.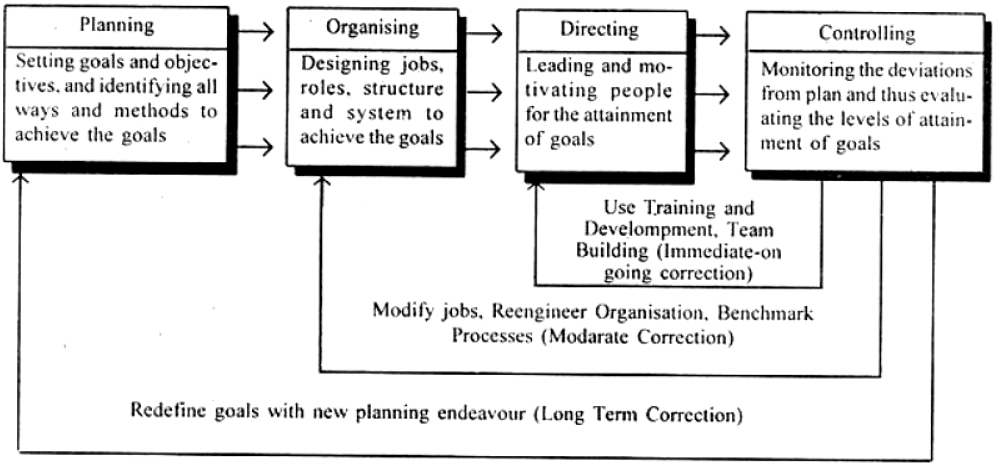
- Planning: Figuring out what needs to be done in the future and creating plans to make it happen.
- Organizing: Efficiently using resources to implement plans successfully.
- Staffing: Analyzing jobs, recruiting, and hiring the right people for specific roles.
- Leading/Directing: Deciding what needs to be done in a situation and guiding people to do it.
- Controlling/Monitoring: Keeping track of progress to ensure it aligns with the plans.
- Motivation: Encouraging employees to work effectively because without motivation, they may not contribute to other management functions.
Planning
- Definition:
- Planning is about looking ahead and creating future action plans.
- It's a preparatory step in management, systematically determining when, how, and who will perform specific tasks.
- Nature of Planning:
- A detailed program outlining future actions.
- Takes into account current and potential human and physical resources for effective coordination and adjustment.
- Importance:
- Often quoted as "Well plan is half done," emphasizing its crucial role.
- Involves formulating detailed plans to achieve a balance between needs and available resources.
- Quotes on Planning:
- Urwick sees planning as a mental predisposition to orderly actions based on facts.
- Koontz & O’Donell define planning as deciding in advance what, how, and who will do a task.
- Overall Purpose:
- Bridges the gap from the current state to the desired future state.
- Enables the achievement of predetermined goals by making things happen that might not occur otherwise.
Steps in Planning Function

Planning function of management involves following steps:
1. Establishing Objectives in Planning:
- Systematic Approach:
- Planning requires a step-by-step method.
- Starting Point:
- Begins with setting clear goals and objectives.
- Objectives offer a reason for various activities and guide efforts.
- Direction and Focus:
- Objectives direct managerial attention towards desired outcomes.
- Serve as the core of the planning process, shaping activities.
- Clarity and Precision:
- Objectives should be clear, precise, and unambiguous.
- Lack of clarity can lead to ineffective activities.
- Quantitative Terms:
- Whenever possible, express objectives quantitatively.
- Example: Specify the number of workers, wages, or units produced.
- Qualitative Objectives:
- Goals like evaluating a quality control manager or assessing a personnel manager should be in qualitative terms.
- Practical and Achievable:
- Objectives should be practical, acceptable, workable, and achievable.
- Ensures feasibility and success in the planning process.
2. Establishing Planning Premises:
- Definition:
- Planning premises are assumptions about future events.
- They serve as a foundation for planning.
- Basis of Planning:
- Essential for determining potential deviations from plans.
- Helps identify obstacles in the business operations.
- Addressing Deviations:
- Aims to understand causes of deviations from plans.
- Involves taking steps to mitigate these obstacles.
- Obstacle Avoidance:
- Focuses on measures to significantly reduce obstacles.
- Aims to ensure smoother business operations.
- Types of Premises:
- Internal Premises: Controllable factors like capital investment, management philosophy.
- External Premises: Non-controllable factors like socio-economic, political changes.
- Controllability:
- Internal premises are within the company's control.
- External premises are beyond the company's control.
3. Choice of alternative course of action
- Introduction:
- Once forecasts and planning premises are in place, various alternative actions are considered.
- Evaluation Process:
- Each alternative is thoroughly assessed, considering its pros and cons.
- Evaluation is based on available resources and organizational needs.
- Consideration Factors:
- Merits, demerits, and consequences of each option are carefully examined.
- Informed choices are essential for effective decision-making.
- Objective Decision-Making:
- Best alternatives are selected after an objective and scientific evaluation process.
- The aim is to choose the option that aligns with organizational goals.
- Quantitative Techniques:
- Planners utilize quantitative techniques to assess the stability of each alternative.
- These techniques provide a more structured and data-driven approach.
4. Formulation of derivative plans
- Introduction:
- Derivative plans are secondary plans supporting the main goal.
- They aid in achieving the primary plan more efficiently.
- Relationship with Basic Plan:
- Derivative plans stem from the fundamental or main plan.
- Their purpose is to enhance and facilitate the accomplishment of the core plans.
- Detailed Components:
- Include policies, procedures, rules, programs, budgets, and schedules.
- Examples: If profit maximization is the main goal, derivative plans focus on sales, production, and cost aspects.
- Supporting Main Objectives:
- Designed to contribute to the achievement of primary goals.
- Serve as building blocks for the overall success of the organization.
- Time and Sequence:
- Specify timelines and the order of tasks to achieve the main plan.
- Provide a structured approach to reaching various objectives.
5. Securing Co-operation
- Introduction:
- After finalizing plans, it's beneficial to involve subordinates or implementers in the process.
- Importance of Involvement:
- Boosts motivation among subordinates as they feel part of the decision-making.
- Enables the organization to receive valuable suggestions for better plan formulation and implementation.
- Employee Engagement:
- Employees become more interested and invested in the execution of plans.
- Key Purposes:
- Motivation: Involvement leads to increased motivation as employees feel a sense of ownership.
- Ideas and Improvements: It brings forth valuable suggestions for enhancing plans.
- Employee Interest: Boosts enthusiasm and commitment towards plan execution.
6. Follow up/Appraisal of plans
- Implementation of Chosen Plan: Once a specific course of action is selected, it is put into action.
- Effectiveness Appraisal: After implementation, it's crucial to assess the plan's effectiveness.
- Feedback Mechanism: Evaluation is based on feedback from relevant departments or individuals involved.
- Correction and Modification: Management can correct deviations or modify the plan based on received information.
- Linking Planning and Controlling: This step establishes a connection between the planning and controlling functions.
- Follow-up Process:
- Simultaneous Monitoring: Follow-up goes hand in hand with plan implementation.
- Realistic Future Plans: Observations during follow-up aid in making future plans more realistic.
Organizing
Organizing in Management
- Following Planning: Organizing is a management function that comes after the planning phase.
- Synchronization and Combination: It involves coordinating human, physical, and financial resources for effective outcomes.
- Resource Importance: Human, physical, and financial resources are all essential for achieving desired results.
- Result Achievement: Organizational function contributes to the accomplishment of results crucial for a business's operation.
- Chester Barnard's Perspective: According to Chester Barnard, organizing establishes role positions, defines jobs, and ensures coordination between authority and responsibility.
- Continuous Managerial Activity: Managers consistently engage in organizing to drive successful outcomes.
Organizing Function in Management: Steps Simplified
- Identification of Activities: Recognize all tasks within the organization, such as accounting, sales, record-keeping, quality control, and inventory management.
- Departmental Organizing: Group similar activities into units or departments. This division is known as departmentation.
- Classifying Authority: Assign authority levels to managers based on the established departments, creating a hierarchy. Top management formulates policies, middle-level management supervises departments, and lower-level management oversees foremen.
- Coordinating Authority and Responsibility: Establish clear relationships to facilitate smooth interactions for achieving organizational goals. Each individual understands their authority, knows whom they report to, and is aware of their accountability. This involves creating a transparent organizational structure that all employees understand.
Controlling
Definition
Controlling involves checking if activities align with plans, issued instructions, and established principles. It ensures effective use of organizational resources to achieve planned goals. Controlling assesses deviations from standard performance, identifies causes, and guides corrective actions.
Expert Perspectives
- Brech defines controlling as systematically checking actual performance against standards to ensure progress and learn from experiences for future needs.
- Donnell likens it to a navigator constantly checking readings to confirm the enterprise is on the right course.
Key Purposes of Controlling
- Facilitating Coordination: Controlling helps harmonize activities within the organization, ensuring they work together seamlessly.
- Aiding in Planning: It contributes to the planning process by providing insights gained from monitoring actual performance, aiding in future decision-making.
Features of Controlling Function
- End Function: Controlling is performed after activities are carried out according to plans, making it a concluding step in the management process.
- Pervasive Function: Managers at all levels and in various types of organizations engage in controlling, emphasizing its widespread application.
- Forward Looking: Controlling isn't just about past actions; it looks ahead to the future. Future-oriented control enables adjustments and improvements as needed.
- Dynamic Process: Controlling involves continuous review and adaptability. It is a dynamic process that evolves over time with changing circumstances.
- Related to Planning: Controlling and planning are interconnected functions. They rely on each other; planning sets the stage for controlling, and effective control validates the planning process.
FAQs on Managerial Functions (Planning, Organizing, Controlling) - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the main managerial functions? |  |
| 2. What is the role of planning in managerial functions? |  |
| 3. How does organizing contribute to the managerial functions? |  |
| 4. Explain the importance of controlling in managerial functions. |  |
| 5. What is the significance of managerial functions in organizational success? |  |


















