Map Based Questions: Nationalism in India | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
Q.1: Locate and label the following Indian National Congress Sessions on the given political outline map of India with appropriate symbols:
1. Calcutta Session (Sept. 1920)
2. Nagpur Session (Dec. 1920)
3. Madras Session (1927)
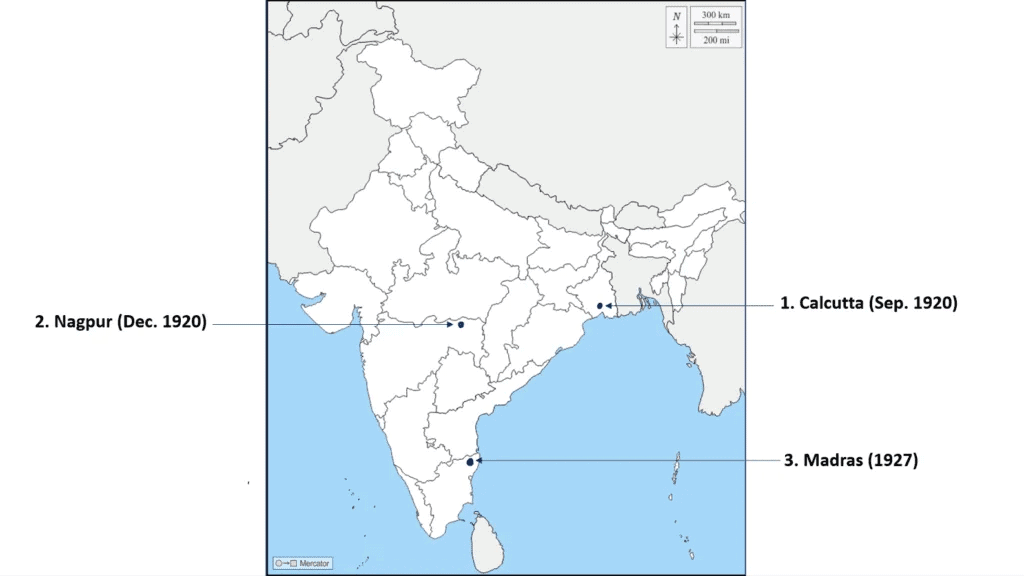
Ans: Indian National Congress Sessions
1. Calcutta Session (Sept. 1920) – Kolkata, West Bengal: This session supported Gandhi’s proposal of launching the Non-Cooperation Movement.
2. Nagpur Session (Dec. 1920) – Nagpur, Maharashtra: At this session, the Congress formally adopted the Non-Cooperation Movement.
3. Madras Session (1927) – Chennai (Madras), Tamil Nadu: The Congress resolved to oppose British policies and declared the goal of Purna Swaraj (Complete Independence).
Q.2: Locate and level the following important centres of Indian National Movement.
1. Champaran – Movement of Indigo Planters.
2. Kheda related to Peasant Satvagraha.
3. Ahmedabad centre of Cotton Mill Workers Satyagraha
4. Amritsar related place to Jallianwala Bagh Incident
5. Dandi Starting place of Civil Disobedience Movement. Ans: Important Centres of Indian National Movement
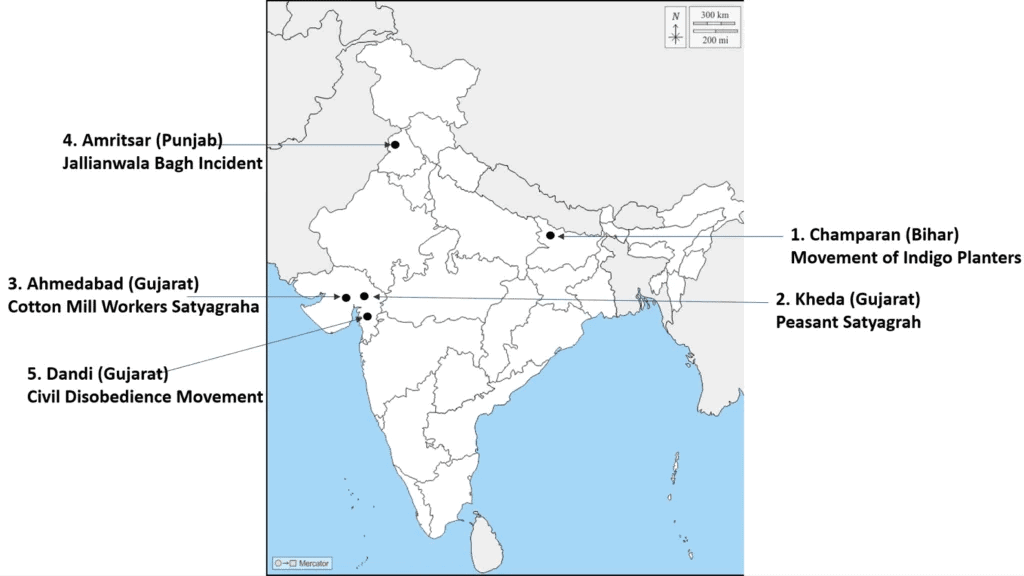
Ans: Important Centres of Indian National Movement
1. Champaran – Bihar: The site of Gandhi’s first Satyagraha in India (1917) against forced Indigo cultivation by British planters.
2. Kheda – Gujarat: In 1918, Gandhi led a movement demanding tax relief for farmers affected by crop failure.
3. Ahmedabad – Gujarat: Gandhi supported a strike by cotton mill workers demanding better wages (1918).
4. Amritsar – Punjab: Site of the Jallianwala Bagh massacre (1919), where British troops killed hundreds during a peaceful gathering.
5. Dandi – Gujarat: Starting point of the Salt March (1930), which launched the Civil Disobedience Movement against British salt laws.
Q.3: On the given political map of India, name and locate the following.
1. The place where the first Session of Indian National Congress was held in 1885
2. The place where the Indian National Congress Session was held in 1929.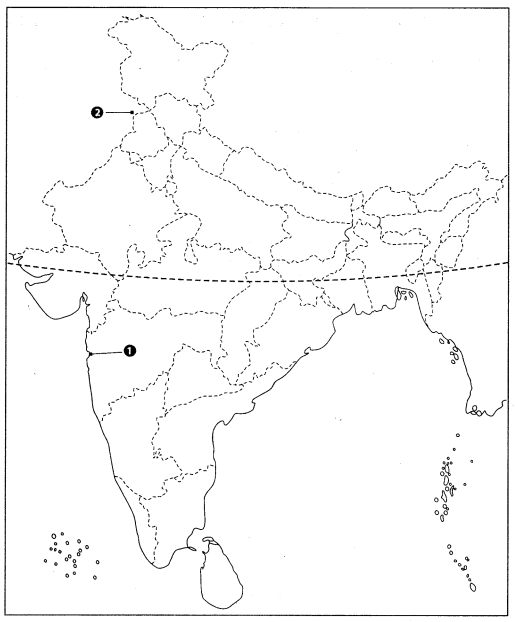 Ans: INC Sessions – Locations
Ans: INC Sessions – Locations
1. Bombay (Mumbai) – Maharashtra: The first session of the Indian National Congress
2. Lahore – Now in Pakistan: The 1929 session presided over by Jawaharlal Nehru, where the Purna Swaraj (Complete Independence) resolution was passed.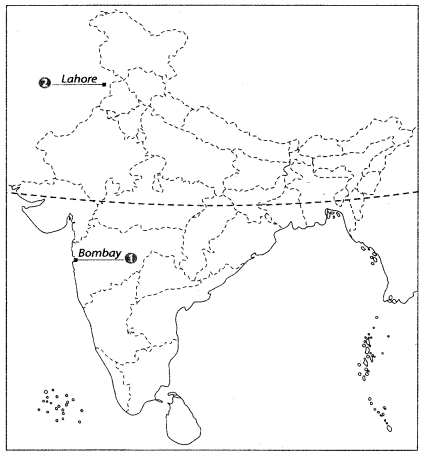
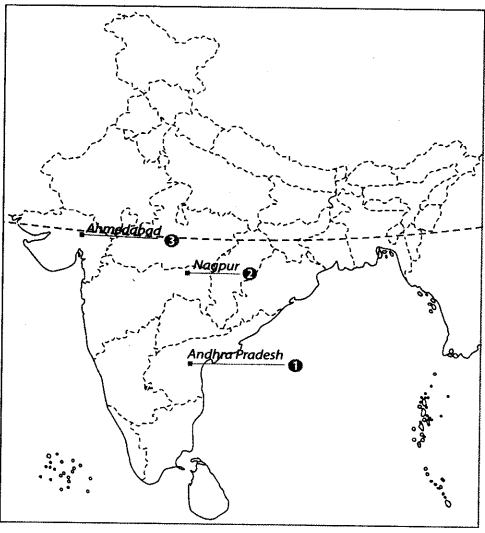
Q.4: On the given political map of India, name and locate the following:
1. The state to which the Gudem rebels belonged.
2. The place where the session of the Indian National Congress was held in December 1920.
3. The place where Gandhiji started Satyagraha in favour of cotton mill workers.
 Ans: Located as below:
Ans: Located as below:1. Gudem Rebels – Andhra Pradesh: Tribal uprising against British forest laws led by Alluri Sitarama Raju in the Gudem Hills.
2. Nagpur – Maharashtra: Venue of the 1920 Congress session that adopted the Non-Cooperation Movement.
3. Ahmedabad – Gujarat: Gandhi’s leadership in the Cotton Mill Workers’ strike marked his use of non-violent protest in labor issues.
Q.5: Features are marked by numbers in the given political map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked in the map.
1. The centre/place of calling off/withdrawing of the Non-Cooperation Movement.
2. The place is known for the movement of Indigo peasants during the British Period.
3. The place where Gandhiji started the Satyagraha in favour of cotton mill workers.
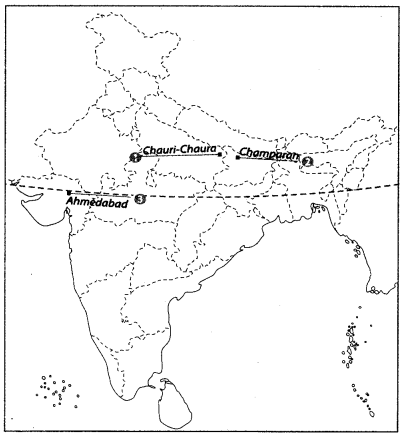
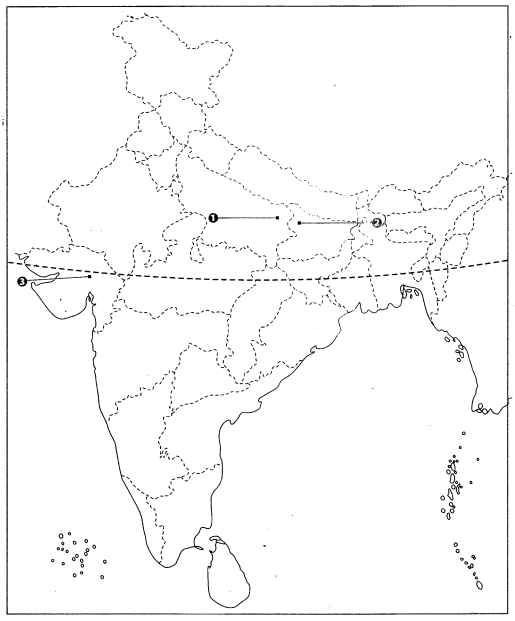 Ans: Features by Number as below:
Ans: Features by Number as below:1. Chauri Chaura – Uttar Pradesh: In 1922, a violent clash between protestors and police led Gandhi to suspend the Non-Cooperation Movement.
2. Champaran – Bihar: Known for Gandhi's first successful mass Satyagraha in India.
3. Ahmedabad – Gujarat: Site of labor Satyagraha led by Gandhi in support of cotton mill workers.
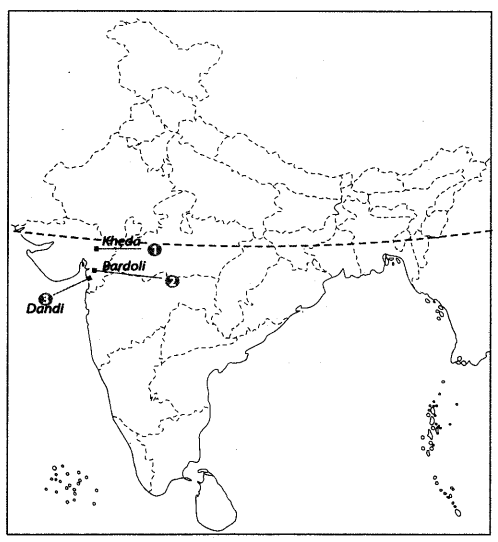
Q.6: On the given political map of India, name and locate the following.
1. The place where Gandhiji started the Satyagraha in support of the peasants of Gujarat in 1917.
2. A place associated with the ‘No Tax Campaign’.
3. The place from where the Civil Disobedience Movement/ Salt Satyagraha was started. Ans: Locations of Key Movements
Ans: Locations of Key Movements
1. Champaran – Bihar: 1917 Indigo Satyagraha; Gandhi's first civil disobedience campaign in India.
2. Bardoli – Gujarat: No Tax Campaign led by Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel in 1928 against increased land revenue.
3. Dandi – Gujarat: Start of Salt Satyagraha in 1930; Gandhi walked 240 miles to protest the British salt monopoly.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Map Based Questions: Nationalism in India - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What were the key factors that contributed to the rise of nationalism in India? |  |
| 2. How did the First World War affect Indian nationalism? |  |
| 3. What role did the Indian National Congress play in the nationalist movement? |  |
| 4. What was the significance of the Quit India Movement? |  |
| 5. How did the partition of India influence nationalist sentiments? |  |

















