UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC > Masonry Principles
Masonry Principles | Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Masonry principles are fundamental guidelines that govern the construction of brick or stone structures. These principles ensure the structural stability, durability, and aesthetic appeal of masonry work. Some key masonry principles include:
- Materials Selection: Choosing high-quality bricks, stones, or blocks that meet specified standards is essential. The materials should be durable, free from defects, and suitable for the intended use.
- Bonding: Proper bonding between individual units (bricks, stones, or blocks) is crucial for the strength and stability of the structure. Various bonding patterns, such as stretcher bond, header bond, or Flemish bond, are used to achieve this.
- Mortar Mix: The mortar used to bond masonry units together should have the appropriate composition and consistency. It should provide sufficient strength, adhesion, and weather resistance while allowing for some flexibility to accommodate movement.
- Joints: Uniformity in joint thickness and proper filling of joints with mortar are important for structural integrity and aesthetics. The joint thickness should be consistent, typically not exceeding a certain specified dimension.
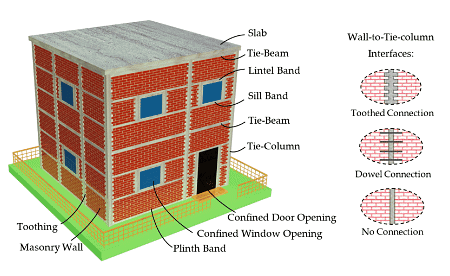
- Plumb and Level: Walls and other masonry elements should be built vertically plumb and horizontally level to ensure uniformity and stability. The use of a plumb bob and spirit level is essential during construction to maintain accuracy.
- Frog Position: Bricks or blocks should be laid with the frog (the indentation on one face) facing upwards to facilitate better bonding with mortar and prevent water accumulation.
- Curing: Proper curing of masonry work is necessary to achieve the desired strength and durability. Curing involves keeping the masonry moist for a specified period after construction to allow for proper hydration of the mortar.
- Expansion Joints: Expansion joints are incorporated at intervals to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction, preventing cracking and damage to the masonry.
- Lintels and Arches: Lintels and arches are used to distribute loads and provide structural support over openings such as doors and windows.
- Weatherproofing: Masonry structures should be protected from moisture penetration through the use of appropriate waterproofing materials and techniques, such as sealants and damp-proof courses.

By adhering to these principles, masonry structures can be constructed to withstand various loads and environmental conditions while maintaining their structural integrity and appearance over time.
- Supervising brick masonry construction involves adhering to several key guidelines:
- Ensure that the bricks meet all specifications, including being sound, hard, uniformly burnt, and consistent in color, shape, and size.
- Prior to use, immerse bricks in freshwater for at least two hours.
- Avoid using broken bricks unless necessary for maintaining structural integrity.
- Lay bricks in their designated bond pattern with the frog facing upward.
- Minimize the use of brick bats.
- Maintain joint thickness below 13 mm.
- Continuously check the verticality of masonry walls using a plumb bob.
- Raise brickwork uniformly, not exceeding 90 cm above adjacent sections.
- For delayed construction, rake back the work in successive courses.
- Refrain from filling large voids with mortar alone due to inefficiency.
- Utilize cement mortar to encase all iron fixtures in doors and windows.
- Facilitate bonding for plastering and pointing by raking facing mortar joints to a depth of 13-19 mm when the mortar is still fresh.
- Cure finished brick masonry for at least seven days.
- Limit daily construction of brick masonry walls to 1.5 m.
- Incorporate piers, buttresses, and counterforts along with main walls, ensuring proper bonding.
- Employ suitable scaffolding for working at elevated levels, securely anchored to the new masonry.
The document Masonry Principles | Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















